Jaundice makes your skin and eyes look yellow. It happens when bilirubin builds up. This yellow pigment comes from broken-down red blood cells. Seeing a doctor quickly is key to treating jaundice and hyperbilirubinemia.
Table of Contents
ToggleKnowing the early signs of jaundice helps you act fast. This can protect your health.
Jaundice can happen to anyone, at any age. Spotting the symptoms is the first step to getting help. Signs include jaundice, dark urine, pale stools, feeling tired, itchy skin, nausea, stomach pain, fever, and yellow eyes.
Seeing a doctor fast is important. They can find the cause and start treatment.
Understanding Hyperbilirubinemia
Hyperbilirubinemia is a health issue where there’s too much bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin is made when the body breaks down red blood cells. The liver usually filters it out. But, if there’s too much or the liver can’t handle it, hyperbilirubinemia happens.
What is Hyperbilirubinemia?
Hyperbilirubinemia means there’s too much bilirubin in the body. This makes the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes turn yellow. This is called jaundice. It can happen for many reasons, like liver problems, blocked bile ducts, or too many red blood cells.
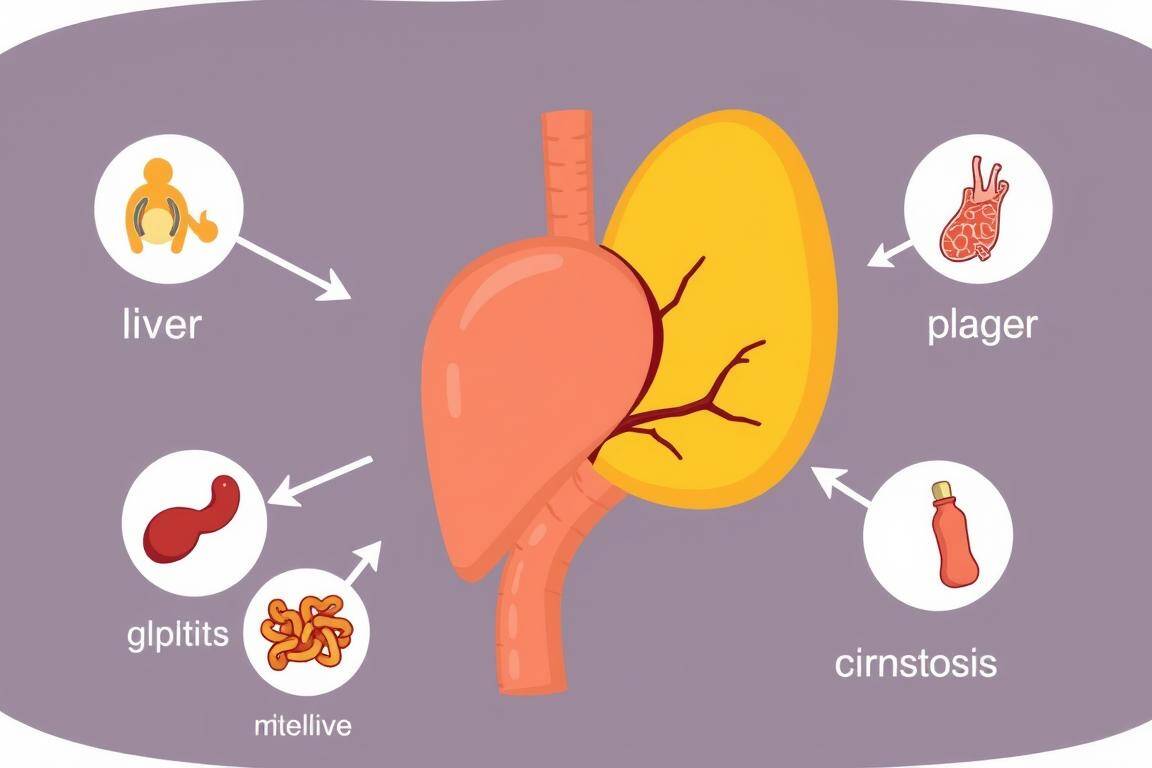
Causes of Elevated Bilirubin Levels
- Prehepatic jaundice: This is caused by an excessive breakdown of red blood cells, leading to an overproduction of bilirubin.
- Hepatic jaundice: This is caused by liver problems, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis, which impair the liver’s ability to properly process and excrete bilirubin.
- Posthepatic jaundice: This is caused by a blockage in the bile ducts, preventing the proper flow of bilirubin from the liver to the intestines.
- Obstructive jaundice: This is caused by a blockage in the bile ducts, often due to gallstones, tumors, or other conditions that obstruct the flow of bile.
Knowing why someone has hyperbilirubinemia is key to treating it. Doctors can figure out the cause and make a plan to help. This plan aims to fix the problem and ease symptoms.
Symptoms of Hyperbilirubinemia in Adults
Visual Signs: Jaundice and Yellowing
The main sign of hyperbilirubinemia in adults is yellow skin and eyes. This yellow color comes from bilirubin, a byproduct of breaking down red blood cells. Jaundice, or yellow skin, is often the first sign that makes people go to the doctor.
Other Potential Symptoms
Adults with hyperbilirubinemia may also have other symptoms. These include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Itchy skin
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Fever and chills
- Dark-colored urine
- Pale or clay-colored stools
These symptoms can show how serious the problem is. They might mean liver disease, bile duct blockage, or genetic disorders. It’s important to see a doctor quickly, as untreated hyperbilirubinemia can cause big problems.

Spotting the signs of hyperbilirubinemia early is crucial. By watching for yellow skin and other symptoms, adults can get help fast. This helps keep their health in check.
Types of Hyperbilirubinemia
It’s key to know the different types of hyperbilirubinemia. This condition, or high bilirubin levels, has four main types. These are prehepatic jaundice, hepatic jaundice, posthepatic jaundice, and obstructive jaundice. Finding the cause is vital for the right diagnosis and treatment.
Prehepatic jaundice happens when too many red blood cells break down. This makes more bilirubin than the liver can handle. Hepatic jaundice is when the liver can’t break down and get rid of bilirubin. Posthepatic jaundice is when bilirubin builds up after leaving the liver, often because of a blockage.
Obstructive jaundice is a type of posthepatic jaundice. It happens when bile ducts are blocked. This stops bile from flowing, causing bilirubin to build up. Gallstones, tumors, or other problems in the biliary system can cause this.
Knowing the types of hyperbilirubinemia helps doctors make the right diagnosis. They can then create a treatment plan that targets the cause. This helps patients manage their condition better.
Diagnostic Tests for Hyperbilirubinemia
If you have hyperbilirubinemia, your doctor will run several tests. These tests check your bilirubin levels, liver function, and overall health.
Blood Tests for Bilirubin and Liver Function
A blood test is often the first step. It measures your bilirubin levels. Your doctor will also check your liver function tests, like hepatitis tests.
Imaging Studies and Liver Biopsy
After blood tests, your doctor might suggest imaging studies. These include CT scans, ultrasounds, or MRCP to find blockages. Sometimes, a liver biopsy is needed to check for damage.
Prothrombin time tests also check your liver’s function. These tests help your doctor find the cause of your hyperbilirubinemia. They then create a treatment plan for you.

hyperbilirubinemia in adults symptoms
Hyperbilirubinemia is when there’s too much bilirubin in the blood. This shows up as yellow skin, eyes, and mucous membranes, known as jaundice. The yellow color comes from bilirubin, a bile pigment.
People with this condition may also feel other symptoms. These include:
- Dark-colored urine
- Pale or clay-colored stools
- Fatigue and lethargy
- Itchy skin
- Nausea and abdominal pain
- Fever and chills
In severe cases, it can cause serious brain problems. These can be confusion, drowsiness, and even coma. It’s very important to see a doctor quickly if you notice these signs.
Spotting the early signs of hyperbilirubinemia is key. It helps get the right treatment fast. By watching for yellow skin and other symptoms, you can act quickly. This helps fix the problem and get you feeling better.
Treatment Approaches for Hyperbilirubinemia
If you have hyperbilirubinemia, finding and fixing the main cause is key. This might mean taking medicines for liver diseases or infections. Or, it could mean surgery to remove gallstones or clear bile duct blockages. While fixing the main problem, your doctor might also suggest ways to ease your symptoms. For example, using cholestyramine to help with itchy skin.
Addressing the Underlying Cause
Managing hyperbilirubinemia starts with treating the main cause. This could be medicines for liver diseases or infections. Or, it might need surgery to remove gallstones or clear bile ducts. Fixing the main issue helps get bilirubin levels back to normal and stops more problems.
Symptom Management Strategies
- Cholestyramine: This medicine can help with itchy skin often seen with hyperbilirubinemia.
- Phototherapy: Sometimes, light therapy can break down bilirubin and help it leave the body.
- Dietary Modifications: Your doctor might suggest eating less fat or cholesterol to help your liver and symptoms.
By treating the main cause and managing symptoms, your doctor can help you get better. This way, you can avoid more serious problems from hyperbilirubinemia.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Some things can make you more likely to get hyperbilirubinemia. This is when too much bilirubin builds up in your blood. It can cause jaundice and other health problems. Knowing these risk factors and taking steps to prevent them can help.
Lifestyle Modifications to Reduce Risk
Heavy alcohol intake is a big risk factor for hyperbilirubinemia. Drinking too much alcohol can hurt your liver. This makes it hard for your liver to get rid of bilirubin. To lower your risk, drink less alcohol and eat a balanced diet that’s good for your liver.
Being active through exercise is also important. Exercise helps your liver work better. It also lowers the chance of liver problems that can raise bilirubin levels. Also, try to stay away from harmful toxins. These can include some medicines, chemicals, and pollutants in the environment.
By changing your lifestyle, you can lower your risk of hyperbilirubinemia. This helps keep your liver healthy. It also prevents jaundice and other problems.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If your skin, eyes, or mucous membranes turn yellow, get medical help fast. This is called jaundice and means you have a health issue. Look out for fever, stomach pain, and dark urine too.
Other warning signs include pale stools, flu-like symptoms, and itchy skin. Also, watch for unexplained weight loss, confusion, and easy bruising. Bloody vomiting is another red flag.
These symptoms could mean serious problems like liver or gallbladder issues. Getting help quickly is key to avoid worse problems. Don’t hesitate to see a doctor if you notice these signs.
Your doctor will do tests to find out what’s wrong. They might check your blood, urine, or use imaging like ultrasounds. This helps them figure out what’s causing your yellow skin and how to treat it.
Jaundice is a warning sign, not a disease itself. Seeing a doctor early can help fix the problem and ease your symptoms.

Hyperbilirubinemia in Special Populations
Hyperbilirubinemia in Newborns and Infants
Hyperbilirubinemia is more common in newborns and infants than in adults. It affects about 60% of newborns. This condition, also known as newborn jaundice or infant jaundice, happens when red blood cells break down. The liver is not mature enough to handle bilirubin, a yellowish pigment.
Newborn jaundice is usually not serious. But, it’s key to know the causes and get treatment quickly. Common causes include blood type differences, breastfeeding issues, and other health problems. In severe cases, phototherapy or a blood transfusion might be needed.
To prevent hyperbilirubinemia, regular check-ups and breastfeeding support are important. Managing any health issues is also crucial. By being vigilant and getting medical help when needed, you can keep your baby’s bilirubin levels healthy.
Conclusion
Hyperbilirubinemia, or jaundice, can happen to adults. It’s often due to liver diseases, infections, gallstones, or too much alcohol. Look out for yellow skin and eyes. If you see these signs, get help fast.
Tests like blood work and scans can find the cause. This lets doctors treat it right. Some cases can’t be stopped, but you can lower your risk.
Eating well, drinking less, and avoiding harmful stuff helps. Catching it early and managing it well is key. Knowing about it helps keep your liver healthy.
Dealing with hyperbilirubinemia needs a full plan. It’s about finding the cause and acting fast. Watch your health closely and get help when needed. This way, you can avoid serious problems.
FAQ
What is hyperbilirubinemia?
Hyperbilirubinemia is when your body has too much bilirubin. This yellow-orange pigment comes from broken-down red blood cells. It makes your skin, eyes, and mucous membranes turn yellow.
What are the main types of hyperbilirubinemia?
There are four main types. Prehepatic jaundice is from too much red blood cell breakdown. Hepatic jaundice is due to liver problems. Posthepatic jaundice is when bilirubin builds up after leaving the liver. Obstructive jaundice is from blocked bile ducts.
What are the symptoms of hyperbilirubinemia?
The main sign is yellow color in the skin and eyes. You might also feel fever, stomach pain, and chills. Dark urine and pale stools are other signs. You could feel flu-like, itchy, or confused.
How is hyperbilirubinemia diagnosed?
Doctors use blood tests to check bilirubin levels and liver function. They might also do imaging tests like CT scans and MRCP. A liver biopsy could be needed in some cases.
How is hyperbilirubinemia treated?
Treatment starts with fixing the cause, like liver diseases or gallstones. This might mean medicines or surgery. Your doctor might also give you medications to manage symptoms, like cholestyramine for itchy skin.
What are the risk factors for developing hyperbilirubinemia?
Heavy alcohol use, liver diseases, and gallstones increase your risk. Lifestyle changes like drinking less alcohol and eating well can help. Avoiding harmful substances also helps.
When should I seek medical attention for hyperbilirubinemia?
See a doctor right away if your skin, eyes, or mucous membranes turn yellow. Also, seek help for fever, stomach pain, chills, and other symptoms.
How common is hyperbilirubinemia in newborns and infants?
It’s more common in newborns and infants, affecting about 60%. It’s usually from red blood cell breakdown and liver immaturity. Quick treatment is key to avoid problems.
Source Links
- Best Liver Specialist In Delhi | Dr Nivedita Pandey
- What Is Jaundice and How to Self Care in Jaundice?
- Jaundice in Adults – Jaundice in Adults – Merck Manual Consumer Version
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Nivedita Pandey, MD, DM (Gastroenterology)
Dr. Nivedita Pandey is a U.S.-trained gastroenterologist and hepatologist with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating liver diseases and gastrointestinal disorders. She specializes in liver enzyme abnormalities, fatty liver disease, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and digestive health.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current clinical guidelines.