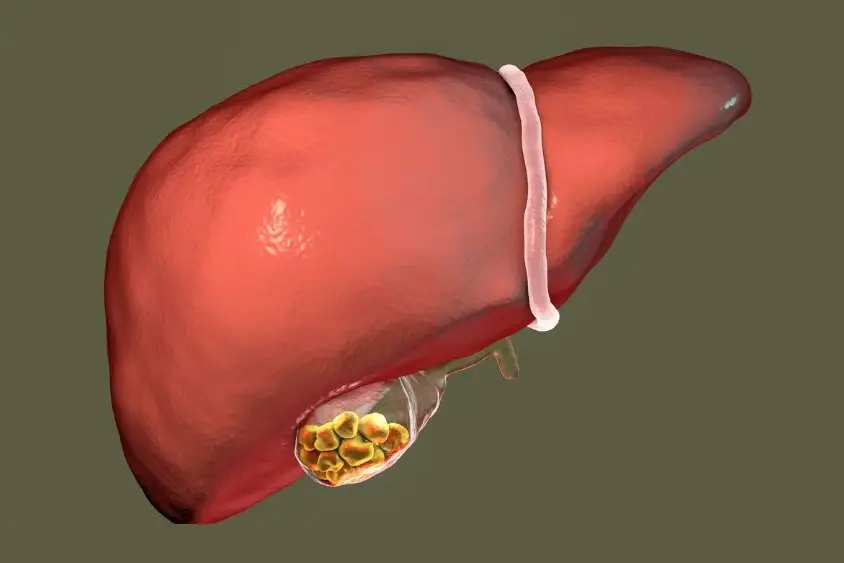
Fatty liver, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a common condition. It happens when fat builds up in liver cells. This can harm the liver’s important functions.
Table of Contents
ToggleThere are two main types of fatty liver: alcoholic and non-alcoholic. You might not notice fatty liver disease at first. But symptoms include weight loss, loss of appetite, and feeling very tired.
To manage fatty liver, you need a full plan. This includes changing your lifestyle, diet, and sometimes medical help. Knowing the causes and getting professional advice can help. Making lasting lifestyle changes can improve your liver health.
The liver is your body’s detox center. When fat builds up in it, it can slowly damage the organ, leading to severe liver disease if ignored. In this blog, we will walk you through everything about fatty liver and treatment, the symptoms, diet tips, causes, and how to manage it the right way.
What is Fatty Liver Disease?
Fatty liver disease, also called hepatic steatosis, happens when fat makes up more than 5-10% of your liver’s weight. This can make your liver inflamed and less able to do its job properly. If not treated early, it may lead to serious damage.
What happens inside your liver when you have fatty liver?
Your liver helps clean your blood, digest food, and store energy. But when too much fat enters the liver:
- Liver cells swell due to fat
- The liver becomes inflamed
- Liver enzymes increase in your blood (like ALT and AST levels)
- Scar tissue starts forming (called fibrosis)
Over time, this damage leads to cirrhosis stages, which may require a liver transplant.
What are the two types: NAFLD vs. AFLD?
There are two main types:
- NAFLD (Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease): Caused by poor diet, obesity, diabetes
- AFLD (Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease): Caused by heavy alcohol use
NAFLD treatment focuses on weight loss and healthy eating. AFLD needs quitting alcohol completely.
What are the Early and Late Symptoms of Fatty Liver?
Fatty liver symptoms are often silent at the beginning. You may not feel anything until serious damage starts.
What are silent signs of fatty liver disease?
In the early stages, you might have:
- Constant tiredness
- Bloating or gas
- Mild belly pain (right upper side)
- Poor appetite
- Trouble concentrating
These signs are easy to ignore, which is dangerous.
Can fatty liver cause tiredness and pain?
Yes. As fat builds up, the liver struggles to work properly, which can:
- Make you feel weak
- Cause right-side belly discomfort
- Reduce energy levels
What symptoms mean liver damage is getting worse?
When fatty liver symptoms become serious, it means the disease is progressing.
| Stage | Common Symptoms | Medical Concern |
|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 | Mild discomfort, fatigue | Often reversible |
| Grade 2 | Belly pain, bloating, high enzymes | Needs timely treatment |
| Grade 3 | Yellow skin, confusion, swelling | Liver failure risk |

What Causes Fatty Liver Disease?
Knowing the cause helps treat fatty liver and treatment early.
How does obesity contribute to hepatic steatosis?
Obesity is the biggest reason for hepatic steatosis. When body fat increases, fat also deposits in the liver.
- Especially belly fat is risky
- Obese people are 5 times more likely to develop liver disease
- In children, obesity is the top reason for pediatric fatty liver
Can diabetes, high cholesterol, or PCOS cause fatty liver?
Yes. These conditions increase fat storage in the liver.
- Diabetes: Sugar is stored as fat
- High cholesterol: Fat builds up in arteries and liver
- PCOS: Hormonal changes affect fat metabolism
- Insulin resistance worsens fat storage
Is alcohol always the reason?
No. Most cases are non-alcoholic fatty liver. But regular drinking can cause alcoholic fatty liver, which may lead to cirrhosis faster.
Can skinny people also get fatty liver?
Yes. Even if your weight is normal, you can get it due to:
- Poor diet (junk food)
- Lack of exercise
- Genetics
- Weight loss and liver fat changes
How is Fatty Liver Diagnosed by Doctors?
Early diagnosis saves your liver.
What blood tests are done to detect fatty liver?
Doctors may order:
- Liver enzymes (ALT and AST levels)
- Lipid profile (cholesterol)
- Blood sugar (HbA1c)
If enzymes are high, further imaging is advised.
Is ultrasound or FibroScan better for diagnosis?
Both are safe, but FibroScan gives more details.
| Test | Use | Accuracy |
| Liver Ultrasound | Finds fat in liver | 70% |
| FibroScan | Measures liver stiffness (fibrosis) | 90%+ |
What does a liver biopsy show?
A liver biopsy gives the most accurate result. It tells:
- How much fat is there
- If there’s fibrosis or cirrhosis
- The exact cirrhosis stage
What Are the Best Treatment Options for Fatty Liver?
Fatty liver and treatment depend on how early you catch it.
Can fatty liver be reversed completely?
Yes, fatty liver can be reversed in early stages. If no fibrosis, simple lifestyle changes work.
How long does it take to treat fatty liver?
- Grade 1: 3 to 6 months
- Grade 2: 6 to 12 months
- Grade 3: Long-term, needs close care
What medications do doctors prescribe?
No fixed drug yet. But doctors may give:
- Vitamin E (antioxidant)
- Pioglitazone (for diabetes-linked cases)
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Metformin (if diabetic)
Can weight loss really cure fatty liver?
Yes. Just 7-10% weight loss can reduce liver fat.
- Reduces liver enzymes
- Improves sugar and cholesterol
- Heals mild hepatic steatosis
Is liver transplant needed in severe cases?
Only when there’s liver failure due to cirrhosis. This is rare if treated early.
Treatment Flow Chart:
| Grade | Treatment Plan |
| Grade 1 | Diet, exercise, follow-ups |
| Grade 2 | Add medicine, lose weight |
| Grade 3 | Specialist care, transplant prep |
What is the Right Diet Plan for Fatty Liver Patients?
A healthy fatty liver diet is your best medicine.
What foods should you avoid if you have a fatty liver?
Avoid:
- Fried items
- Red meat
- Sugary drinks
- White bread
- Alcohol
What are the best foods to heal your liver?
Include:
- Leafy greens
- Fruits (like apples, berries)
- Dal and whole grains
- Nuts and seeds
- Coffee (in moderate amount)
Read: Creating an Effective Liver Cleanse Diet Plan
Table: Foods to Eat vs. Avoid
| Eat These | Avoid These |
| Leafy greens, dal, fruits | Fried food, red meat |
| Nuts, seeds, oats | Sugary drinks, soda |
| Coffee (1-2 cups daily) | Refined carbs, maida |
Is coffee good or bad for fatty liver?
Good, if limited. Coffee lowers liver inflammation.
Read: The Liver Detox Diet: Cleanse and Rejuvenate Your Liver Naturally
Can intermittent fasting help?
Yes. Helps with:
- Weight loss
- Insulin sensitivity
- Lowering liver enzymes

Is alcohol completely off-limits?
Yes. For all liver grades, alcohol worsens fat buildup.
Doctor-Recommended 30-Day Liver Health Plan
- Week 1: Cut sugar, start 15-min walk
- Week 2: Add fruits, nuts
- Week 3: Begin 30-min workouts
- Week 4: Monitor enzymes, consult specialist
Managing Complications of Advanced Fatty Liver
Fatty liver disease can get worse and lead to serious problems. If it turns into liver cirrhosis, the risk of portal hypertension goes up. This can cause swelling in the esophageal veins and increase the risk of bleeding.
People with cirrhosis from fatty liver disease also face liver failure. They are at a higher risk of getting liver cancer, called hepatocellular carcinoma.
Liver Cirrhosis
Liver cirrhosis is a serious problem from advanced fatty liver disease. It happens when the liver gets severely scarred and can’t work right. Patients may get fluid in the belly (ascites), bleeding in the stomach, and changes in thinking or mood (hepatic encephalopathy).
Liver Transplantation
When fatty liver disease causes severe liver damage, a liver transplant might be needed. A healthy liver from a donor replaces the failing one. This surgery is life-saving but risky and needs careful management by experts.
Patients who get a liver transplant for fatty liver disease might face a higher risk of the disease coming back in the new liver.
Dealing with advanced fatty liver disease complications needs a detailed plan. This includes watching the patient closely, managing symptoms well, and sometimes a liver transplant. Finding and treating the disease early is key to stop it from getting worse and to lower the risk of serious problems.
Integrative Approach to Fatty Liver Management
Managing fatty liver disease needs a team effort. Hepatologists focus on liver health. They work with family doctors to care for the whole patient. Dietitians and fitness professionals help make lifestyle plans for each patient.
Collaboration Between Healthcare Providers
This team works together for fatty liver interdisciplinary care. They share knowledge and plan treatments. This ensures patients get the support they need to manage fatty liver disease.
Patient Education and Support
Teaching patients about fatty liver disease is key. The team helps set health goals and offers support. This helps patients succeed in managing fatty liver disease.
This approach makes patients active in their care. It leads to better health and a better life.

How is Fatty Liver Different in Pregnant Women, Kids, and Elderly?
Each group needs different care.
Can fatty liver cause problems during pregnancy?
Yes. Can lead to:
- High BP (pre-eclampsia)
- Premature birth
- Gestational diabetes
Read: How Fatty Liver Disease Affects Pregnancy
How does pediatric fatty liver differ?
In kids, it’s often due to:
- Obesity
- Sugary diets
Early detection and diet changes help.
How is fatty liver treated in seniors?
Care must be gentle. Doctors avoid risky drugs. Focus is on diet and walking.
How Often Should You Follow Up with a Liver Specialist?
Check-ups help monitor liver health.
What tests to monitor your progress?
- Liver enzymes
- Ultrasound or FibroScan
- Sugar, cholesterol, weight
Can you stop medication if liver improves?
Only after doctor approval. Stopping early can bring fat back.
When to consult a hepatologist?
- Liver enzymes rising
- Pain, swelling, tiredness
- No improvement after 3 months
What Can Dr. Nivedita Pandey Do to Help You?
How does Dr. Pandey approach fatty liver treatment?
Dr. Nivedita Pandey, known as the best fatty liver doctor, uses:
- Diet-based healing
- Non-invasive testing like FibroScan
- Monitoring of liver enzymes and sugar
- Personalized treatment plans
Success stories and case studies
Many patients reversed Grade 2 fatty liver in 6-8 months under her care.
Consultation and treatment options in Delhi
Visit her clinic at Sitaram Bhartia Institute or book online. She offers full care for liver, gut, and hormonal issues.

Book Your Liver Check-Up with Dr. Nivedita Pandey Today
Fatty liver disease is serious but fixable. With the right care and diet, your liver can recover. Don’t wait for symptoms to get worse.
Dr. Nivedita Pandey, MBBS, Diplomate American Board (Internal Medicine & Gastroenterology), is a US-trained, board-certified liver specialist in Delhi. She has helped hundreds of patients reverse fatty liver and treatment plans with expert care. Whether it’s diet, scans, or advanced care, she can guide you from start to full recovery.
FAQ
What is fatty liver disease?
What are the types of fatty liver disease?
What are the common symptoms of fatty liver disease?
How is fatty liver disease managed?
What are the risk factors for fatty liver disease?
How is fatty liver disease diagnosed?
What are the lifestyle changes recommended for managing fatty liver disease?
What are the medical interventions for fatty liver disease?
Can vitamin E and antioxidants help with fatty liver disease?
What are the potential complications of advanced fatty liver disease?
When is a liver transplant required for fatty liver disease?
How can healthcare providers help in managing fatty liver disease?
What are the latest advancements in fatty liver disease research?
Researchers are finding new treatments. They’re looking at medications that reduce inflammation and improve liver function.
Source Links
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Nivedita Pandey, MD, DM (Gastroenterology)
Dr. Nivedita Pandey is a U.S.-trained gastroenterologist and hepatologist with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating liver diseases and gastrointestinal disorders. She specializes in liver enzyme abnormalities, fatty liver disease, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and digestive health.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current clinical guidelines.