A gastroenterologist is a trained expert in the digestive system. The word gastrologist is a common nickname people use online and in speech. Your safest pick for stomach, liver, and intestinal care is the board-trained GI doctor.
Table of Contents
ToggleGastrologist vs Gastroenterologist matters because the right expert cuts delays, lowers risk, and improves results.
What Is A Gastrologist?
Meaning And Common Usage Of The Term “Gastrologist”
You see “gastrologist” on search pages and clinic ads because the word sounds like a stomach doctor. It is casual speech. It is not a formal title in medicine. When a clinic says “gastrologist,” they almost always mean a gastroenterologist. That is where gastrologists and gastroenterologists start to confuse people. If you hear the casual word at a front desk, ask for the doctor’s specialty and board status.
Why “Gastrology” Isn’t A Recognized Medical Specialty
There is no residency named “gastrology.” There is no licensing exam for it. Medical boards do not list it. Hospitals do not credential it as a specialty. So, gastrologist qualifications do not exist in a formal sense. When you compare a Gastrologist vs a Gastroenterologist, one path has defined training and exams. The other does not.
Misconceptions About Gastrologists And Digestive Health
Common myths:
- A “gastrologist” treats only the stomach: The title is not recognized, so there is no set scope.
- A “gastrologist” does simple tests while GI doctors do hard ones: Again, there is no defined training for that title.
- Using the casual word is enough when booking care: It is not. You should confirm that the doctor is a gastroenterologist with fellowship training.
What Is A Gastroenterologist?
Definition And Medical Background
A gastroenterologist is a physician who focuses on the digestive system. That includes the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, colon, rectum, liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, and pancreas. This doctor learns to diagnose and treat problems across all of these organs. The path is long and structured, which is why gastroenterologist qualifications carry weight.
You will see a Gastroenterologist come up when people need help for reflux, ulcers, IBS, IBD, liver disease, or screening for colon cancer.
Areas Of Expertise: Stomach, Liver, And Intestines
You get help for:
- Upper tract issues like reflux, swallowing trouble, heartburn, and ulcers.
- Small bowel problems like celiac disease and hidden bleeding.
- Colon problems like polyps, colitis, and diverticulitis.
- Liver conditions such as hepatitis and fatty liver.
- Gallbladder and bile duct problems, like stones and infections.
- Pancreas problems, such as pancreatitis.
These are the day-to-day settings where Gastrologist vs Gastroenterologist makes a real difference.
Conditions Gastroenterologists Diagnose And Treat
Your GI specialist evaluates:
- Ongoing chest burn and sour taste from acid reflux
- Nausea, vomiting, bloating, gas, and early fullness
- Belly pain that wakes you at night
- Change in bowel habits, diarrhea, or constipation
- Black stool, red blood, or anemia
- Weight loss without trying
- Hepatitis, cirrhosis, and fluid in the belly
- Pancreatitis with severe upper belly pain
- Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis
- Colon polyps and colon cancer risk
When you read Gastrologist vs Gastroenterologist, remember that only the GI specialist has a fixed path to learn these areas.
Gastrologist vs Gastroenterologist: Key Differences
Qualifications And Medical Training Comparison
Here is a clear side-by-side view you can use while booking:
| Path | Training Steps | Exams | Scope of Care |
| Gastroenterologist | Medical school, internal medicine residency, GI fellowship, optional advanced endoscopy or hepatology year | National board exams in internal medicine and gastroenterology, regular renewal with continuing education | Full digestive system care, endoscopy, colonoscopy, polyp removal, bleeding control, and advanced procedures |
| “Gastrologist” | No formal path | No board exam for “gastrology” | No defined scope in the medical system |
Clinical Expertise And Procedural Scope
Your gastroenterologist performs:
- Upper endoscopy to view and treat the esophagus and stomach
- Colonoscopy to find and remove polyps
- Endoscopic ultrasound for close imaging from inside the gut
- ERCP to open blocked bile ducts and place stents
- Capsule endoscopy for a camera pill that scans the small bowel
- Dilation for narrowed areas and banding to stop bleeding
- Biopsy to sample tissue for lab review
Recognition By Medical Boards And Associations
National and state boards recognize gastroenterology as a subspecialty of internal medicine. Hospitals and insurers require proof of training for advanced GI procedures.
There is no official registry for “gastrology.” This directly affects your access to care. Board recognition helps ensure safe sedation, sterile technique, and proper response to emergencies.
Qualifications: Gastroenterologist vs Gastrologist
Education And Residency Requirements For Gastroenterologists
Expect this sequence for a gastroenterologist:
- Medical school to learn the basics of body systems and patient care.
- Three years of internal medicine residency to manage adult diseases.
- Two to three years of GI fellowship to master digestive care.
- An optional extra year for advanced endoscopy or liver focus.
During a fellowship, your doctor logs case numbers for key skills. Examples:
- Hundreds of colonoscopies with polyp removal
- Many upper endoscopies with biopsy and bleeding control
- Training in safe sedation, airway support, and emergency steps
- Hands-on time with ERCP or endoscopic ultrasound if they pursue that track
These steps form the backbone of gastroenterologist qualifications and support consistent results across hospitals and clinics.
Why “Gastrologist” Isn’t Recognized In Medical Licensing
Licensing requires a defined field, a curriculum, faculty oversight, case minimums, and exams. “Gastrology” lacks these. There is no accrediting body that sets the rules. Since there is no formal training track, gastrologist’s qualifications cannot be verified or renewed.
Difference In Certifications And Specialization Years
Certification is another bright line:
- A gastroenterologist passes internal medicine boards, then GI boards, then renews knowledge on a schedule.
- A “gastrologist” has no GI board to pass because the specialty label is not in the system.
The time investment also differs:
- A GI doctor spends at least five to six years after medical school to complete residency and fellowship. Many add extra time for advanced procedures.
- The casual title does not link to any set number of years.
Gastrologist vs Gastroenterologist For Stomach Issues
When To See A Gastroenterologist For Digestive Problems
You need a gastroenterologist if you have gut-related symptoms. Seek a GI visit if you have:
- Heartburn three or more times a week
- Food sticking when you swallow
- Ongoing nausea or vomiting
- Belly pain after meals that lasts more than two weeks
- Bloating with early fullness or sudden change in bowel habits
- Blood in stool or black, tar-like stools
- Unplanned weight loss
- Iron deficiency or anemia on lab tests
Conditions That Require Specialist Evaluation (GERD, IBS, Ulcers)
Some issues need a GI specialist early:
- GERD, which is chronic acid reflux that can scar the esophagus
- IBS, which is a pattern of belly pain with diarrhea or constipation
- Peptic ulcers, which are sores in the stomach or duodenum
- Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, which are immune-driven bowel diseases
- Celiac disease, which is gluten-driven small bowel damage
- Barrett’s esophagus, which is a change in the lining from long-term reflux
These conditions demand the skill set learned in the fellowship. That is why the difference between a gastrologist and a gastroenterologist has a direct impact on your workup and treatment plan.
Why Primary Care Doctors May Refer You To A Gastroenterologist
Your primary care doctor is your first point of contact. They will treat simple reflux or gastritis at first. They refer you to GI when:
- Red flags appear, like bleeding or weight loss
- Symptoms do not improve with first-line care
- You need a scope, imaging, or specialized tests
- You need treatment choices that carry higher risk or need sedation
The referral goes to the trained GI expert who can scope, sample, and treat in one place.
What Conditions Does A Gastroenterologist Treat?
Stomach And Intestinal Disorders
You can expect help for:
- Reflux and heartburn
- Gastritis and ulcers caused by H. pylori bacteria or medicines like NSAIDs
- Celiac disease with nutrient loss and anemia
- IBS with pain and bowel habit change
- IBD, which includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis
- Small intestinal bleeding or absorption problems
- Diverticulitis with left lower belly pain
Each area has clear, stepwise care. That is why Gastrologist vs Gastroenterologist is not just about words. It shapes your testing and follow-up.
Liver, Gallbladder, And Pancreas Diseases
A GI specialist treats:
- Hepatitis and fatty liver disease
- Cirrhosis with swelling or confusion caused by toxin buildup
- Gallstones that cause fever or right upper belly pain
- Bile duct blockage that needs ERCP to open the duct
- Pancreatitis with severe upper belly pain that moves to the back
Only a gastroenterologist has the combination of clinic care and scope-based procedures for many of these problems.
Colon Health And Cancer Screening
Colon cancer screening starts at age 45 for most people. If you have a strong family history, your start age may be earlier. Your GI doctor:
- Chooses the right test based on your risk
- Removes polyps during colonoscopy
- Sets the timing for repeat tests
- Reviews diet, medicines, and lifestyle that affect risk
This is another practical place where Gastrologist vs Gastroenterologist matters to your future health.
Procedures Performed By Gastroenterologists
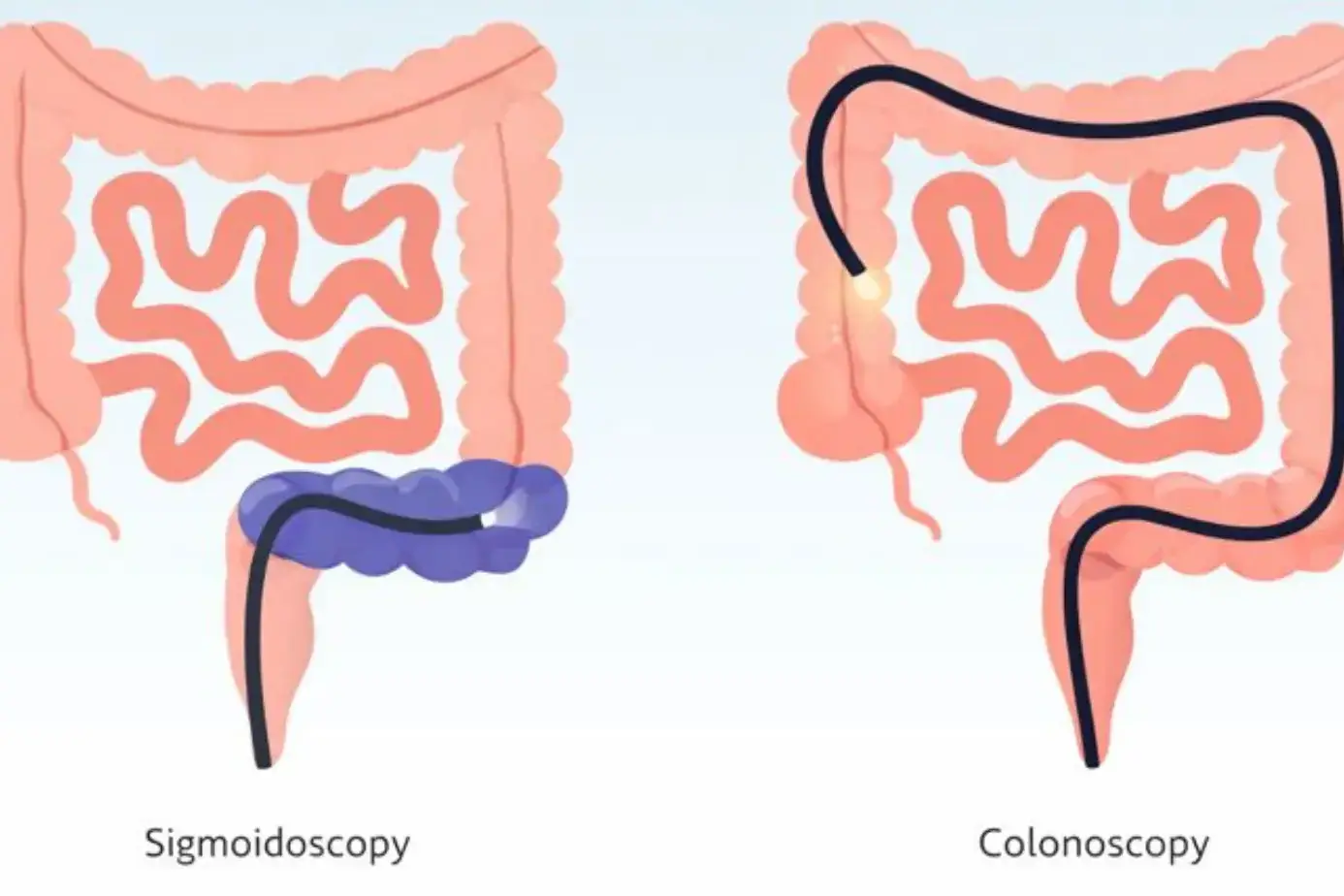
Endoscopy And Colonoscopy
Upper endoscopy uses a thin camera to view your esophagus, stomach, and the first part of the small bowel. A colonoscopy checks your colon and rectum. These tests can:
- Find bleeding and stop it
- Remove polyps before they turn into cancer
- Stretch narrow areas so you can swallow better
- Take biopsies to confirm the diagnosis
These tools are core to GI care. They mark the difference you care about in Gastrologist vs Gastroenterologist decisions.
ERCP And Capsule Endoscopy
ERCP combines endoscopy and X-ray to treat bile duct and pancreatic duct problems. Capsule endoscopy uses a pill camera to view the small bowel. These tests require specialized training and a careful team. Again, the right term and the right specialist line up here.
Advanced GI Imaging And Biopsy Techniques
Endoscopic ultrasound provides high-detail images from inside the GI tract. Your doctor can sample tissue through the scope to diagnose masses or cysts. They can map blood vessels to reduce risk during treatment. These services depend on the training you only get in a GI fellowship.
When Should You Visit A Gastroenterologist?
Persistent Stomach Pain Or Bloating
If pain in your stomach keeps returning, it is not something to ignore. When pain lasts more than two weeks or when bloating becomes a daily problem, it is time to see a gastroenterologist. Your digestive system should not cause discomfort every day. If it does, a specialist has the tests to find the cause. Only the real GI doctor can perform scoping tests, imaging, or sampling if needed.
Chronic Acid Reflux Or Swallowing Issues
Reflux is more than heartburn. It can damage the esophagus if it continues. Some people feel burning in their chest after eating. Others taste acid when they lie down. Some have trouble swallowing. A gastroenterologist checks the esophagus to keep it from scarring.
Blood In Stool Or Unexplained Weight Loss
Blood in stool can look red or black. Both are warning signs that should not wait. Unplanned weight loss is another serious sign. A gastroenterologist will use endoscopy or colonoscopy to find the cause. These are advanced tests that require training.
This is why the Gastrologist vs Gastroenterologist distinction is not small. Safety depends on training.
Regular Colon Screening After Age 45
Colon screening lowers your chance of colon cancer. Most adults start routine screening at age 45. Earlier screening may be needed if someone in your family has had colon cancer.
A gastroenterologist performs these tests and removes polyps before they turn into cancer. Since there is no formal path for gastrologist qualifications, you only want a board-trained GI doctor for this.
How To Choose The Right GI Specialist
Factors To Consider When Selecting A Gastroenterologist
Choosing the right specialist affects your care and comfort. Look for:
- Board certification in gastroenterology
- Completion of internal medicine residency and GI fellowship
- Experience with the procedure you need
- Hospital or clinic quality
- Availability for follow-up care
These reflect gastroenterologist qualifications and help ensure you are in safe hands.
Questions To Ask Before Scheduling An Appointment
You can call the clinic and ask clear, direct questions:
- Who performs the procedures here?
- How many of these procedures are done each year?
- What is the sedation method?
- How soon are results shared?
- Is the specialist board-certified?
These questions help you avoid relying on the casual term gastrologist and instead confirm that you are seeing the correct expert.
Verifying Credentials And Hospital Affiliations
You can check board certification online. Many hospital websites list specialists and their training. This step protects you. It ensures your doctor has passed exams and maintains ongoing study. This is the strongest way to choose correctly in the Gastrologist vs Gastroenterologist comparison.
FAQs
Is A Gastrologist A Real Doctor?
The word gastrologist is a common word people use, but it is not a recognized medical specialty. A gastroenterologist is the correctly trained specialist who treats the digestive system. The difference between a gastrologist and a gastroenterologist is that one has board training and one does not.
Who Should I See For Chronic Stomach Pain?
For ongoing stomach pain, you should see a gastroenterologist. They can perform proper evaluations, run imaging or scope tests, and create a treatment plan. Always choose the real GI specialist.
What Is The Difference Between A Gastrologist And A Gastroenterologist?
A gastroenterologist completes medical school, internal medicine residency, and gastroenterology fellowship. They pass board exams. The term gastrologist does not refer to a certified specialty. That is the main difference between a gastrologist and a gastroenterologist in medical practice.
Can A Gastroenterologist Treat Liver Or Pancreas Diseases?
Yes. A gastroenterologist treats liver diseases such as hepatitis and fatty liver, gallbladder problems, bile duct issues, and pancreatitis. This care is part of standard gastroenterologist qualifications training during a fellowship.
What Tests Does A Gastroenterologist Perform?
A gastroenterologist performs endoscopy, colonoscopy, capsule endoscopy, ERCP, biopsies, and imaging-guided procedures. Since there are no defined gastrologist qualifications, only a GI doctor trained in these methods should perform them.
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Nivedita Pandey, MD, DM (Gastroenterology)
Dr. Nivedita Pandey is a U.S.-trained gastroenterologist and hepatologist with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating liver diseases and gastrointestinal disorders. She specializes in liver enzyme abnormalities, fatty liver disease, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and digestive health.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current clinical guidelines.