Bilirubin in urine means your urine contains a yellow waste pigment that normally leaves the body through bile, not through the kidneys. Bilirubin forms when old red blood cells break down, and a healthy liver processes it before sending it into the digestive system.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhen liver cells get inflamed, damaged, or blocked from draining bile, processed bilirubin can leak into the blood and pass into urine. This finding often shows up before obvious symptoms like yellow skin or eye discoloration.
Bilirubin in urine can point toward liver stress, bile duct blockage, or medication-related liver injury. Because urine testing can detect changes early, this marker often triggers deeper blood tests and imaging.
What Is Bilirubin In Urine?
Your body replaces old red blood cells every day. This normal cleanup creates bilirubin as a yellow waste pigment. Your liver takes bilirubin and adds a sugar to it. This step turns it into “conjugated” bilirubin (water-soluble).
After that, your liver sends conjugated bilirubin into bile. Bile moves through the bile ducts into your gut. Gut bacteria change bilirubin into urobilinogen and related pigments. Some leaves are in the stool, and a small amount of urobilinogen leaves in the urine.
Why bilirubin should normally not appear in urine
In a healthy person, urine should not contain bilirubin. Your liver should push conjugated bilirubin into bile, not into blood. When bile flow slows or liver cells get injured, conjugated bilirubin can build up in the blood.
Your kidneys then filter it, so bilirubin in urine shows up. Urine bilirubin can appear before visible jaundice.
Difference between blood bilirubin and urine bilirubin
Blood tests measure total bilirubin and often split it into direct and indirect. Indirect bilirubin does not dissolve in water, so your kidneys cannot remove it. Urine bilirubin reflects conjugated bilirubin, not unconjugated bilirubin.
So, bilirubin in urine usually lines up with “direct bilirubin” rising in the blood. That pattern often points to liver disease or bile duct blockage.
Bilirubin In Urine Causes
Doctors group the causes of bilirubin in urine into liver cell problems and bile-flow problems. Each group creates different clues in your symptoms and lab pattern.
Liver diseases cause bilirubinuria
Your liver cells handle bilirubin like a sorting system. When those cells get damaged, they leak conjugated bilirubin into the blood. Common intrahepatic causes include viral hepatitis and fatty liver inflammation. It also lists autoimmune hepatitis and genetic conditions like Dubin-Johnson syndrome.
In these cases, bilirubin in urine often comes with tiredness and appetite loss. Your blood work may show higher ALT and AST (liver enzymes).
Bile duct blockage and gallstones
Your bile ducts act like narrow tubes that drain bile. A gallstone can block the common bile duct, and bile backs up. Bile-duct blockage is a key reason bilirubin enters urine.
With blockage, bilirubin in urine may come with pale stools and itching. Some people get sharp right-upper belly pain after fatty meals. Severe blockage can also bring fever, which needs urgent care.
Hepatitis and liver inflammation
Hepatitis means liver inflammation (swelling and injury). Viruses can cause it, and alcohol can too. When inflammation disrupts bile flow inside the liver, conjugated bilirubin can rise. Urine bilirubin can show up in acute viral hepatitis before jaundice appears. So bilirubin in urine can act as an early lab clue, even when your eyes still look normal.
Drug-induced liver injury
Some medicines irritate liver cells in some people. This problem can happen with prescriptions, over-the-counter drugs, and some supplements.
If a drug triggers liver injury, bilirubin in urine may appear with nausea and new fatigue. You should not stop medicines on your own, because safe changes depend on your condition.
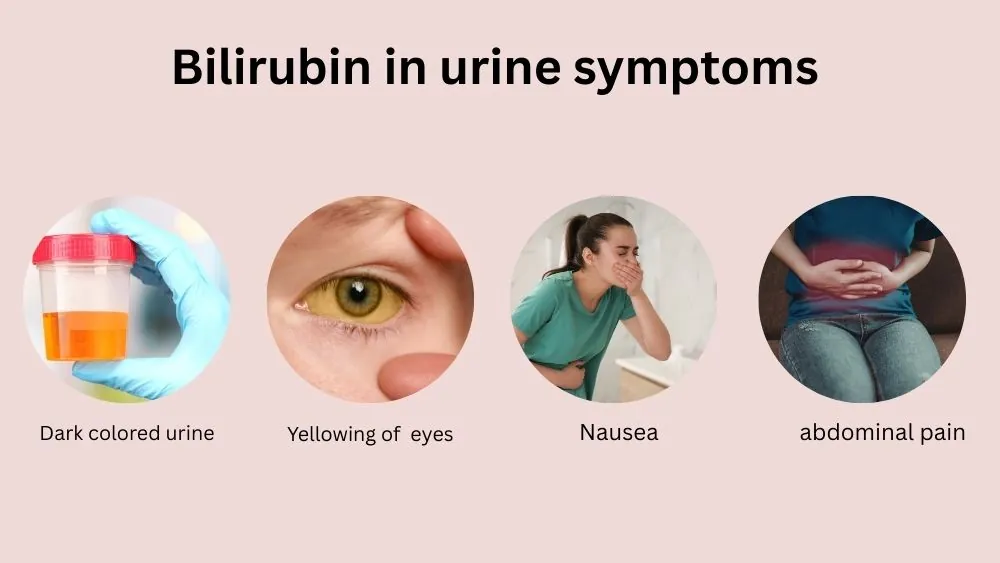
Bilirubin In Urine Symptoms
The test result itself does not cause symptoms. The condition behind it causes the signs. Many symptoms of bilirubin in urine point to bile buildup in your body.
Dark or tea-colored urine
When conjugated bilirubin rises, it can darken your urine. People often describe “tea or cola-colored” urine with conjugated hyperbilirubinemia. If you notice dark urine and a report shows bilirubin in urine, you should contact a clinician soon.
Yellowing of skin and eyes (jaundice)
Jaundice means yellowing of the skin and the whites of your eyes. Jaundice often becomes visible around bilirubin levels near 2 to 3 mg/dL.
You can have bilirubin in urine before you see jaundice. Still, jaundice plus urine bilirubin often signals a stronger problem.
Fatigue, nausea, and abdominal discomfort
Fatigue, nausea, belly pain, and low appetite are common liver or bile-duct warning signs. When these signs come with bilirubin in urine, doctors often order blood bilirubin and liver enzymes the same day.
Symptoms that indicate serious liver disease
Some signs need urgent evaluation because they can signal severe disease. You should treat fever with right-upper belly pain as urgent. You should also treat confusion, severe sleepiness, or easy bleeding as urgent. These signs can occur when liver function drops quickly.
Bilirubin Positive Urine Test
A bilirubin-positive urine test means the dipstick detected bilirubin on the strip pad. This result usually points to conjugated bilirubin reaching your urine.
What a positive urine bilirubin result means
Bilirubin in urine can signal liver disease, like hepatitis or cirrhosis. It can also signal a bile-duct blockage. So a bilirubin-positive urine test narrows the search to liver and bile drainage problems.
How urine dipstick tests detect bilirubin
Dipsticks use a color reaction on a reagent pad. Many strips use a diazo coupling reaction that forms a colored azo dye. The color shift helps the lab grade results as negative, trace, or positive. Because this method relies on color, urine color and storage conditions matter. That explains why doctors sometimes repeat testing.
False positives and false negatives
False results happen more often than most people expect. An older review in American Family Physician lists false positives from phenazopyridine (a urinary pain medicine) and chlorpromazine. It also lists selenium as another cause.
False negatives occur after vitamin C ingestion, after long sample storage, and when urine contains nitrates. If you take high-dose vitamin C, you should tell your clinician, since it can hide bilirubin on dipsticks.
Bilirubin Positive Urine Test Results
Trace vs clearly positive bilirubin levels
Labs often report “trace,” “small,” or “positive.” Trace means the pad changed slightly, so bilirubin likely sits near the detection limit. A stronger color shift suggests more bilirubin, but it still stays semi-quantitative.
You should match the grade with your symptoms and blood tests, not alone. A trace finding can still matter when you also have jaundice.
When repeat testing is required
You should repeat testing when the sample sat too long in the light. Bilirubin breaks down with light exposure, and that can lower the reading. A 2024 laboratory review notes bilirubin’s light sensitivity in fluids like urine.
You should also repeat if you used phenazopyridine, because it can tint urine and confuse color pads. If your clinician suspects a false result, they often confirm with blood bilirubin tests.
Urine bilirubin vs urobilinogen comparison
Urobilinogen comes from changes inside your gut. High urobilinogen can occur when your liver cannot recycle it well. It can also rise when your body breaks down red blood cells too fast (hemolytic anemia). Little or no urobilinogen can suggest bile fails to reach the intestines, which fits a bile-duct blockage.
Bilirubin In Urine And Liver Disease
How liver damage causes bilirubin leakage into urine
Your liver normally packs bilirubin into bile, then sends bile into your gut. When liver cells get inflamed or injured, that packing system breaks down. Conjugated bilirubin (direct bilirubin) then builds up in your blood. Because conjugated bilirubin dissolves in water, your kidneys can filter it. That is how bilirubin in urine shows up on a test.
This pattern matters because unconjugated bilirubin cannot enter urine. So when you see bilirubin in urine, doctors often focus on liver cell injury or cholestasis (bile flow slowdown).
Conditions where urine bilirubin appears early
Sometimes, bilirubin in urine appears before your skin turns yellow. It can be an early sign of liver damage and may show up before symptoms.
That early timing often happens in:
- Early hepatitis (liver inflammation).
- Early bile duct blockage from a stone or narrowing.
- Alcohol-related liver damage, where labs change before you feel worse.
If your urine turns tea-colored and your test shows bilirubin in urine, you should not wait for jaundice.
Chronic liver disease vs acute liver injury
Acute injury starts fast, over days or weeks. Viral hepatitis and drug injury can do that. Chronic disease builds slowly, often over years. Long-term fatty liver disease and cirrhosis fit here.
With acute injury, you may get sudden nausea, weakness, and dark urine. With chronic disease, you may feel “off” for months, then notice itching or swelling. In both cases, bilirubin in urine can appear when direct bilirubin rises.
How Bilirubin In Urine Is Diagnosed
Urine analysis and dipstick testing
A routine urinalysis often finds bilirubin in urine. The dipstick pad changes color when bilirubin reacts with the strip chemicals. The lab reports negative, trace, or positive.
To avoid errors, a fresh sample helps. Light can break down bilirubin in the cup. Old samples can read lower than the real level. If the results look odd, your clinician may repeat the urine test.
This is also where your clinician checks other urine clues, like urobilinogen. That comparison can help sort liver cell injury from bile blockage.
Blood tests are done alongside urine bilirubin
Urine results alone cannot show the full picture. Doctors usually order a liver panel and bilirubin fractions. These tests often include ALT and AST (enzymes that rise with liver cell injury). They also include ALP and GGT (enzymes that often rise with bile flow blockage).
They may also check:
- Total and direct bilirubin, to confirm the pattern behind bilirubin in urine.
- Blood counts, to look for infection or anemia.
- INR or clotting tests, because severe liver injury can slow clotting.
Imaging tests if obstruction is suspected
If blood tests point toward blockage, imaging helps. Ultrasound often comes first because it can spot gallstones and duct widening. If the ultrasound looks unclear, doctors may use MRCP (a special MRI view of the bile ducts) or CT. These tests help confirm a bile duct obstruction.
If you have pain, fever, and bilirubin in your urine, doctors often move quickly because bile duct infection can become dangerous.
Treatment For Bilirubin In Urine
Treating the underlying liver condition
You do not “treat urine bilirubin” by itself. You treat what caused it. Liver disease and bile duct blockage are major causes, so treatment follows that root cause.
If hepatitis causes bilirubin in urine, treatment depends on the type. Some viral hepatitis need antiviral care. Some cases improve with rest, fluids, and monitoring. If alcohol plays a role, stopping alcohol use becomes a key step. Your clinician may also review your vaccines and exposures.
If fatty liver inflammation contributes, clinicians often focus on weight, diabetes control, and cholesterol management. These changes do not work overnight, but they can lower liver strain.
Managing bile duct obstruction
If a gallstone blocks the bile duct, doctors may remove it using ERCP (a scope procedure). If swelling or scar tissue causes narrowing, they may place a stent (a small tube) to keep bile flowing. When bile flow returns, bilirubin in urine often clears as direct bilirubin falls.
You should not try home “flushes” for suspected blockage. Blockage needs real testing because delays can raise infection risk.
Medication changes if drug-induced
Some medicines can injure your liver in certain people. If your clinician suspects drug injury, they may stop the suspected drug and switch to another option. Dosage varies by age and condition, so your clinician guides this choice.
Also, remember testing pitfalls. A classic review lists phenazopyridine and chlorpromazine as causes of false-positive bilirubin dipsticks. So your clinician may confirm results before blaming a drug.
When To See A Doctor For Bilirubin In Urine
Warning signs that need urgent evaluation
You should seek urgent care if you have:
- Fever with right-upper belly pain and vomiting.
- Confusion, severe sleepiness, or new fainting.
- Yellow skin with severe weakness or poor intake.
- Black stools, vomiting blood, or easy bleeding.
These signs can point to serious liver stress or bile duct infection. In these cases, bilirubin in urine becomes a high-priority clue.
Bilirubin in urine during pregnancy
Pregnancy changes hormones and bile flow. Some pregnancy-related liver conditions can raise bile problems and itching. If you have itching, dark urine, or bilirubin in urine during pregnancy, you should contact your obstetric team quickly. You should not self-treat with supplements or herbal products.
Persistent bilirubinuria without symptoms
Sometimes you feel fine, yet the lab keeps showing bilirubin in urine. Persistent findings still deserve follow-up because silent bile duct problems can exist. Your clinician may repeat urine testing, order blood work, and consider imaging based on the pattern.
FAQs
What does bilirubin in urine mean?
Bilirubin in urine usually means conjugated bilirubin entered your blood, and your kidneys filtered it. This pattern often points toward liver cell injury or slowed bile flow, so doctors confirm with blood tests.
Is bilirubin normally present in urine?
No, bilirubin normally stays out of urine because the liver sends it into bile. When urine shows bilirubin in urine, it usually reflects conjugated hyperbilirubinemia, not normal variation.
What causes bilirubin to appear in urine?
The causes of bilirubin in urine often include hepatitis, cirrhosis, and bile duct blockage. Drug-related liver injury can also cause it. Your clinician matches urine findings with blood tests and symptoms.
Is bilirubin in urine always a sign of liver disease?
Not always, because dipsticks can give false positives. Phenazopyridine and chlorpromazine are false-positive causes. Still, true bilirubin in urine usually needs a liver and bile duct check.
Can gallstones or bile duct blockage cause bilirubin in urine?
Yes, blockage can force conjugated bilirubin back into your blood. Your kidneys then remove it, creating bilirubin in urine. You may also notice pale stools, itching, or right-sided belly pain.
Does hepatitis cause bilirubin in urine?
Yes, hepatitis can disrupt bile handling inside liver cells. Conjugated bilirubin can rise and spill into urine, so bilirubin in urine may appear alongside fatigue, nausea, and dark urine.
Can medications lead to a positive urine bilirubin test?
Yes, some medicines can injure the liver in some people, and some can also skew dipstick readings. That is why a clinician reviews your full medicine list after a bilirubin-positive urine test.
What symptoms are associated with bilirubin in urine?
Common symptoms of bilirubin in urine include tea-colored urine, yellow eyes, itching, nausea, and tiredness. Severe signs like fever with belly pain, confusion, or bleeding need urgent evaluation.
Can dark or tea-colored urine indicate bilirubinuria?
Yes, tea-colored urine can happen when conjugated bilirubin rises and enters urine. Dehydration can also darken urine, so a urinalysis helps confirm whether bilirubin in urine explains the color.
What does a positive urine bilirubin test result mean?
A bilirubin-positive urine test suggests conjugated bilirubin reached your urine, which often links to liver disease or bile duct blockage. Doctors usually confirm with blood bilirubin fractions and liver enzymes.
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Nivedita Pandey, MD, DM (Gastroenterology)
Dr. Nivedita Pandey is a U.S.-trained gastroenterologist and hepatologist with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating liver diseases and gastrointestinal disorders. She specializes in liver enzyme abnormalities, fatty liver disease, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and digestive health.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current clinical guidelines.