Understanding Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis is the disease or irritation of pockets that can shape up in your digestive tracts. These pockets are known as diverticula. The pockets by and large are not unsafe. They can appear at any place in your digestive tracts. Their presence is marked with the medical condition named diverticulosis.
Table of Contents
Toggle
Factors Contributing to Diverticular Disease:
- Lack of dietary fibre
- Genetics
- Decreased immune function
- Obesity
- Lack of physical activity
- Changes in the gut microbiome
- Smoking
- Certain medications (e.g., steroids)
Symptoms of Diverticular Disease:
- Asymptomatic Diverticulosis: Most individuals do not encounter any signs and symptoms.
- Pain: Episodes of torment in the lower abdomen, typically in the lower left half of the midsection, which often come when eating or passing stools.
- Acute Diverticulitis Symptoms:
- Constipation
- Blood in stools
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever
- Abdominal tenderness
Managing Diverticulitis:
- Prevention:
- Taking care of oneself
- Preventing colonic diverticulosis and diverticulitis
- Treatment:
- If symptoms are not severe, medical procedures may not be needed.
- For severe conditions, a gastroenterologist may advise a course of antibiotics or hospital treatment.
- A diverticulitis diet involving a liquid diet can help relieve stress on the digestive tract.
- In severe cases, a colon resection may be necessary. This procedure involves the removal of the affected part of the colon and joining the remaining healthy parts together.
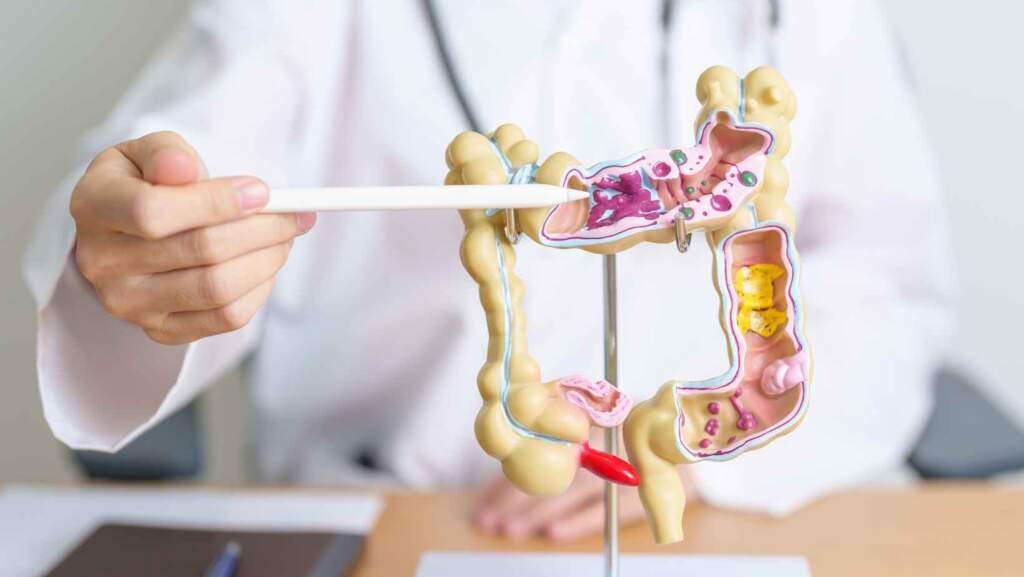
Understanding Diverticular Disease and what to eat with diverticulitis
Now, you must have a fair idea of what diverticular disease of the colon is, how it is caused, its symptoms, and its treatment, what to eat with diverticulitis But what about the foods to avoid with diverticulitis? Don’t worry! We have got everything listed for you.
Liquid Diet for Diverticulitis
At times, a specialist will suggest that someone with diverticulitis take only clear fluids for a few days. These include:
- Water
- Gelatin
- Fruit juices
- Tea and coffee without cream
- Broth
- Ice chips
- Ice pops
A liquid diet is always a primary step in treating diverticulitis.
Low-Fiber Meals for Diverticulitis
Considering meals, someone with diverticulitis should take low-fiber meals to avoid stressing the digestive tract too much. Such food items include:
- Canned Fruits and Seedless Vegetables: Nutritious and easy to digest.
- Eggs, Poultry, and Fish: Highly nutritious and easy to digest.
- Yogurt: Rich in probiotics that help maintain good gut health.
- Refined White Bread: Low in fiber and easy to pass through the digestive tract.
- Pasta, White Rice, and Noodles: Low-carb options ideal for treating diverticulitis.
- Lentils: Prevent spikes in blood sugar and improve bowel function.
- Almonds and Dried Dates: Rich in polyphenols, recommended for an upset stomach.
Diverticulitis Foods to Avoid
Since diverticulitis involves inflammation, it is vital for the individual with an active case to avoid the very food varieties you need to eat to prevent the condition. The list of diverticulitis foods to avoid includes:
- Red and Processed Meats: High levels of nitrosamines can worsen your condition.
- Beans and Legumes (e.g., Chickpeas and Kidney Beans): Contain indigestible carbohydrates that ferment in the gastrointestinal tract, worsening diverticulitis.
- Full-Fat Dairy: Can be difficult to digest and may damage the stomach.
- Fermented Foods: High probiotic content can cause bloating and gas.
- Fried Food: Hard to digest, stressing the digestive tract.
- Hard-to-Chew Foods: Likely to get caught in the pockets of your colon.
- Popcorn: Often consumed quickly, leading to improper chewing and potential issues.
Managing Diverticulitis:
- Low-Fiber Diet: Follow a low-fiber diet until diverticulitis signs decline. Fiber plays a significant role in the digestive process by softening stool and helping it move more easily through the colon. A lack of fiber can cause constipation, making stools harder to pass and putting strain on the colon muscles. This may increase the likelihood of developing diverticula.
By following these dietary guidelines, individuals with diverticulitis can manage their symptoms more effectively and reduce the risk of complications.
About Dr Nivedita Pandey:
- Specialization: Gastroenterologist and Hepatologist based in New Delhi.
- Role: Works as a Transplant Hepatologist and Gastroenterologist, with advanced studies completed in the USA.
- Approach: Known for her benevolent and sympathetic approach towards her patients.
- Expertise:
- Treating patients suffering from obesity, food allergies, and diverticular diseases.
- Nutrition counselling and liver transplant services.
- Dr Good Deed Initiative:
- Established by Dr Nivedita Pandey and her partner.
- Aims to deliver medical care to the most remote parts of the country using technology and communication.
- Conducts virtual consultation sessions for patients unable to visit her clinic, providing instant solutions to many from the comfort of their homes.


