Childhood obesity, also known as pediatric obesity, is one of the most serious public health challenges of the 21st century. It’s more than just a few extra pounds; it’s a complex condition that puts your child at risk of serious medical issues now and in the future.
Table of Contents
ToggleMany parents dismiss it as “baby fat” that will go away on its own. But the reality is: obesity in children is rising fast, and it’s not always harmless.
As a board-certified gastroenterologist, I’ve seen how pediatric obesity affects a child’s health, from digestion and liver health to emotional well-being. In this blog, we will explore what childhood obesity means, what causes it, and how parents can help manage and prevent it with science-backed strategies.
What is Childhood Obesity?
Childhood obesity is a medical condition where a child is significantly over the normal weight for their age and height. It is commonly diagnosed using the Body Mass Index (BMI) percentile:
| BMI Percentile | Classification |
|---|---|
| 85th – 94th | Overweight |
| ≥95th | Obese |
Children with BMI ≥120% of the 95th percentile are considered severely obese. Pediatric obesity often results in lifelong health complications if not addressed early.
What are the Causes of Childhood Obesity?
Childhood obesity doesn’t come from a single source. It’s a result of many overlapping factors:
A. Poor Diet Choices
- High-calorie, low-nutrient foods
- Sugary drinks (colas, juices, sports drinks)
- Large portion sizes
B. Sedentary Lifestyle
- Screen time (TV, phones, video games)
- Lack of outdoor play or physical education
C. Genetic Factors
- Children with obese parents are more likely to be obese
- Specific genes affect metabolism and appetite
D. Emotional and Psychological Factors
- Depression or low self-esteem can trigger emotional eating
- Stress at school or home
E. Hormonal & Medical Issues
- Hypothyroidism
- Cushing’s Syndrome
- Leptin deficiency
| Contributing Factor | Example/Detail |
| Diet | Junk food, sugary drinks |
| Activity | Less than 60 mins/day of physical activity |
| Family | Obese parents, single-parent households |
| Sleep | <8 hours sleep increases risk |
| Environment | Unsafe play areas, fast food availability |
What are the Early Signs of Childhood Obesity Parents Should Watch For?
Recognizing the early childhood obesity symptoms can make a big difference.
- Sudden and continuous weight gain that doesn’t match height growth.
- Increased waist size or belly fat.
- Low energy or less physical activity than usual.
- Clothes are getting too tight too fast.
- Shortness of breath during light activity.
Watching these signs early allows parents to act before complications arise.
Health Complications of Pediatric Obesity
Obesity in childhood impacts almost every organ system:
| System | Common Complications |
| Heart | High blood pressure, high cholesterol |
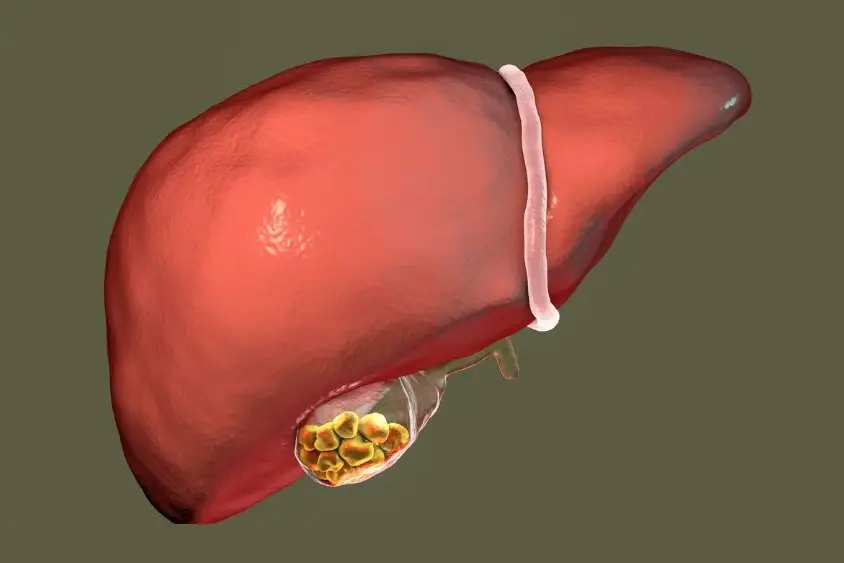
| Liver | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) |
| Endocrine | Type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance |
| Bones | Early arthritis, Blount’s disease |
| Lungs | Asthma, sleep apnea |
| Mental Health | Depression, bullying, low self-esteem |
Early treatment is critical to prevent lifelong health issues.
Read: 8 Powerful Diet and Exercise Tips for Obesity Treatment | Dr. Nivedita Pandey
Childhood Obesity Complications
- Obesity in children often causes complications in their social, emotional, and physical well-being. The complications of childhood obesity include:
- High Blood Pressure and High Cholesterol: An unhealthy diet can lead to the development of either one or both conditions. The arteries thicken and narrow, making it difficult for the heart to pump blood to all parts of the body. This can cause a heart stroke or an attack later in life.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Obesity impacts the way the body processes sugar or glucose. A sedentary lifestyle coupled with obesity can heighten the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Being diabetic also increases the risk of developing other complications like kidney failure and heart disease.
- Joint Pains: Additional weight causes extra pressure on the hip, leg, and foot joints. Obesity can also increase the risk of injuries from falls.
- Breathing Problems: Overweight children are more prone to developing breathing problems. Common diseases likely to create are asthma and obstructive sleep apnea.
- Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: In this condition, fatty deposits build up in the liver, causing scarring and liver damage. The disease with no typical symptoms cannot be diagnosed in the early stages, leading to severe complications.
- Social and Emotional Issues: Obese children may face more bullying or teasing from their peers. They are more likely to suffer isolation, lower self-esteem, and depression. It can lead to anxiety, increased stress, risk of depression, and a tendency to binge eat or eat more comfort foods, leading to a vicious cycle.
How Can Childhood Obesity Be Prevented and Managed at Home?
Home is the best place to begin childhood obesity treatment. Small steps go a long way.
What Are Effective Diet Strategies for Managing Childhood Obesity?
Healthy eating should be easy and consistent.
- Focus on whole foods, fruits, vegetables, and proteins.
- Use the plate method: Half vegetables, quarter protein, quarter grains.
- Avoid sugary drinks like soda or juices.
- Stick to regular mealtimes.
| Food Type | Examples | Notes |
| Fiber-rich Foods | Apples, oats, dal, brown rice | Help in satiety |
| Lean Proteins | Eggs, fish, paneer | Build muscle, burn fat |
| Good Fats | Nuts, olive oil | Important for brain health |
How Can Parents Encourage Physical Activity in Children?
Kids need fun, not forced workouts.
- Encourage 60 mins of active play every day.
- Choose fun over rules: Dance, cricket, cycling.
- Use apps or step counters to keep track.
- Walk instead of taking transport where possible.
Can Healthy Family Habits Reverse Childhood Obesity?
Yes, what the family does together, works better.
- Eat meals as a family.
- Keep gadgets away during eating.
- Parents should model active behavior.
- Set bedtime and mealtime routines.
The whole family wins when lifestyle changes are shared.
| Home Strategy | Action Plan |
| Diet | Pack school lunches with fruits & protein |
| Exercise | Morning walk before school |
| Screen Time | Use apps to limit digital hours |
| Sleep | Set regular bedtime routine |
What are the Non-Surgical Medical Treatments for Childhood Obesity?
For children with moderate to severe obesity, doctors may recommend non-surgical interventions:
A. Multidisciplinary Support
- Involves pediatrician, dietitian, psychologist, and exercise therapist
- Personalized health plans
B. Prescription Medications (only under medical supervision)
| Medication | Use | Side Effects |
| Orlistat | Blocks fat absorption | GI upset, vitamin deficiency |
| Metformin | For insulin resistance | Nausea, stomach pain |
| Liraglutide | Appetite suppression | Injection site reactions |
Note: Medications are used when lifestyle changes alone aren’t enough.
Surgical Treatments (For Severe Pediatric Obesity)
Surgery is considered only when other treatments fail and severe obesity causes life-threatening issues.
A. Eligibility Criteria
- BMI ≥40 with complications (like diabetes)
- Failed non-surgical treatment
B. Types of Bariatric Surgery
| Surgery Type | Description | Risks |
| Gastric Bypass | Reduces stomach size and reroutes digestion | Nutritional deficiency, infection |
| Sleeve Gastrectomy | Removes part of the stomach | Bleeding, reflux |
| Adjustable Gastric Banding | Adjustable band around stomach | Slippage, nausea |
C. Post-Surgery Care
- Lifelong vitamin supplementation
- Regular follow-ups with pediatric bariatric team
Consult a gastrologist and gastroenterologist for better and more informed decision-making in obesity management.
Prevention Tips for Parents
- Breastfeed infants for at least 6 months
- Avoid using food as a reward
- Ensure physical activity from early childhood
- Educate about media literacy (advertising tricks)
- Keep healthy snacks accessible
When to Seek Professional Help
If your child:
- Is gaining weight rapidly
- Has signs of diabetes (excessive thirst, frequent urination)
- Snores or has trouble sleeping
- Struggles with self-esteem or bullying
You should seek expert help. A specialist like Dr. Nivedita Pandey can provide a full evaluation and obesity treatment roadmap.
Connect for an online doctor chat to learn a detailed strategy for child obesity management.
Book a Consultation with Dr. Nivedita Pandey
Childhood obesity is serious but preventable and manageable. You don’t need to handle it alone.
Dr. Nivedita Pandey, MBBS, Diplomate American Board (Internal Medicine & Gastroenterology), is a U.S.-trained, board-certified senior gastroenterologist and hepatologist. She specializes in childhood obesity treatment, liver disorders, gut health, and obesity-related complications.
As one of South Delhi’s few female gastroenterologists, she offers a safe and understanding space for parents and children. Whether it’s creating a meal plan, managing liver complications, or building a routine that fits your child, she is here to guide you.
Book your consultation today and take the first step towards your child’s healthier future.
Also Read
Read How To Heal Leaky Gut Naturally
Abdominal Pain: Types, Causes And Treatment
Tips On Reducing Stomach Gas And Bloating
FAQs
Can a child outgrow obesity naturally?
Yes, but only in some cases. Children may slim down during puberty, especially if their growth in height outpaces weight gain. However, most kids with persistent obesity do not outgrow it without lifestyle changes. Early attention to diet and physical activity gives the best chance of long-term health.
What’s the right age to start weight management?
Weight management should begin as soon as there are signs of unhealthy pediatric weight gain. This could be at any age. It’s not about restricting food, but about forming healthy habits early, even in preschool years.
Are “baby fats” always harmless?
Not always. While infants naturally have more fat, by age 5 it should start balancing out. If the extra weight continues or worsens, it can turn into childhood obesity, especially if eating and activity patterns don’t change.
How does sleep affect childhood obesity?
Poor sleep affects hormones like ghrelin and leptin, which control hunger and fullness. When kids don’t sleep enough, they snack more and move less. Consistent, good-quality sleep (9–12 hours) helps manage hunger and supports weight control.
Is it safe for children to follow a diet plan?
Yes, but only if it’s balanced and supervised. Children need calories to grow, so the goal should never be starvation. Safe childhood obesity management includes portion control, healthy meals, and physical activity, not crash diets or supplements. Avoid extreme diets and consult specialists like Dr. Nivedita Pandey for safe childhood obesity management.
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Nivedita Pandey, MD, DM (Gastroenterology)
Dr. Nivedita Pandey is a U.S.-trained gastroenterologist and hepatologist with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating liver diseases and gastrointestinal disorders. She specializes in liver enzyme abnormalities, fatty liver disease, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and digestive health.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current clinical guidelines.