What Is Liver Cirrhosis?
Liver cirrhosis symptoms start appearing when your liver tissue transforms into scar tissue over time. When scar tissue replaces healthy cells, liver functions become harder to complete.
Table of Contents
ToggleScarring changes the liver’s smooth texture into a bumpy, hardened surface. Blood vessels that normally flow straight through get twisted and compressed. Blood struggles to enter the liver, which creates pressure that forces fluid into your belly and chest.
Your liver needs proper blood flow to work. Each minute, your liver filters about 1.5 liters of blood. When scarring narrows the pathways, blood finds alternate routes through smaller, weaker veins in your esophagus and stomach. These veins weren’t built for high-volume traffic and can burst.
Key Takeaways
- Liver cirrhosis symptoms emerge when chronic liver damage creates scar tissue that disrupts normal organ function
- Early warning signs include persistent fatigue, unexplained weight loss, and reduced appetite, though you show no symptoms initially
- Advanced stages bring jaundice (yellow skin), fluid-filled abdomen, mental confusion, and dangerous internal bleeding
- Complications develop when scarring blocks blood flow and prevents the liver from filtering toxins and producing essential proteins
Note: Liver damage and liver failure are completely different stages.You can have significant liver damage with scarring but still function normally for years. You can survive with just 20% of a healthy liver working properly. Liver failure happens only when so much tissue is destroyed that essential functions stop completely. |
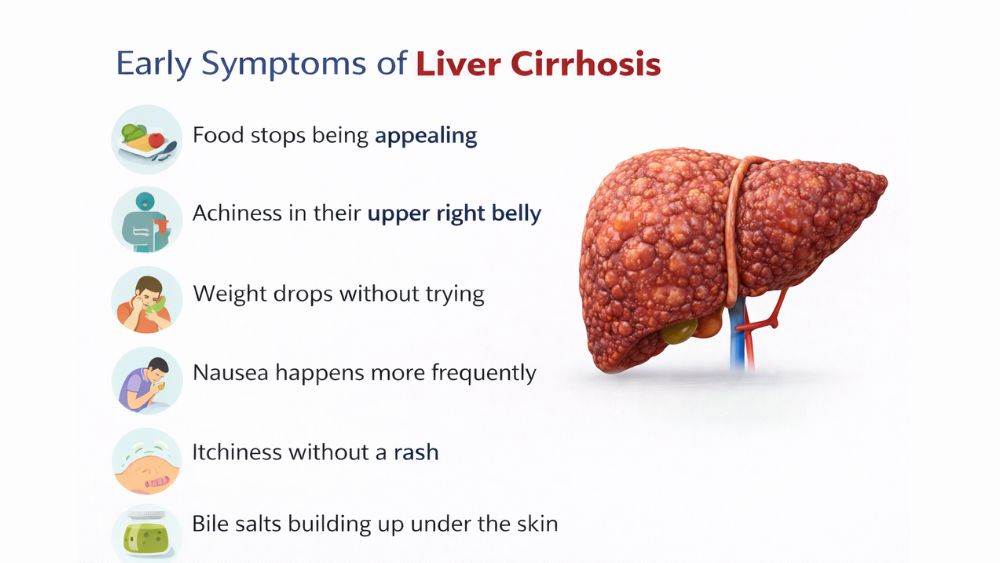
Early Symptoms of Liver Cirrhosis
Your liver has almost no pain nerves inside it. Hence, your liver can lose 75% of its normal function before any liver symptoms appear.
Early symptoms of liver cirrhosis show up as general body problems rather than liver-specific issues. You feel exhausted by mid-afternoon, even after sleeping 8 hours.
Food stops being appealing. You might cook your favorite meal and feel full after three bites. This happens because your damaged liver releases different hormone levels than normal, affecting hunger signals.
You notice mild achiness in their upper right belly , just below their ribs. This discomfort comes and goes. It’s not sharp pain, more like a dull heaviness or fullness. The feeling occurs because your liver is swelling slightly from inflammation and scarring.
Weight drops without trying. Your body isn’t absorbing nutrients efficiently from the food you do eat due to reduced bile production.
Nausea happens more frequently , especially in the morning or after fatty meals. Your digestive system struggles without enough bile to break down food properly.
You develop general itchiness without a rash , caused by bile salts building up under the skin.
Advanced Liver Cirrhosis Symptoms
When liver cirrhosis symptoms progress to advanced stages, your skin turns yellowish (jaundice), starting subtly and becoming more obvious over weeks.
Your belly swells up like a balloon , sometimes gaining 20 to 40 pounds of fluid weight (called ascites) while the rest of your body loses muscle.
Spider angiomas appear on your chest, shoulders, neck, and face. They look like tiny red spiders with a central red dot and thin lines radiating outward. When you press the center, the whole thing blanches white, then refills with blood when you release pressure.
Your palms turn bright pink or red (palmar erythema), particularly at the base of your thumbs and little fingers. The redness doesn’t hurt or itch, but it’s permanent once it develops.
Small cuts bleed longer than they should. You develop frequent nosebleeds or notice your gums bleeding when brushing teeth.
Liver cirrhosis symptoms in men include breast tissue growth (gynecomastia) and testicle shrinkage. Women might stop having periods or experience irregular cycles.
Cirrhosis Complications and Their Symptoms
Cirrhosis complication symptoms are medical emergencies that can kill within hours if untreated.
Variceal bleeding
Blood that can’t flow through your scarred liver backs up into veins in your esophagus (food pipe) and stomach lining. These veins bulge like overfilled water balloons.
When they burst, you vomit massive amounts of bright red blood or dark material resembling coffee grounds. Blood traveling through your intestines turns your stools black, sticky, and tar-like.
Hepatic encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy changes your personality and mental function in strange ways. Ammonia and other toxins that your liver normally filters out accumulate in your bloodstream and cross into your brain.
Cirrhosis complications symptoms from this include forgetting conversations from an hour ago, getting confused about what day it is, having trouble doing simple math, and experiencing personality changes that worry family members.
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis means the fluid in your swollen belly gets infected without any obvious injury or surgery. You develop a fever, belly pain that gets worse when moving, and feel confused or disoriented. Cirrhosis complication symptoms like this need antibiotics within hours.
Hepatorenal syndrome
Hepatorenal syndrome happens when your kidneys suddenly stop working even though nothing is directly wrong with them. Your cirrhotic liver releases chemicals that make kidney blood vessels constrict. Urine output drops dramatically. Waste products build up in blood. Your legs swell more than usual.
Portal hypertensive gastropathy
Portal hypertensive gastropathy means the lining of your stomach becomes swollen and fragile, developing patches that bleed easily. This causes slow chronic blood loss that makes you anemic over weeks. You feel weak, dizzy, and short of breath from low red blood cell counts.
Types of Liver Cirrhosis
Understanding types of liver cirrhosis helps explain why two people with the same disease can feel completely different.
Compensated cirrhosis
Compensated cirrhosis means your liver is scarred but compensating for the damage. Blood tests might show some abnormalities. Imaging reveals scarring. But you feel relatively okay because the remaining healthy liver tissue works overtime to handle daily demands.
You might have mild fatigue or no liver cirrhosis symptoms at all. Compensated cirrhosis can last 10 to 15 years or longer if you stop whatever is damaging your liver. About half of the people with compensated cirrhosis never progress to the next stage if they get proper treatment.
Decompensated cirrhosis
Decompensated cirrhosis means your liver can’t compensate anymore. This is when fluid in your belly, bleeding varices, confusion from toxins, or jaundice. The shift from compensated to decompensated can happen gradually or suddenly after an infection, bleeding episode, or even dehydration from a stomach virus.
Once decompensation occurs, average survival without transplant drops to around 2 years, though this varies widely.
Child-Pugh classification
Child-Pugh classification divides types of liver cirrhosis into grades A, B, and C based on bilirubin levels, albumin levels, clotting time, ascites presence, and encephalopathy severity.
- Grade A patients function well.
- Grade C patients have advanced disease with poor short-term outlook. MELD score (ranging from 6 to 40) predicts three-month mortality risk and determines transplant priority. Higher scores mean sicker patients who need transplants more urgently.
What Causes Cirrhosis?
What causes cirrhosis varies by geography, lifestyle, and genetics, but chronic repeated liver injury is the common thread.
Chronic heavy alcohol consumption tops the list of what causes cirrhosis in many countries. Drinking more than two standard drinks daily for women or three for men over 10 to 20 years significantly raises risk.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is rapidly becoming the leading cause of cirrhosis worldwide. Fat accumulates in liver cells of people who drink little or no alcohol. This happens with obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol, and metabolic syndrome. The fat causes inflammation that progresses to scarring in about 20% of cases.
Chronic hepatitis B and C infections cause cirrhosis in millions of people. Hepatitis C spreads through blood contact and often shows no symptoms until cirrhosis develops 20 to 30 years after infection. Hepatitis B transmits through blood and sexual contact, with higher cirrhosis risk in people infected as infants.
Autoimmune hepatitis occurs when your immune system mistakenly attacks liver cells. Primary biliary cholangitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis destroy bile ducts inside the liver, causing bile backup and scarring.
Hemochromatosis makes your body absorb too much iron from food, and excess iron deposits damage the liver over time.
Wilson disease causes copper buildup. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency leaves abnormal proteins trapped in liver cells.
How Cirrhosis Symptoms Progress Over Time
Liver cirrhosis symptoms progress from diagnosis to severe complications within 2 years. Others live 20 years with stable, mild disease. The difference depends on what’s damaging the liver, whether that damage continues, and individual genetic factors.
Early progression happens silently. Scarring spreads through the liver without producing signs of cirrhosis of the liver that you’d notice. Fibrosis (early scarring) takes 5 to 20 years to become true cirrhosis in most chronic liver diseases. During this phase, stopping the damage can prevent cirrhosis entirely.
Once cirrhosis develops, progression depends heavily on whether the underlying cause gets treated. Someone who stops drinking completely might stay compensated for decades. Someone who continues heavy drinking typically decompensates within 5 years.
Hepatitis C patients who achieve sustained virological response (virus elimination) with treatment have dramatically slower progression than untreated patients.
When Are Cirrhosis Symptoms a Medical Emergency?
Certain signs of cirrhosis of the liver mean calling emergency services immediately.
Vomiting blood or black material signals active bleeding from varices or stomach lining. You need blood transfusions and emergency endoscopy to stop bleeding. Without treatment, you can bleed to death in hours. Even if bleeding stops on its own, the risk of fatal rebleeding within 6 weeks is about 70% without intervention.
Severe confusion that’s rapidly worsening , especially if you can’t wake someone up normally, indicates high-grade hepatic encephalopathy. Ammonia levels in the brain cause swelling that can lead to coma and death. Treatment with lactulose and rifaximin must start urgently.
Your belly swelling up dramatically over 2 to 3 days, accompanied by fever and abdominal tenderness, likely means infected ascites fluid. This bacterial peritonitis requires IV antibiotics within hours to prevent septic shock.
Black tarry stools or maroon-colored stools mean significant gastrointestinal bleeding. Black indicates upper GI bleeding (varices or ulcers), while maroon suggests lower GI or very rapid upper GI bleeding. Either way, you’re losing blood that needs replacement.
Yellow skin deepening rapidly over days suggests acute-on-chronic liver failure. Your already damaged liver is failing completely, often triggered by infection, medications, or dehydration.
Can Liver Cirrhosis Symptoms Improve?
Liver cirrhosis symptoms can definitely improve even though the scars themselves never disappear.
Treating the underlying cause changes everything. Stopping alcohol, viral clearance with hepatitis C medications, and losing 7 to 10% of body weight through diet and exercise improve fatty liver disease dramatically.
Diuretics remove 10 to 30 pounds of ascites fluid, making breathing easier and reducing belly discomfort. Lactulose clears toxins from your gut and blood, improving mental clarity and reversing confusion. Beta-blockers lower portal pressure, reducing bleeding risk and allowing some people to feel more energetic.
Liver transplant completely eliminates liver cirrhosis symptoms by replacing the diseased organ with a healthy one. Five-year survival after transplant exceeds 75% at experienced centers. Many transplant recipients return to normal activities, work full-time, and enjoy excellent quality of life.
FAQs About Liver Cirrhosis Symptoms
What are the first symptoms of liver cirrhosis?
Persistent fatigue that doesn’t improve with rest, unexplained weight loss exceeding 10 pounds over 2 to 3 months, reduced appetite where you feel full after small portions, and vague upper right belly discomfort are typically the first liver cirrhosis symptoms people notice before more obvious signs develop.
Can cirrhosis exist without symptoms?
Yes, compensated liver cirrhosis symptoms are often completely absent for 10 to 15 years because your liver maintains about 25 to 30% function, which is enough for daily activities, explaining you discover cirrhosis accidentally during routine blood work or imaging done for unrelated reasons .
Does cirrhosis always cause jaundice?
No, jaundice appears only in advanced decompensated liver cirrhosis symptoms when bilirubin levels exceed 2.5 to 3 mg/dL, and many people with compensated cirrhosis never develop yellow skin because their liver still eliminates bilirubin adequately despite scarring throughout the entire disease course.
Is confusion a symptom of cirrhosis?
Yes, hepatic encephalopathy causes confusion, personality changes, and memory problems when ammonia levels reach 3 to 4 times normal because your scarred liver can’t filter toxins properly, and these cirrhosis complication symptoms require immediate lactulose treatment to prevent progression to coma within 24 to 48 hours.
Are cirrhosis symptoms reversible?
Liver cirrhosis symptoms can improve significantly through treating underlying causes and managing complications, though scarring remains permanent, meaning fatigue, ascites, and confusion often resolve with proper medication while liver architecture stays damaged but stable enough to function adequately for years.
Can cirrhosis progress suddenly?
Yes, stable compensated liver cirrhosis symptoms can shift to life-threatening decompensation within 3 to 7 days after infections, bleeding, dehydration, or certain medications stress the liver beyond its limited capacity, which is why immediate medical attention for fever or vomiting prevents rapid deterioration and death.
Is cirrhosis life-threatening?
Compensated liver cirrhosis symptoms allow 10 to 15-year survival with treatment, but decompensated cirrhosis with complications like variceal bleeding (30% mortality per episode), severe encephalopathy, or kidney failure carries 50% two-year mortality without transplant, making early detection and cause treatment absolutely critical for survival .
Should mild symptoms be ignored?
No, even subtle signs of cirrhosis of the liver, like fatigue and appetite loss warrant liver function tests and ultrasound because detecting cirrhosis in the compensated stage allows treatment that prevents life-threatening complications, while waiting until jaundice or ascites appears means missing the window for best outcomes and longest survival .
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Nivedita Pandey, MD, DM (Gastroenterology)
Dr. Nivedita Pandey is a U.S.-trained gastroenterologist and hepatologist with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating liver diseases and gastrointestinal disorders. She specializes in liver enzyme abnormalities, fatty liver disease, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and digestive health.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current clinical guidelines.