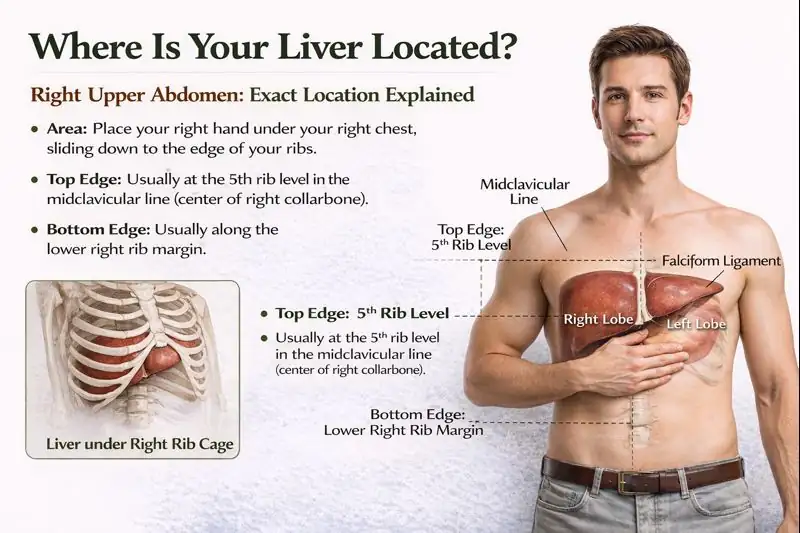
Your liver is located high on the right side of your upper belly, just under your right rib cage and just below the diaphragm (the breathing muscle under your lungs). It lies mostly in the right upper quadrant of your abdomen and is almost fully covered by your lower ribs.
Table of Contents
ToggleThis spot is the same for almost everyone, although liver size and shape can vary a bit with age, sex, and body size. Knowing where the liver is located in the body helps you understand pain in that region and talk clearly with your doctor.
Where Is Your Liver Located?
Right-Side Upper Abdomen: Exact Location Explained
To feel the basic area of where the liver is located in the body , place your right hand on the area under your right chest. Slide your hand down to the edge of your ribs. That zone is where the bulk of the liver lies.
Doctors describe the right-side upper abdomen using lines on the body. The top of the liver usually reaches the fifth intercostal space (the space between the fifth and sixth ribs) in the midclavicular line, which is an imaginary line that runs straight down from the middle of your collarbone. The bottom edge reaches the right costal margin, which is the lower edge of the rib cage.
The liver is located high on the right, between the fifth rib level and the lower right rib edge.
Liver Position Under The Right Rib Cage
Most of the liver is hidden in the liver position under the ribs . The ribs and the muscles between them form a strong shield. In a healthy adult, the upper border of the liver is deep behind the ribs, and the lower edge often sits just at or slightly above the right rib margin when you breathe out.
Because of this deep liver position under the ribs , you usually cannot feel the liver yourself. Even many doctors cannot feel it clearly in a slim, healthy person. They use a mix of tapping (percussion) and careful pressing (palpation) to check the borders.
This hidden position explains why injuries to the right chest or upper belly can hurt the liver even if the skin looks normal. The ribs protect the organ, but a strong blow can still affect it.
Liver Structure: Right Lobe vs Left Lobe
Understanding the shape of the liver makes it easier to picture. The liver has two main lobes:
- The right lobe is large and fills most of the upper right abdomen.
- The left lobe is smaller and stretches across the midline toward the left side, lying over the upper part of the stomach.
A thin fold of tissue called the falciform ligament (a strip of connective tissue) separates the right and left lobes on the front surface and anchors the liver to the front body wall. Because the right lobe is bigger, the liver is still mainly on the right even though it crosses the center.
How The Liver Sits Relative To The Stomach, Gallbladder, And Intestines
The liver shares its space with other organs. Just under the right side of the liver, the gallbladder sits in a small hollow on the underside of the right lobe. Behind and below the liver are the right kidney and part of the colon.
Under the left lobe lies the stomach, and just beneath the liver on the right is the first part of the small intestine, called the duodenum.
Liver Position In The Abdomen
Surface Anatomy Landmarks Used To Locate The Liver
Doctors do not see the liver directly during a regular exam, so they rely on surface anatomy. They use the midclavicular line, the breastbone line, and the rib margins to estimate where the liver is located in the body .
By tapping on the chest and upper belly, they can find the change from lung sound to liver sound, which feels “dull” instead of “hollow.” Studies show that the normal liver span in the midclavicular line is usually around 6 to 12 centimeters in adults, with some variation by sex, height, and weight.
These landmarks make it possible to estimate the size and border of the liver without any machines, although imaging tests are more exact.
Upper Right Quadrant (RUQ) And What It Means
Doctors divide the belly into four quadrants. The liver occupies most of the right upper quadrant, or RUQ, and also extends into the upper middle area, called the epigastric region.
So if you report pain in the RUQ, your doctor thinks first about the liver and gallbladder, along with the upper part of the intestines and sometimes the right kidney or lung.
How The Diaphragm Protects The Liver
The liver rests just under the diaphragm. The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle that helps you breathe. When you breathe in, the diaphragm moves down, and the liver moves down slightly with it. When you breathe out, both move up again.
This close contact protects the liver but also affects symptoms. For example, if the liver capsule (the thin outer covering) is stretched by swelling, deep breaths can make pain worse because the diaphragm pushes down on the sore organ.
Where The Liver Edges Can Be Felt During Examination
During an exam, your doctor may ask you to lie flat and take deep breaths. They place their hand just below your right rib margin and feel upward as you breathe in. The lower edge of the liver may slide down to touch their fingertips.
In many healthy adults, the lower edge is not easy to feel. In children, a small segment of the liver edge below the ribs can still be normal, because their livers are relatively larger compared with their body size.
This difference in the liver location in the human body between adults and children is supported by studies that show liver weight is about 2-3% of body weight in adults but can be close to 5% in young children.
Liver Location In The Human Body
Does Liver Position Differ Between Men And Women?
Research shows that liver size is often larger in men than in women, even after adjusting for body size. This may slightly change the measured liver span, but the basic liver location is the same in both. In men and women, the liver lies under the right ribs, below the diaphragm, and above the upper loops of the intestines.
Data on small differences in exact height or tilt of the liver between sexes are limited, and not all studies agree, so any small variations are still being studied.
Liver Placement Changes With Age & Body Size
The location of the liver stays similar across life, but the organ’s relative size and shape change. In taller or larger people, the liver may appear slightly broader. In people with a high body mass index, fatty liver is more common, and this can enlarge the organ.
A larger liver volume can bring the lower border a little farther down in the abdomen , making it easier to feel on examination. Clinical research also shows that imaging often measures liver size more accurately than tapping or feeling alone, so doctors may combine both methods for a clearer view.
Why Children’s Livers Extend Lower Than Adults’
In children, especially infants and toddlers, the liver takes up a greater share of body space than in adults. Studies suggest that the liver may be about 4-5% of body weight in young children compared with 2-3% in adults.
Because of this, the lower edge of the liver often rests a few centimeters below the right rib margin, even in a healthy child. Doctors expect this when they examine the liver in pediatrics. Only when the edge is much lower than expected, or when the liver feels very firm or tender, do they worry about serious disease.
Liver Position Under The Ribs
Almost the entire liver sits deep behind the lower right rib cage. The upper surface rests just under the diaphragm and lies roughly behind ribs 7 to 11 on the right side. Only the bottom edge of the liver comes close to the rib margin, which is why you usually cannot feel it from the outside.
If the liver becomes larger, the lower edge can move below the ribs. Doctors call this hepatomegaly. An enlarged liver may reach several centimeters below the right costal margin and can sometimes be seen or felt as a firm edge in the upper belly.
Common reasons include viral hepatitis, fatty liver disease, heart failure, some blood cancers, and storage diseases where extra substances build up in liver cells. You might notice a feeling of fullness under the ribs or a dull ache, but many people have no clear symptoms, and enlargement is only found during an exam or on imaging.
Rib pain and liver pain can feel very different. Rib pain usually feels sharp and sits right on the bone or in the muscles between ribs. It often worsens when you press the area or twist your upper body.
Liver pain sits deeper, more like pressure or heaviness in the region of the liver position under the right ribs. It can come with nausea, tiredness, or a feeling of fullness. Sometimes liver or gallbladder pain spreads to the right shoulder or back because of shared nerve paths between the diaphragm and the shoulder region.
What Causes The Liver To Change Position?
Hepatomegaly (Enlarged Liver)
Hepatomegaly means the liver is larger than normal. When this happens, the lower border moves downward, so the liver’s position in the abdomen changes slightly, even though the top still lies under the diaphragm.
Doctors see hepatomegaly in many conditions, including viral infections, alcohol-related disease, metabolic conditions, and congestion from heart failure. On exam, they may feel a liver edge that is lower than expected, or that feels firm or nodular instead of soft and smooth.
Imaging and blood tests help confirm why the liver is bigger, since a low edge alone does not always prove serious disease
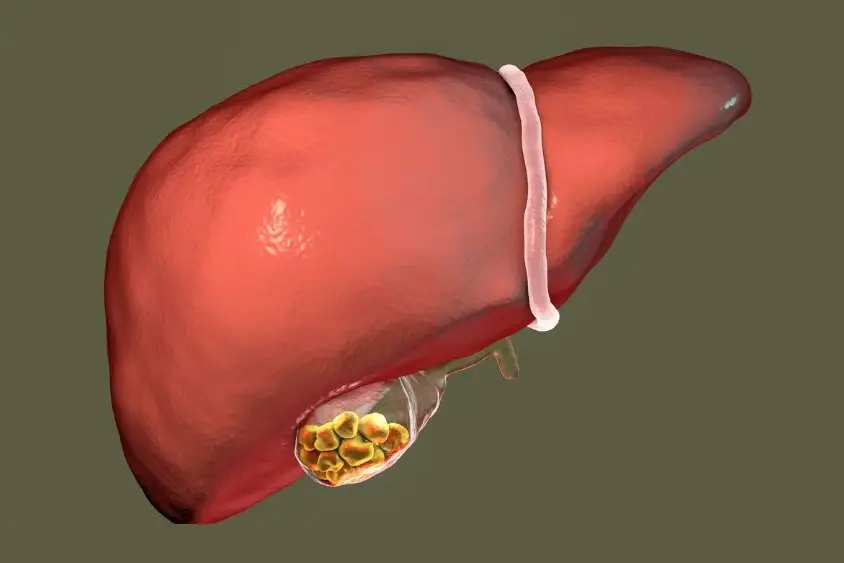
Fatty Liver Disease Shifting Liver Boundaries
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and related conditions cause fat to build up inside liver cells. This extra fat can increase total liver weight and volume, which makes the organ broader and heavier.
Studies show that fatty change often raises liver weight and can make the lower edge easier to feel below the ribs. Over time, this can move the practical liver position a little lower, although the organ still sits mainly in the right upper quadrant.
Because fatty liver can stay silent for years, imaging tests are often the first clue, especially when the scan also shows a larger-than-expected liver size.
Liver Cysts, Tumors, And Structural Changes
Cysts, benign tumors, and cancers can change the shape of the liver. A large growth on the lower surface may push the edge downward or outward, altering what you feel from the outside, even if the basic liver location is unchanged.
On exam, the edge may feel irregular, firm, or very tender. Imaging helps doctors see whether the liver outline is smooth or distorted and how much nearby organs, such as the stomach and right kidney, are being pressed by the enlarged area.
Pregnancy And Liver Displacement
During pregnancy, the growing uterus pushes many organs upward. The liver tilts slightly and may sit a bit higher in the chest, without changing the basic liver position under the ribs .
Most pregnant people do not feel this shift, and liver function stays normal. However, serious conditions such as preeclampsia and HELLP syndrome can cause liver swelling, capsule stretch, and sharp pain under the right ribs, sometimes with nausea, headache, or vision changes. These problems need urgent medical care because they can harm both parent and baby if they are not treated in time.
What Liver Pain Feels Like Based On Its Location
Pain Under Right Ribs
Liver-related pain usually appears as a dull ache, pressure, or sense of fullness under the right side of your rib cage, close to where the liver is positioned under the ribs . You may notice it more when you bend, take a deep breath, or eat a large meal.
Some people describe it as a “heavy” feeling instead of sharp pain. This kind of discomfort often comes with other liver signs such as tiredness, poor appetite, or swelling in the belly, although not everyone has all these symptoms.
Referred Pain To The Right Shoulder Or Back
Because the liver and diaphragm share nerve pathways with the right shoulder region, irritation of the liver capsule can cause referred pain. That means you can feel discomfort in your right shoulder blade or upper back, even though the organ sits in the upper abdomen. This pattern often appears in gallbladder flare-ups or in infections around the liver. It can confuse people, since shoulder pain is easy to blame on muscle strain.
Sharp Vs Dull Liver Pain—Clinical Differences
Dull, steady pain is more typical when the liver capsule stretches slowly. This can happen with moderate enlargement from fatty liver, congestion, or slowly growing masses. Sharp or sudden pain is more likely when there is acute inflammation or blockage, such as severe gallbladder attack, liver abscess, or bleeding injury.
Very strong pain with fever, vomiting, or trouble breathing needs urgent care. Doctors do not rely on pain alone, because many people with serious disease in the area of the liver location feel little or no discomfort until late stages.
Imaging Techniques That Show Liver Location
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is often the first test used to check the liver. A small probe on your skin sends sound waves into the body and receives the echoes. The machine then creates a live image that clearly shows the liver’s position , its size, and its texture.
Ultrasound can spot fatty change, cysts, gallstones, and simple enlargement. It avoids radiation and is widely used, although deep or very small lesions may still need other scans for full detail.
CT Scan
A CT scan uses X-rays taken from many angles to build cross-sectional slices of the body. These images show the outline of the liver, its relation to the stomach, kidneys, and intestines, and any large growths or injuries.
CT is very helpful in trauma, where doctors need to see if the liver has torn or is bleeding into the belly. Because CT involves radiation and sometimes iodine contrast, doctors weigh the benefits and risks, especially in children and pregnant people.
MRI
MRI uses strong magnets and radio waves, not X-rays. It gives very clear pictures of soft tissues and helps tell harmless lesions from more risky ones. MRI also maps blood vessels and bile ducts, which is useful before surgery or complex procedures.
It is especially valuable when CT or ultrasound leave questions about the true nature of a liver mass or when doctors want to track subtle changes in the liver location or inner structure over time.
Liver Location Diagrams From Imaging
Modern scanners produce detailed images that act like a personal liver location diagram for you. Doctors can scroll through slices from top to bottom and from front to back. This shows exactly how far the liver extends under the ribs, how close it sits to the heart, lungs, and bowel, and whether the shape is smooth or distorted.
Factors That Affect Liver Position
Body Fat Distribution
Fat carried around the waist can push the abdominal organs inwards and slightly change the liver’s position . Obesity also raises the risk of fatty liver, which itself increases organ size.
Together, these changes can bring the lower edge of the liver closer to the front wall and make it easier to feel on exam. Lifestyle studies show that weight loss often reduces liver fat and may reduce liver volume over time.
Posture Changes
When you slouch, your chest narrows, and your belly pushes forward. This posture can tilt the liver and make fullness under the right ribs more noticeable, especially if the organ is already enlarged.
Standing tall or lying flat allows the liver to settle back into its usual position. The shift is small, but people with sensitive livers or gallbladder issues sometimes feel the difference quite clearly.
Tight Clothing Or Compression
Very tight belts, shapewear, or clothing that presses on the upper abdomen can increase pressure on the liver position under the ribs. This does not truly move the liver, but it can make minor discomfort feel worse.
Doctors usually suggest looser clothes for people with marked enlargement, fluid in the belly, or tenderness in the right upper quadrant, because external pressure adds to the internal stretch that the liver capsule already feels.
Liver Movement During Breathing
With every breath, the diaphragm moves and the liver moves with it. When you breathe in deeply, the diaphragm goes down, and the liver drops a few centimeters. When you breathe out, both move up again. This small motion explains why doctors ask you to take deep breaths while they feel for your liver and why some people feel more pain during deep breathing when the liver capsule is inflamed.
When To See A Doctor For Liver-Area Pain
Warning Signs Of Liver Disease
You should talk with a doctor if you feel ongoing discomfort in the upper right belly, together with warning signs such as yellow eyes or skin, dark urine, pale stools, easy bruising, strong tiredness, or swelling of your legs or abdomen. These clues suggest that the problem involves more than simple muscle strain, and they often point to conditions like hepatitis, advanced fatty liver, or bile flow blockage.
Symptoms That Require Emergency Evaluation
Some symptoms need urgent care. These include sudden severe pain under the right ribs, pain with high fever or shaking chills, vomiting blood, black or tar-like stools, confusion, or trouble staying awake.
Pain after a strong blow to the upper right abdomen also needs quick assessment, since a damaged liver can bleed inside the belly. In these cases, emergency teams often use ultrasound or CT quickly to view the liver location and check for bleeding or infection.
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
When you see a doctor for pain near the liver region, it helps to bring clear questions. You might ask where your liver edge sits compared with normal, whether imaging showed a typical liver position in the abdomen , and if any enlargement is mild or marked. You can also ask how lifestyle changes, medicines, or further tests might affect your liver health over time.
FAQ
Is the liver on the right or left side of the body?
The liver sits mainly on the right side under the lower ribs, with a smaller part crossing toward the left. A good liver location diagram shows it filling most of the right upper quadrant.
Can the liver hurt even if labs are normal?
Yes, you can feel deep aching under the right ribs even when blood tests look fine. Mild capsule stretch, fatty change, or nearby muscle problems may cause pain without clear lab changes.
Why does liver pain feel like shoulder pain?
Nerves from the diaphragm and liver connect with nerves that serve the right shoulder. When the capsule is irritated, your brain may feel the signal as pain at the shoulder tip instead.
Does liver size vary between individuals?
Liver size differs with height, sex, and body weight. Some people have a naturally larger organ but still have normal function, so doctors interpret measurements together with lab tests and symptoms.
Can the liver shift position after weight loss or gain?
Large weight gain, especially around the waist, can enlarge the liver and push it slightly downward. Weight loss and lower liver fat may let it sit a bit higher while staying in the same quadrant.
How low can the liver descend if enlarged?
In marked enlargement, the lower edge may come down toward the belly button region. The upper part still sits under the ribs, but the larger size makes more of it reachable during an exam.
Can fatty liver change the liver’s position?
Fatty liver increases organ volume, which may move the lower margin downward in the abdomen. The liver keeps the same basic spot, yet its borders on the exam and scans expand outward.
Does liver location affect digestion?
The liver’s place near the stomach and intestines lets bile flow quickly into the gut to help digest fats. Small shifts rarely affect digestion, but scarring or bile blockage can change how you process food.
Which side to sleep on for liver discomfort relief?
Some people feel better lying on the left side, which may ease pressure on the liver area. Others prefer their back. If pain persists, location alone is not enough, so medical review is important.
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Nivedita Pandey, MD, DM (Gastroenterology)
Dr. Nivedita Pandey is a U.S.-trained gastroenterologist and hepatologist with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating liver diseases and gastrointestinal disorders. She specializes in liver enzyme abnormalities, fatty liver disease, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and digestive health.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current clinical guidelines.