Diffuse liver steatosis, also known as fatty liver disease, is a condition where fat builds up in the liver. It can cause serious health problems if not treated. Dr. Nivedita Pandey’s guide covers the causes, symptoms, and treatments for this condition. It helps you take steps to keep your liver healthy.
Table of Contents
ToggleDiffuse liver steatosis, or fatty liver, affects how your liver works. It happens when too much fat builds up in liver cells. This can lead to health issues if not managed well. We’ll look at the causes, symptoms, and treatments for this condition. This will help you take care of your liver health.
What is Diffuse Liver Steatosis?
Diffuse liver steatosis, also known as fatty liver disease, is when too much fat builds up in the liver. This is a metabolic disorder that makes liver cells store more triglycerides. If not treated, it can lead to serious liver diseases like non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and cirrhosis.
Definition and Overview of Diffuse Liver Steatosis
Diffuse liver steatosis means fat is in more than 5% of liver cells. It can be mild or severe, based on how much fat is in the liver. Too much fat can cause inflammation, scarring, and harm liver function if not fixed.
- Diffuse liver steatosis is a common liver metabolic disorder, affecting an estimated 40 million adults in the United States.
- It is strongly associated with obesity, type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, and metabolic syndrome.
- Diffuse liver steatosis can also occur in individuals with chronic viral hepatitis, drug-induced liver injury, and excessive alcohol consumption.
Knowing about diffuse liver steatosis is key for early detection and treatment. By tackling the root causes, people can help keep their liver healthy. This reduces the chance of getting worse liver diseases.
Causes of Diffuse Liver Steatosis
Diffuse liver steatosis, also known as fatty liver disease, has many causes. The main ones are non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), alcoholic liver disease, metabolic disorders, and some medicines or toxins.
Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is the top reason for diffuse liver steatosis. It’s linked to insulin resistance, obesity, and type 2 diabetes. In NAFLD, fat builds up in the liver, causing inflammation and damage.
Alcoholic Liver Disease
Drinking too much alcohol is another big cause. Alcoholic liver disease happens when alcohol harms the liver. This leads to fat buildup and inflammation.
Metabolic Disorders
Some metabolic disorders can also cause diffuse liver steatosis. These include high cholesterol and triglycerides, and metabolic syndrome. These conditions often come with insulin resistance and obesity.
Medications and Toxins
Some medicines and toxins can also cause it. For example, certain antidepressants, corticosteroids, and exposure to chemicals or pollutants.
Every cause of diffuse liver steatosis leads to fat buildup in the liver. If not treated, it can get worse and lead to serious liver problems.
Symptoms of Diffuse Liver Steatosis
Diffuse liver steatosis, also known as fatty liver disease, can be tricky to spot. It has many non-specific symptoms. But, there are common signs and symptoms you should know about.
Fatigue and Weakness
Fatigue and weakness are common symptoms. You might feel very tired, even after sleeping well or being active. This tiredness can really affect your daily life.
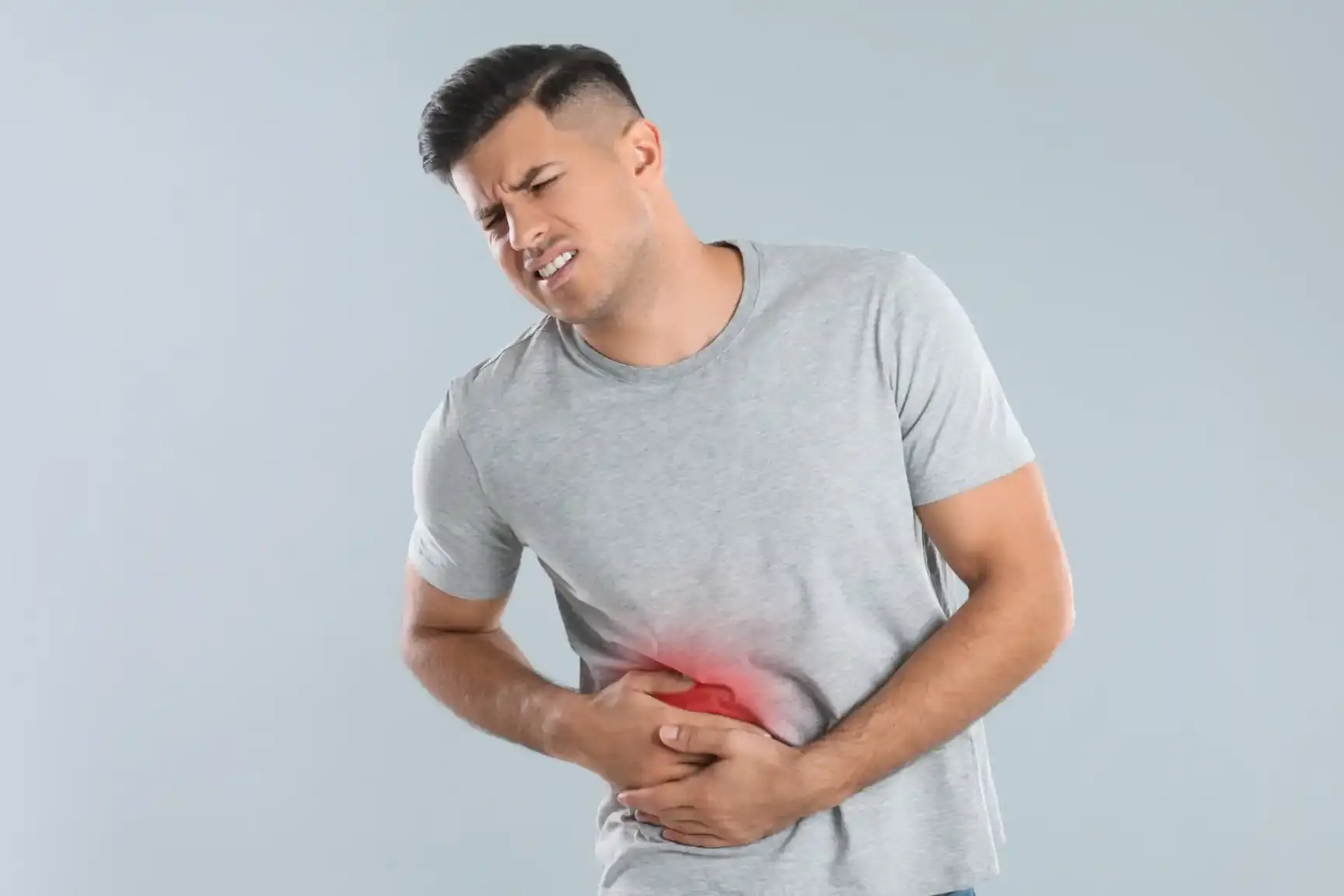
Abdominal Discomfort or Pain
Abdominal discomfort or pain is another symptom. You might feel a dull ache or fullness in your upper right abdomen. This pain can also spread to your back or shoulder.
Unexplained Weight Loss
Diffuse liver steatosis can also cause unexplained weight loss. You might lose weight without changing your diet or exercise. This weight loss is a sign that needs medical attention.
If you notice these symptoms, see your healthcare provider. They can run tests to find the cause and suggest treatments. Catching and treating diffuse liver steatosis early can prevent serious problems.
Diagnosis of Diffuse Liver Steatosis
Diagnosing diffuse liver steatosis, also known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), uses blood tests, imaging studies, and sometimes a liver biopsy. These methods help see how much fat is in the liver. They also check for other liver diseases.
Blood Tests
Blood tests show how well the liver is working. High levels of liver enzymes like ALT and AST suggest fatty liver disease. They also check cholesterol, triglycerides, and glucose levels, which are linked to NAFLD.
Imaging Studies
Imaging like ultrasound, CT scan, and MRI shows how much fat is in the liver. Ultrasound is often first because it’s simple and cheap. CT and MRI give more detailed views, especially for more severe cases.
Liver Biopsy
A liver biopsy might be needed to confirm the diagnosis and check liver damage. It removes a small liver sample for microscopic examination. While it’s the best way to diagnose, it’s not always used because of its risks.
Diagnosing diffuse liver steatosis usually combines these methods. The goal is to accurately find the problem and choose the right treatment.
Risk Factors for Diffuse Liver Steatosis
Many factors can raise your risk of getting diffuse liver steatosis, also known as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). These include obesity, type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol and triglyceride levels, and metabolic syndrome.
Obesity
Being overweight, especially around the belly, can lead to fat in the liver. This excess weight can cause liver fat to build up, raising the risk of NAFLD.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance are closely linked to fatty liver disease. People with high blood sugar levels are more likely to have liver fat.
High Cholesterol and Triglyceride Levels
Dyslipidemia, or high cholesterol and triglyceride levels, can also increase the risk of diffuse liver steatosis. This imbalance can lead to fat in the liver.
Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome, a group of conditions like obesity, high blood pressure, and high blood sugar, is linked to a higher risk of diffuse liver steatosis.

Knowing and tackling these risk factors can help prevent or manage diffuse liver steatosis. This can lower the risk of more serious liver problems.
Complications of Diffuse Liver Steatosis
If left untreated, diffuse liver steatosis can lead to serious liver problems. One major issue is non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). It causes inflammation and damage to the liver. NASH can also cause liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, which are severe conditions.
Liver Cancer
People with diffuse liver steatosis are at higher risk of liver cancer. This shows why early diagnosis and treatment are crucial. Untreated liver disease can cause a lot of damage.
Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)
NASH is a more serious form of NAFLD. It involves inflammation and injury to liver cells. This can lead to liver fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis
Liver fibrosis can turn into cirrhosis, a severe condition. Cirrhosis is marked by extensive liver scarring. It can cause liver failure, portal hypertension, and increase liver cancer risk.
Treatment for Diffuse Liver Steatosis
Treating diffuse liver steatosis, or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), focuses on the root causes. It aims to stop further liver harm. Key treatments include lifestyle changes, like eating right and exercising, and losing weight for those who are too heavy.
Lifestyle Modifications: Diet and Exercise
Eating well and staying active are key to managing diffuse liver steatosis. A diet full of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean meats helps reduce liver fat. Exercise, like cardio and strength training, boosts insulin sensitivity and aids in weight loss, both vital for liver health.
Weight Loss
Keeping a healthy weight is crucial for treating diffuse liver steatosis. Losing 3-5% of body weight can greatly reduce liver fat. Losing 10% or more can also lower liver inflammation and scarring.
Medication Management
Doctors might prescribe medicines for diffuse liver steatosis. These can include drugs that make the body more sensitive to insulin or lower cholesterol. The right medication depends on the person’s health and how severe their condition is.
Surgical Interventions (in severe cases)
In severe cases, especially for those who are very overweight, surgery might be an option. Bariatric surgery can lead to lasting weight loss. This can improve liver fat and overall liver health.
It’s vital to work with a healthcare provider to create a treatment plan. This plan should meet the unique needs of each person with diffuse liver steatosis.

Prevention of Diffuse Liver Steatosis
Stopping diffuse liver steatosis early is key. It can prevent worse liver problems. By making a few lifestyle changes, you can lower your risk of fatty liver disease. This helps keep your liver healthy.
Maintaining a Balanced Diet
Eating whole, unprocessed foods is important. Focus on fruits, veggies, lean proteins, and complex carbs. These foods help your liver work better and burn fat.
Regular Physical Activity
Exercise is key. Do aerobic and strength training to improve insulin use and burn liver fat. Try to do 150 minutes of moderate exercise a week. This keeps your weight healthy and supports your liver.
Achieving and Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Keeping a healthy weight is vital. Too much weight, especially around the belly, can lead to liver fat. Eat well and exercise regularly to stay at a healthy weight.
Limiting Alcohol Consumption
Too much alcohol is bad for your liver. Drinking less or not at all can protect your liver. This reduces your risk of diffuse liver steatosis.
By following these tips, you can keep your liver healthy. This lowers your risk of getting diffuse liver steatosis.
Diffuse Liver Steatosis and Other Health Conditions
Diffuse liver steatosis, or fatty liver disease, is linked to serious health issues. These include heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. It’s important to understand these connections for your overall health.
Cardiovascular Disease
People with fatty liver disease face a higher risk of heart attacks and strokes. This is because both conditions share metabolic problems. A healthy lifestyle and caring for your liver can lower these risks.
Type 2 Diabetes
Fatty liver disease is closely tied to type 2 diabetes. Both have common causes like insulin resistance and obesity. Treating fatty liver can help manage or prevent type 2 diabetes.
Metabolic Syndrome
Fatty liver disease is a key part of metabolic syndrome. This syndrome includes high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and belly fat. Managing these factors is vital for your health.
Understanding the links between fatty liver disease and other health issues is key. By tackling these related problems, you can better manage your liver health and avoid more serious issues.

Living with Diffuse Liver Steatosis
Living with diffuse liver steatosis means you need a big plan. You must stick to your treatment, go to follow-up visits, and make lifestyle changes. Also, don’t forget to get emotional and psychological support. By being active in managing your condition, you can face challenges and stay well.
Adhering to Treatment Plans
Following your treatment plan is key to managing diffuse liver steatosis. This might include eating differently, being more active, and taking medicines. Sticking to your plan helps you stay healthy, improves your liver, and stops the condition from getting worse.
Regular Follow-up Visits and Monitoring
Seeing your doctor regularly is very important. Doctors like gastroenterologists or hepatologists can check your liver health. They can also change your treatment if needed and help you stay on track.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Eat a balanced diet that’s low in bad fats, sugars, and refined carbs.
- Do regular exercise like walking, swimming, or strength training to stay healthy and improve your liver.
- Drink less alcohol because it can hurt your liver more.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Having a chronic liver condition can be tough on your mind and heart. Getting help from a counselor, therapist, or support group can help. Remember, taking care of your mind is just as important as your body.
By focusing on sticking to your treatment, going to doctor visits, making lifestyle changes, and getting emotional support, you can manage your diffuse liver steatosis. This will help you live a better life.
Conclusion
Diffuse liver steatosis, or fatty liver disease, is a big health problem. It needs our attention and action. Knowing its causes, symptoms, and risks helps us protect our liver.
By making lifestyle changes, managing weight, and sometimes getting medical help, we can stop or reverse fatty liver. This is good news for our liver health.
In the U.S., about 40 million adults have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. This is a big issue. Obesity, type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, and metabolic syndrome can lead to fatty liver.
Eating well, staying active, and keeping a healthy weight can lower your risk. These steps are key to avoiding fatty liver.
If you have fatty liver, working with doctors like Dr. Nivedita Pandey is crucial. They can help you create a treatment plan. This might include lifestyle changes, medicines, or surgery in serious cases.
Following your treatment plan and getting regular check-ups is important. This way, you can keep an eye on your condition and take care of your liver.
FAQ
What is diffuse liver steatosis?
Diffuse liver steatosis, also known as fatty liver disease, is when fat builds up in the liver. It can cause serious health problems if not treated.
What are the common causes of diffuse liver steatosis?
What are the typical symptoms of diffuse liver steatosis?
How is diffuse liver steatosis diagnosed?
What are the risk factors associated with diffuse liver steatosis?
What are the potential complications of diffuse liver steatosis?
How is diffuse liver steatosis treated?
How can diffuse liver steatosis be prevented?
How is diffuse liver steatosis associated with other health conditions?
What are the important considerations for living with diffuse liver steatosis?
Living with it means following your treatment plan and making lifestyle changes. Regular check-ups and emotional support are also important.
Source Links
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Nivedita Pandey, MD, DM (Gastroenterology)
Senior Gastroenterologist & Hepatologist
Dr. Nivedita Pandey is a U.S.-trained gastroenterologist and hepatologist with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating liver diseases and gastrointestinal disorders. She specializes in liver enzyme abnormalities, fatty liver disease, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and digestive health.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current clinical guidelines.
About Author | Instagram | Linkedin