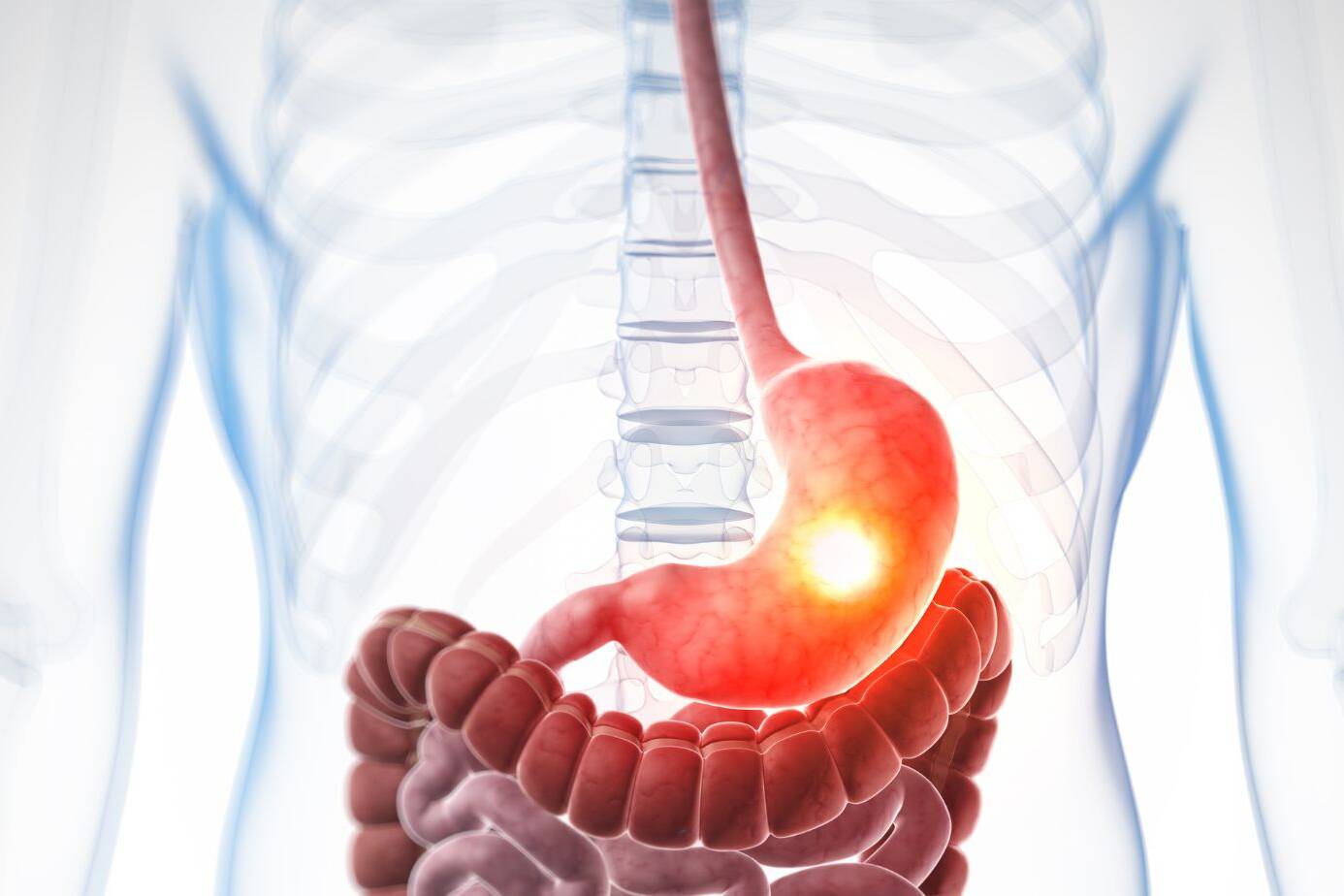
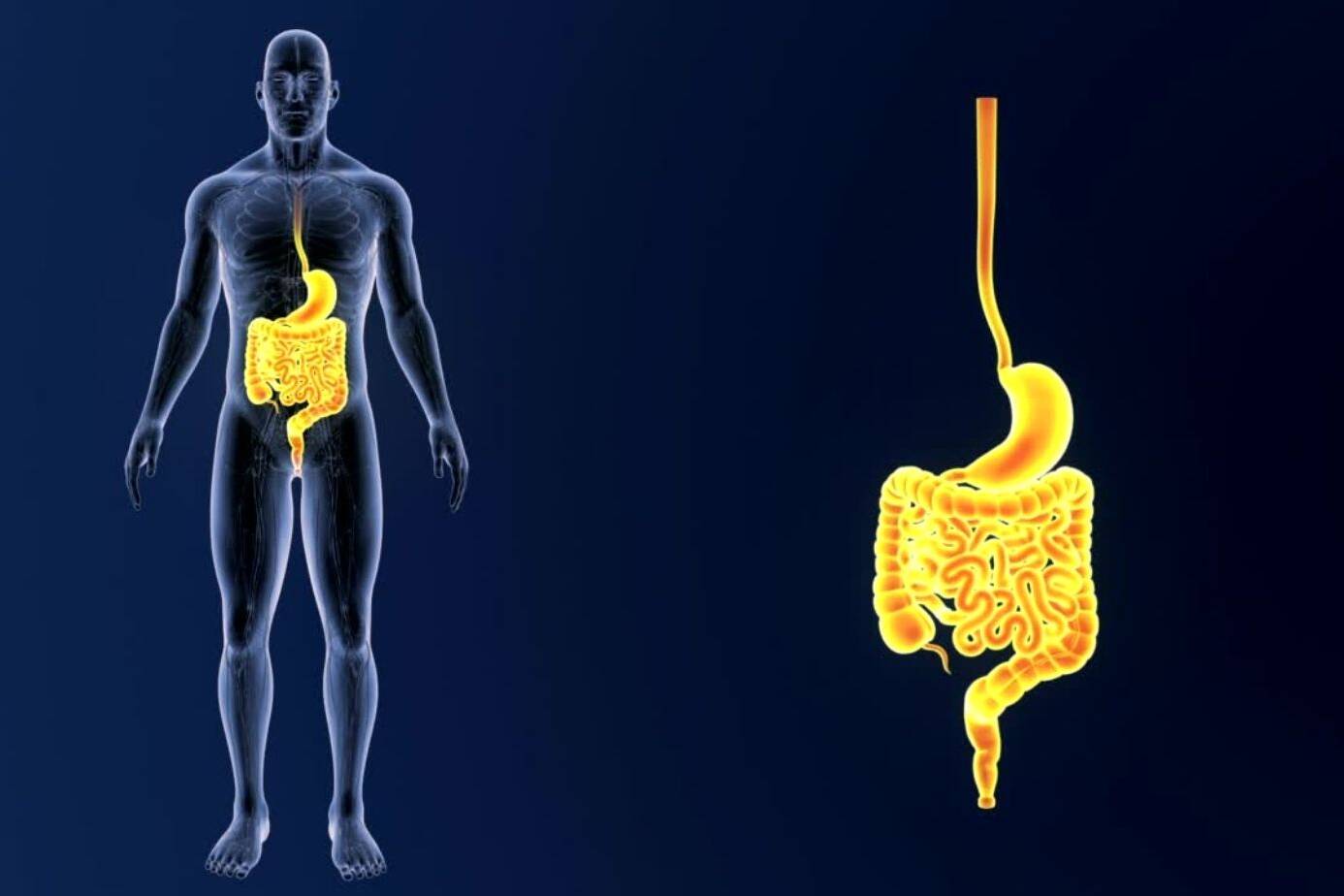
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Barrett’s esophagus, a condition that can have a significant impact on your health. In this article, we will explore the potential risks of developing cancer associated with Barrett’s disease and provide you with essential prevention strategies to safeguard your well-being.
Table of Contents
ToggleBarrett’s esophagus is a condition where the lining of the esophagus becomes damaged due to long-standing gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). While the risk of developing esophageal cancer in individuals with Barrett’s esophagus is relatively small, it is crucial to be proactive and prioritize your health by regularly attending check-ups, undergoing imaging tests, and biopsies to detect any precancerous cells.
To provide you with comprehensive information and practical insights, our article is divided into multiple sections. We will begin by explaining what Barrett’s esophagus is and how it contributes to cancer risks. Then, we will dive into the symptoms, diagnosis, causes, and risk factors associated with Barrett’s disease. We will also discuss the potential complications and the importance of early detection for effective management.
In subsequent sections, we will explore the diagnosis process, available treatment options, and the importance of incorporating prevention strategies into your lifestyle. We will also discuss the potential impact of Barrett’s esophagus on your quality of life and provide insights into current research and advances in the field.
By staying informed and taking appropriate preventive measures, you can reduce the risks associated with Barrett’s esophagus and ensure your long-term health. Now, let’s delve deeper into the details of this condition and equip you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions about your well-being.
What is Barrett’s Esophagus?
Barrett’s esophagus is a condition that occurs when the normal flat lining of the esophagus is replaced with a thick, red lining. This change in the lining is believed to be caused by long-standing gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), which is characterized by frequent heartburn and regurgitation of stomach contents.
The acid and chemicals from the stomach that wash back into the esophagus can cause damage to the esophagus lining, leading to the development of Barrett’s esophagus.
Symptoms of Barrett’s Esophagus
While Barrett’s esophagus may not cause any symptoms on its own, the underlying GERD symptoms are often present. These include:
- Frequent heartburn
- Regurgitation of stomach contents
- Chest pain
- Difficulty swallowing
Diagnosing Barrett’s Esophagus
Barrett’s esophagus is typically diagnosed through an endoscopy procedure, where a flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the esophagus to examine the lining. Biopsies may be taken during the procedure to confirm the presence of abnormal cells.
Regular screenings and check-ups are important for individuals with GERD or other risk factors for Barrett’s esophagus to detect any changes in the esophageal lining.
Treatment Options
The treatment for Barrett’s esophagus depends on the severity of the condition and the presence of dysplasia or precancerous cells. Some treatment options include:
- Lifestyle changes to manage GERD, such as maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding trigger foods, and elevating the head of the bed while sleeping.
- Medications to reduce stomach acid production, such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs).
- Endoscopic treatments to remove abnormal cells or prevent cancerous growth.
- Surgery may be necessary in more advanced cases to remove the affected section of the esophagus.
Risk Factors for Barrett’s Esophagus
| Factors | Description |
|---|---|
| GERD | Long-standing gastroesophageal reflux disease is the primary risk factor for developing Barrett’s esophagus. |
| Age | Risk increases with age, particularly in individuals over 50. |
| Gender | Men are more likely than women to develop Barrett’s esophagus. |
| Ethnicity | Caucasians are at a higher risk compared to other ethnic groups. |
| Obesity | Being overweight or obese is a risk factor for Barrett’s esophagus. |
| Smoking | Smoking can increase the risk of developing Barrett’s esophagus. |
| Family History | A family history of Barrett’s esophagus or esophageal cancer increases the risk. |
Symptoms and Diagnosis
If you’re experiencing symptoms such as frequent heartburn, regurgitation of stomach contents, and difficulty swallowing, it could be a sign of Barrett’s esophagus, often associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). However, it’s important to note that around half of people diagnosed with Barrett’s esophagus may not have any symptoms of acid reflux. Therefore, it’s crucial to consult a doctor if you have any concerns regarding your digestive health and the possibility of Barrett’s esophagus.
Proper diagnosis is essential to determine the presence of Barrett’s esophagus and its severity. Your doctor may recommend the following:
- Imaging tests: These may include an upper endoscopy, where a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera is used to examine the esophagus. This test allows the doctor to visualize any changes in the esophageal lining that may indicate Barrett’s esophagus.
- Biopsies: During an endoscopy, your doctor may take small tissue samples, called biopsies, from the esophagus for further examination. These biopsies can help confirm the presence of Barrett’s esophagus and assess if any precancerous changes have occurred.
It’s important to follow your doctor’s recommendations and undergo the necessary tests to ensure an accurate diagnosis. Early detection and monitoring of Barrett’s esophagus can help in the prevention and management of potential complications.
| Symptoms of Barrett’s Esophagus | Diagnostic Procedures |
|---|---|
|
|
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of Barrett’s esophagus is unknown, but it is commonly associated with long-standing gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). When you have GERD, the acid and chemicals from your stomach can damage the lining of the esophagus, leading to the development of Barrett’s esophagus. What’s interesting is that even individuals with “silent reflux” or minimal GERD symptoms may also develop this condition.
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing Barrett’s esophagus:
- A family history of Barrett’s esophagus or esophageal cancer
- Being male
- Being of white ethnicity
- Being above 50 years of age
- Experiencing chronic heartburn and acid reflux
- Smoking
- Being overweight
While these risk factors can increase your chances of developing Barrett’s esophagus, it’s important to note that they do not guarantee its occurrence. Anyone, regardless of their risk factors, should be aware of the potential risks and take proactive steps to manage reflux symptoms and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Image: This image represents the risk factors associated with Barrett’s esophagus.
Complications and Esophageal Cancer Risk
Barrett’s esophagus poses complications that can increase the risk of developing esophageal cancer. Although the actual risk of progression to cancer is relatively small, it is important to be proactive in monitoring and managing the condition. Precancerous changes in esophageal cells, known as dysplasia, can heighten the risk. Regular checkups, imaging tests, and biopsies are critical for identifying and treating precancerous cells to prevent the development of esophageal cancer.
In individuals with Barrett’s esophagus, the presence of precancerous cells signifies a higher risk of esophageal cancer. By detecting these abnormal cells early, healthcare professionals can implement appropriate interventions to minimize the risk of cancer progression. Regular monitoring through checkups, imaging tests such as endoscopy, and biopsies helps identify precancerous cells and guide timely treatment decisions.
To illustrate the risk levels associated with Barrett’s esophagus and the importance of early detection and treatment, see the table below:
| Condition | Risk |
|---|---|
| Barrett’s Esophagus without dysplasia | Low risk of esophageal cancer |
| Barrett’s Esophagus with low-grade dysplasia | Moderate risk of esophageal cancer |
| Barrett’s Esophagus with high-grade dysplasia | Significantly increased risk of esophageal cancer |
It is crucial for individuals with Barrett’s esophagus to stay vigilant about regular checkups and follow healthcare professionals’ recommendations for imaging tests and biopsies. By actively monitoring the presence of precancerous cells, healthcare providers can devise personalized management strategies to mitigate the risk of esophageal cancer.
Regular monitoring and early intervention are key to addressing the complications of Barrett’s esophagus and minimizing the risk of esophageal cancer. By working closely with healthcare professionals and adhering to recommended check-up schedules, individuals with Barrett’s esophagus can take proactive steps towards managing their condition and ensuring their long-term health and well-being.
Diagnosis and Screening
Diagnosis of Barrett’s esophagus involves a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional. To accurately assess the condition, various imaging tests such as endoscopy may be performed. Endoscopy allows for the visualization of the lining of the esophagus, providing valuable insights into any abnormalities. During this procedure, the healthcare professional can also take biopsies of the esophagus for further examination.
Extensive biopsies play a crucial role in the diagnosis of Barrett’s esophagus. By analyzing the tissue samples obtained through biopsies, healthcare professionals can detect any precancerous changes in the cells of the esophagus. This step is essential for identifying potential risks and determining appropriate treatment strategies.
If you have a history of long-standing gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or other risk factors associated with Barrett’s esophagus, regular screening is highly recommended. These screenings can help detect any changes in the esophagus early on, allowing for timely intervention and improved management of the condition.
Benefits of Diagnosis and Screening
The timely diagnosis and screening of Barrett’s esophagus offer several benefits:
- Early detection of precancerous cells: By detecting precancerous changes in the esophagus cells, healthcare professionals can initiate necessary treatment interventions to prevent the progression to esophageal cancer.
- Improved prognosis: Early detection and management of Barrett’s esophagus can significantly improve the prognosis and overall outcomes for individuals at risk.
- Precision in treatment: Accurate diagnosis allows healthcare professionals to tailor the treatment plan according to individual needs, ensuring targeted and effective therapies.
- Peace of mind: Regular screenings provide peace of mind, knowing that proactive measures are being taken to monitor and manage the condition.
Regular check-ups and screenings are crucial for individuals with Barrett’s esophagus. By prioritizing these proactive measures, you can take control of your health and work towards the prevention or early detection of any potential complications.
Treatment and Management
When it comes to treating Barrett’s esophagus, the approach depends on the presence of precancerous cells or dysplasia. The aim is to prevent the progression to esophageal cancer. Here are some of the treatment options:
Lifestyle Changes and Dietary Modifications
One of the first steps in managing Barrett’s esophagus is making lifestyle changes. Losing weight, avoiding trigger foods that worsen acid reflux, and eating smaller meals can help reduce reflux symptoms and minimize damage to the esophagus lining.
Medication
Medication may be prescribed to reduce acid production and alleviate symptoms. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are commonly prescribed to inhibit acid production in the stomach, reducing the likelihood of acid reflux and providing relief from heartburn and regurgitation.
Surgical Interventions and Endoscopic Procedures
In some cases, more invasive interventions may be necessary to remove or destroy the precancerous cells. Surgical options such as esophagectomy, which involves removing a portion of the esophagus, may be considered. Alternatively, endoscopic procedures like photodynamic therapy or radiofrequency ablation can be performed to target and eliminate the abnormal cells.
It’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the most suitable treatment plan for your specific situation. Regular follow-ups and adherence to the prescribed treatment are essential to effectively manage Barrett’s esophagus and reduce the risk of progression to esophageal cancer.
| Treatment Options | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Lifestyle Changes and Dietary Modifications | – Minimizes acid reflux symptoms – Promotes overall digestive health |
– Requires long-term commitment – Results may vary depending on individual response |
| Medication (Proton Pump Inhibitors) | – Reduces acid production – Provides relief from heartburn |
– Potential side effects with long-term use – May not eliminate the risk of esophageal cancer |
| Surgical Interventions and Endoscopic Procedures | – Targets and removes precancerous cells – Can be curative in some cases |
– Invasive procedures – Potential risks and complications |
Prevention Strategies
Preventing Barrett’s esophagus involves adopting healthy lifestyle habits and reducing acid reflux. By making a few simple changes, you can reduce the risks associated with this condition and improve your overall digestive health. Here are some prevention strategies to consider:
Avoid Triggers
- Avoid foods and beverages that trigger acid reflux, such as spicy foods, citrus fruits, caffeinated drinks, and carbonated beverages.
- Avoid eating large meals or lying down immediately after eating.
- Consider keeping track of your diet and noting any triggers that worsen your acid reflux symptoms.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight can put pressure on your stomach, leading to acid reflux. By maintaining a healthy weight, you can reduce the risk of developing Barrett’s esophagus. Incorporate regular exercise into your routine and follow a balanced diet filled with nutritious foods.
Avoid Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
Smoking weakens the lower esophageal sphincter, which can contribute to acid reflux and increase the risk of developing Barrett’s esophagus. Similarly, excessive alcohol consumption can irritate the esophagus and worsen acid reflux symptoms. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake can significantly improve your digestive health.
Practice Good Eating Habits
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day instead of consuming large meals.
- Take your time while eating, chewing your food thoroughly and avoiding rushing through meals.
- Avoid eating close to bedtime, as lying down soon after a meal can increase the likelihood of acid reflux.
Exercise Regularly and Manage Stress
Engaging in regular exercise not only helps maintain a healthy weight but also improves digestion. Activities like walking, jogging, or yoga can promote digestive health and reduce symptoms of acid reflux. Additionally, managing stress through techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, and relaxation techniques can help alleviate acid reflux symptoms.
By incorporating these prevention strategies into your lifestyle, you can reduce the occurrence of acid reflux and lower the risks associated with Barrett’s esophagus. Remember to consult with your healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance tailored to your specific needs.
Importance of Regular Check-Ups
Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional are crucial for individuals with Barrett’s esophagus. These check-ups play a significant role in early detection and monitoring of any changes in the esophageal lining. During these check-ups, the healthcare professional may recommend various imaging tests, such as endoscopy, to visualize the esophagus and take biopsies if necessary. These imaging tests are a vital tool for detecting precancerous cells or dysplasia, which can help prevent or minimize the risk of developing esophageal cancer.
By undergoing regular check-ups, you can ensure that any potential abnormalities or changes in your esophagus are identified and addressed promptly. This proactive approach to your health allows for early intervention and appropriate treatment, significantly improving your prognosis and overall well-being.
Benefits of Regular Check-Ups for Barrett’s Esophagus
- Early detection of precancerous cells: Regular check-ups enable healthcare professionals to monitor the progression of Barrett’s esophagus and detect any precancerous changes in the esophageal cells. This allows for timely intervention and the implementation of preventive measures to minimize the risk of developing esophageal cancer.
- Monitoring the condition: By scheduling routine follow-up appointments, you can ensure that any changes in your esophageal lining are closely monitored. This helps healthcare professionals assess the effectiveness of your current treatment plan and make necessary adjustments to optimize your care.
- Peace of mind: Regular check-ups provide you with peace of mind, knowing that you are actively managing and taking control of your health. The knowledge that you are receiving regular medical attention can alleviate anxiety and reduce the stress associated with the uncertainties of a complex condition like Barrett’s esophagus.
Remember, early detection plays a pivotal role in the successful management of Barrett’s esophagus. Therefore, make it a priority to schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare professional and follow their recommended imaging tests and biopsies. By doing so, you are taking proactive steps towards your well-being and reducing the risk of complications associated with Barrett’s esophagus.
| Benefits of Regular Check-Ups for Barrett’s Esophagus | Regular Check-Ups | No Regular Check-Ups |
|---|---|---|
| Early detection of precancerous cells | Allows for timely intervention and preventive measures | Potential for delayed detection and increased cancer risk |
| Monitoring the condition | Close monitoring for optimal treatment and care adjustments | Lack of ongoing evaluation and possible treatment delays |
| Peace of mind | Provides reassurance and reduces anxiety | Increased stress and uncertainty about condition progression |
Impact on Quality of Life
Living with Barrett’s esophagus can have a significant impact on your quality of life. The presence of GERD symptoms and the need for ongoing treatment and monitoring can create challenges that affect your daily activities and well-being.
GERD symptoms such as frequent heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing can be bothersome and uncomfortable, making it difficult to enjoy meals or participate in social activities. The chronic nature of these symptoms can also lead to frustration, anxiety, and a decreased sense of well-being.
However, it is important to remember that with proper management and adherence to treatment plans, the impact on your quality of life can be minimized. Working closely with healthcare professionals, following prescribed medications, and making necessary lifestyle changes can significantly improve your symptoms and overall well-being.
Adopting strategies to reduce GERD symptoms and manage stress can also help improve your quality of life. This may include avoiding trigger foods and beverages, eating smaller meals more frequently, maintaining a healthy weight, and practicing stress-reducing techniques like meditation or yoga.
Furthermore, seeking support from healthcare professionals and connecting with support groups or online communities can provide valuable resources for managing Barrett’s esophagus. These platforms can offer guidance, encouragement, and a space to share experiences with others facing similar challenges.
To summarize, while living with Barrett’s esophagus can impact your quality of life, taking proactive steps to manage GERD symptoms, seeking support, and making necessary lifestyle changes can lead to improved well-being. By working with healthcare professionals and adopting strategies that reduce symptoms, you can regain control and maintain a fulfilling and enjoyable life.
Treatment Options
If you are diagnosed with Barrett’s esophagus, your healthcare professional will work closely with you to develop an individualized treatment plan. The goals of treatment are to reduce acid reflux, monitor and manage the health of your esophagus, and minimize the risk of developing esophageal cancer.
Treatment options for Barrett’s esophagus may include:
- Lifestyle Changes: Making lifestyle modifications such as losing weight if overweight, avoiding trigger foods and beverages that worsen acid reflux, and maintaining healthy eating habits can help reduce symptoms and improve your overall health.
- Medication: Your healthcare professional may prescribe medications such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) to reduce acid production, neutralize stomach acid, and promote healing of the esophagus lining.
- Endoscopic Treatments: In some cases, endoscopic procedures may be recommended to remove or destroy abnormal cells in the esophagus. These procedures can include endoscopic resection, ablation, or radiofrequency therapy.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular check-ups, imaging tests, and biopsies are essential to monitor the health of your esophagus and detect any changes or the development of precancerous cells.
Your healthcare professional will determine the most appropriate treatment options for you based on the severity of your condition, the presence of dysplasia (precancerous changes), and other factors specific to your individual situation.
Remember, it is important to consult with your healthcare professional before making any changes to your treatment plan or lifestyle. They will provide personalized guidance and support to help manage your condition effectively.
Current Research and Advances
Ongoing research in the field of Barrett’s esophagus aims to enhance our understanding of the condition and improve treatment outcomes. Scientists and medical professionals are making significant progress in developing early detection methods and advancing treatment options. Stay informed about the latest research and advancements to make informed decisions about your healthcare.
Advances in Early Detection Methods
Researchers are exploring innovative approaches to detect Barrett’s esophagus at its earliest stages. One promising area of research involves molecular biomarkers, which are specific genetic or protein signals associated with the condition. By identifying these biomarkers, doctors may be able to diagnose Barrett’s esophagus more accurately and efficiently.
Advanced Imaging Techniques
Advancements in imaging technologies, such as high-definition endoscopy and confocal laser endomicroscopy, are revolutionizing the diagnosis and surveillance of Barrett’s esophagus. These techniques enable doctors to visualize the esophagus with exceptional clarity, identifying any abnormal tissue changes that may indicate the presence of the condition.
New Treatment Options
Medical researchers are constantly exploring new treatment strategies for Barrett’s esophagus. One emerging approach is the use of advanced endoscopic techniques to remove or destroy the precancerous cells in the esophagus. These minimally invasive procedures offer alternatives to traditional surgery, minimizing complications and promoting faster recovery.
| Treatment Advances | Description |
|---|---|
| Cryotherapy | A technique that uses extreme cold to freeze and destroy abnormal cells in the esophagus. |
| Radiofrequency Ablation | The application of controlled heat energy to remove precancerous cells, allowing healthy tissue to regrow. |
| Photodynamic Therapy | A treatment that combines light-sensitive drugs with laser light to selectively destroy abnormal cells. |
These innovative treatment options offer patients less invasive alternatives, reducing the need for major surgery and improving patient outcomes.
Staying up-to-date with the latest research and advances in the field of Barrett’s esophagus can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their healthcare. Consult with your healthcare provider to understand how these research developments may impact your diagnosis, treatment, and overall management of the condition.
Conclusion
Barrett’s Esophagus is a condition where the lining of the esophagus is replaced with a thick, red lining, and it carries a small but increased risk of developing esophageal cancer. To effectively manage this condition, regular check-ups, imaging tests, and biopsies are essential for the early detection of precancerous cells. By staying informed and working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals with Barrett’s Esophagus can take a proactive approach to their health and well-being.
Prevention strategies play a vital role in reducing the risks associated with Barrett’s Esophagus. Lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding smoking and alcohol consumption, and practicing good eating habits, can help minimize the occurrence of acid reflux and promote overall digestive health. Additionally, adhering to proper medical treatment, including prescribed medications and relevant surgical interventions, can further reduce cancer risks.
In conclusion, individuals with Barrett’s Esophagus must prioritize their health by undergoing regular check-ups and adhering to prevention strategies. By being proactive and taking steps to minimize cancer risks, individuals can effectively manage Barrett’s Esophagus and maintain a high quality of life. Remember, your healthcare provider is your best ally in this journey, so don’t hesitate to seek their guidance and support.
FAQ
What is Barrett’s esophagus?
Barrett’s esophagus is a condition where the normal flat lining of the esophagus is replaced with a thick, red lining. It is believed to be caused by long-standing gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
What are the symptoms of Barrett’s esophagus?
Symptoms of Barrett’s esophagus can include frequent heartburn, regurgitation of stomach contents, and difficulty swallowing. However, approximately half of those diagnosed may not experience any symptoms of acid reflux.
What causes Barrett’s esophagus?
Barrett’s esophagus is commonly associated with long-standing GERD, where stomach acid and chemicals damage the esophagus lining. However, even individuals with minimal GERD symptoms may develop it. Risk factors include a family history, being male, being white, age above 50, chronic heartburn, acid reflux, smoking, and being overweight.
Does Barrett’s esophagus increase the risk of esophageal cancer?
Yes, Barrett’s esophagus is associated with an increased risk of developing esophageal cancer. However, the actual risk is relatively small. Regular check-ups, imaging tests, and biopsies are important for detecting and treating precancerous cells.
How is Barrett’s esophagus diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Barrett’s esophagus typically involves a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional. Imaging tests such as endoscopy may be used to visualize the esophagus and take biopsies for examination.
What are the treatment options for Barrett’s esophagus?
Treatment may involve lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and dietary modifications, as well as medications to reduce acid production. In some cases, surgical interventions or endoscopic procedures may be necessary to remove or destroy precancerous cells.
How can Barrett’s esophagus be prevented?
Prevention strategies for Barrett’s esophagus include reducing acid reflux by avoiding triggers, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding smoking and alcohol consumption, and practicing good eating habits.
Why are regular check-ups important for individuals with Barrett’s esophagus?
Regular check-ups, including imaging tests and biopsies, are crucial for detecting any changes in the esophageal lining, such as precancerous cells. Early detection can minimize the risk of developing esophageal cancer.
How does Barrett’s esophagus affect quality of life?
Barrett’s esophagus can impact an individual’s quality of life due to the presence of GERD symptoms and the need for ongoing treatment and monitoring. However, with proper management and treatment, the impact can be minimized.
What are the current research and advances in Barrett’s esophagus?
Ongoing research is being conducted to improve understanding and treatment options for Barrett’s esophagus. This includes advances in early detection methods and new treatment options to reduce the risk of esophageal cancer.
What is the conclusion regarding Barrett’s esophagus and cancer risks?
Regular check-ups, proper treatment, and lifestyle changes can help manage the risks associated with Barrett’s esophagus. It is important for individuals to stay informed and work closely with healthcare professionals to adopt a proactive approach to their health and well-being.
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Nivedita Pandey, MD, DM (Gastroenterology)
Dr. Nivedita Pandey is a U.S.-trained gastroenterologist and hepatologist with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating liver diseases and gastrointestinal disorders. She specializes in liver enzyme abnormalities, fatty liver disease, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and digestive health.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current clinical guidelines.