An endoscopy can identify acid-related injury, such as GERD, open sores seen in peptic ulcer disease, long-term immune inflammation like inflammatory bowel disease, active internal bleeding, structural problems such as strictures and hernias, infections like H. pylori, precancerous polyps, and early-stage cancers of the esophagus, stomach, and colon. It also detects bile duct blockages, abnormal tissue changes, and hidden sources of anemia or weight loss.
Table of Contents
ToggleBy showing real-time tissue damage and allowing biopsy at the same moment, endoscopy provides clarity that scans and blood tests often cannot.
Scope Test Diseases
A scope test uses a thin flexible tube with a camera and light. The tube enters through your mouth or rectum. The camera sends live images to a screen. Doctors look at color, shape, texture, and movement of tissue. This direct view explains why diseases that can be detected by an endoscopy include both mild and life-threatening conditions.
Digestive Tract Diseases Detected by the Scope Test
The digestive tract includes the food pipe, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. A scope test detects inflammation (swelling), erosion (surface damage), ulcers (open sores), strictures (narrowed areas), and abnormal growths. Many diseases that can be detected by an endoscopy do not show on blood tests or scans. Small surface damage often appears only through a camera.
Doctors also take biopsies during the test. A biopsy means removing a tiny tissue piece for lab testing. This step confirms infection, immune disease, or cancer.
Upper GI Conditions
Upper GI endoscopy checks the esophagus (food pipe), stomach, and duodenum (first part of the small intestine). Doctors identify acid damage, ulcers, tumors, and bleeding sources. Problems here often cause heartburn, chest pain, nausea, or black stools.
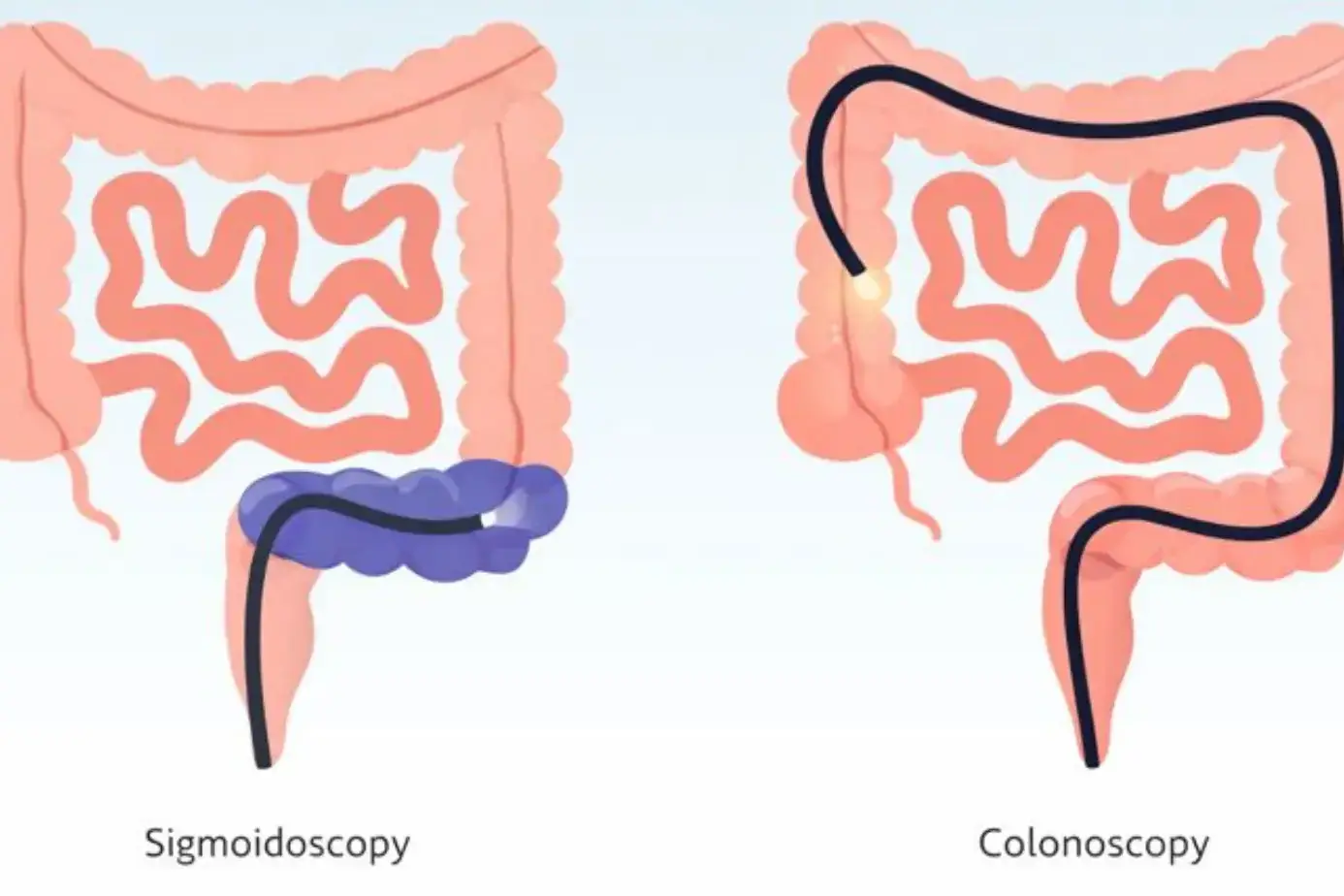
Lower GI Conditions
Lower GI endoscopy, called colonoscopy, examines the colon and rectum. Doctors look for polyps, long-term inflammation, bleeding, and cancer. Colonoscopy also prevents disease. Removing polyps stops cancer before it forms.
When A Scope Test Is Recommended
Doctors suggest a scope test when symptoms last longer than expected. Ongoing pain, trouble swallowing, unexplained anemia (low blood count), or blood in stool matter. Age also plays a role. Risk rises after age forty-five. Family history increases risk further. These factors guide testing for diseases that can be detected by an endoscopy .
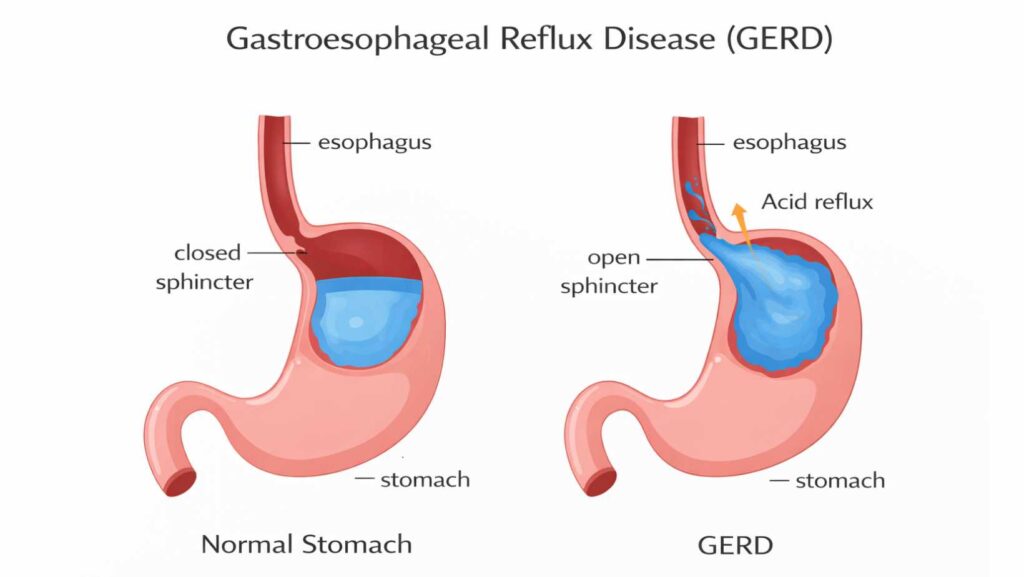
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Endoscopy distinguishes simple acid reflux from structural damage caused by gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) . It reveals chronic acid exposure effects like inflammation, ulcers, and cell changes that increase cancer risk. This guides long-term treatment decisions.
How GERD Appears On Endoscopy
The camera shows redness, swelling, or breaks in the lining of the food pipe. Severe cases show deep cuts. These findings prove gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) instead of simple heartburn.
Esophagitis And Acid Damage
Esophagitis means inflammation of the esophagus. Acid exposure weakens the protective lining. Over time, scarring may narrow the tube. This makes swallowing hard. These changes place reflux among important diseases that can be detected by an endoscopy .
Barrett’s Esophagus Detection
Long-term acid exposure can change normal cells into abnormal cells. This condition raises cancer risk. Endoscopy spots these changes early. Biopsies confirm them. Early detection allows close follow-up.
GERD Complications Seen On Endoscopy
Doctors may see ulcers, strictures, or bleeding. These complications explain pain, choking, or anemia. Endoscopy separates simple reflux from advanced gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) that needs stronger care.
Peptic Ulcer Disease Endoscopy
Endoscopy identifies ulcer size, depth, and bleeding risk in peptic ulcer disease . It also allows bacterial testing through biopsy, which determines whether infection or medication damage caused the ulcer. This prevents repeat ulcer formation.
Stomach Ulcers
Stomach ulcers appear as round or oval sores. The edges look inflamed. Some ulcers bleed slowly. Others bleed suddenly. Endoscopy shows depth and size, which predicts risk.
Duodenal Ulcers
Duodenal ulcers sit just beyond the stomach. Pain often improves with food but returns later. Endoscopy confirms location and severity. This helps doctors choose treatment length for peptic ulcer disease .
Bleeding Ulcers
Bleeding ulcers appear with active blood flow or dark clots. This finding explains vomiting blood or black stools. Endoscopy can treat bleeding during the same session.
H. pylori–Related Ulcer Findings
Many ulcers link to H. pylori bacteria. Doctors take biopsies during endoscopy to detect it. Treating the infection reduces ulcer return. This approach lowers repeat peptic ulcer disease episodes.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Endoscopy confirms inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) by showing inflammation patterns that differ between Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. It also measures healing at the tissue level, which symptoms alone cannot show. This affects medication choice.
Crohn’s Disease Findings
Crohn’s disease affects any gut section. Endoscopy shows patchy inflammation, deep ulcers, and narrowed areas. Healthy tissue sits beside damaged areas. These patterns define Crohn’s within inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) .
Ulcerative Colitis Findings
Ulcerative colitis affects only the colon. Inflammation starts at the rectum and spreads upward in a continuous line. The lining bleeds easily. Endoscopy shows severity and spread, which guides treatment.
Intestinal Inflammation And Ulcers
IBD causes chronic inflammation that damages tissue over time. Endoscopy reveals whether ulcers are shallow or deep. This detail predicts flare risk. It also places IBD among serious diseases that can be detected by an endoscopy .
Monitoring IBD Progression
Doctors repeat endoscopy to track healing. Symptom relief alone does not prove recovery. Visual healing lowers long-term complications. This makes follow-up vital for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) control.
Gallbladder And Biliary Diseases
Endoscopy does not directly view the gallbladder, but advanced scope-based procedures allow doctors to assess bile flow and bile ducts. Many bile-related problems cause pain, fever, jaundice (yellow skin), or abnormal liver tests. These conditions often overlap with diseases that can be detected by an endoscopy when symptoms point toward blocked bile movement.
Bile Duct Obstruction
Bile duct obstruction blocks bile from reaching the intestine. Endoscopy shows narrowing, compression, or blockage inside the duct. Causes include stones, swelling, or tumors. Without relief, bile buildup damages the liver and causes infection.
Gallstones Affecting Bile Ducts
Gallstones sometimes move from the gallbladder into bile ducts. Endoscopy detects their size and location. Doctors can remove stones during the same procedure. This prevents pancreatitis (pancreas inflammation) and serious infection.
Cholangitis
Cholangitis is an infection of the bile ducts. Endoscopy reveals pus, swelling, and blocked bile flow. This condition progresses fast and can become life-threatening. Early detection places it among urgent diseases that can be detected by an endoscopy .
Role Of ERCP In Biliary Disease Detection
ERCP combines endoscopy and imaging to examine bile ducts. Doctors use it to diagnose and treat blockages. It expands the reach of diseases that can be detected by an endoscopy beyond the stomach and intestines.
Other Conditions Detected By Endoscopy
Endoscopy finds structural and immune-related problems that mimic common digestive issues. Many of these conditions cause vague symptoms but carry serious risks if untreated. Visual confirmation prevents misdiagnosis.
Esophageal Strictures
Strictures are narrowed sections of the food pipe. They form from scarring due to acid or injury. Endoscopy shows the tight area and allows stretching to improve swallowing.
Hiatal Hernia
A hiatal hernia occurs when part of the stomach moves above the diaphragm. Endoscopy shows this shift and explains reflux symptoms. Large hernias raise complication risk.
Celiac Disease
Celiac disease damages the small intestine when gluten is consumed. Endoscopy shows flattened lining and reduced folds. Biopsies confirm diagnosis. Early detection prevents nutrient loss.
Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Bleeding may come from ulcers, tumors, or fragile blood vessels. Endoscopy finds the exact source. Doctors can stop bleeding during the test, which saves time and blood loss.
Polyps And Precancerous Lesions
Polyps are abnormal tissue growths. Some turn into cancer over time. Endoscopy allows removal before danger develops. This prevention step defines the value of diseases that can be detected by an endoscopy .
Cancers Detected By Endoscopy
Endoscopy detects early cancer changes before tumors spread or cause severe symptoms. Biopsies taken during the procedure confirm cell type and stage. Early detection sharply improves survival rates.
Esophageal Cancer
Endoscopy reveals hard masses, irregular surfaces, or bleeding areas. Biopsies confirm cancer type. Early-stage detection improves survival rates.
Stomach Cancer
Stomach cancer may appear as thickened folds or shallow ulcers. These signs look harmless early. Endoscopy separates benign ulcers from cancer.
Colorectal Cancer
Colonoscopy finds tumors and large polyps. Removing growths early prevents cancer spread. Screening reduces death risk significantly.
Early Cancer Detection Through Biopsy
Biopsy samples provide cellular proof. This step confirms cancer stage and guides treatment. It places cancer among the most serious diseases that can be detected by an endoscopy .
When Should You Get An Endoscopy?
Persistent or unexplained digestive signs often signal deeper tissue damage. Early endoscopy prevents delayed diagnosis of diseases that can be detected by an endoscopy .
Persistent Digestive Symptoms
Long-term pain, bloating, or nausea signals deeper issues. Endoscopy identifies causes missed by medication trials.
Unexplained Weight Loss
Weight loss without diet change often reflects absorption problems or cancer. Endoscopy clarifies the cause.
Chronic Acid Reflux
Ongoing reflux damages tissue. Endoscopy checks for complications related to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) .
Blood In Stool Or Vomiting Blood
These signs demand urgent care. Endoscopy finds bleeding sources and treats them immediately.
Benefits Of Early Disease Detection
Early findings reduce complications like bleeding, strictures, and cancer spread. Treatment works better when tissue damage stays limited. This lowers long-term health risks and repeat procedures.
Preventing Disease Complications
Treating early prevents scarring, bleeding, and spread. This limits lifelong damage.
Early Treatment Planning
Doctors tailor care based on real findings. This improves response rates.
Reduced Cancer Risk
Removing precancerous tissue lowers future cancer development. This highlights why diseases that can be detected by an endoscopy matter.
FAQs
What Diseases Can Be Detected By An Endoscopy?
Endoscopy detects ulcers, reflux damage, infections, tumors, bleeding sources, polyps, and cancer. It also confirms immune-related conditions and structural problems missed by scans or blood tests.
Can Endoscopy Detect GERD Accurately?
Endoscopy shows acid damage, inflammation, and complications linked to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) . It confirms severity and separates simple reflux from advanced disease.
Is Endoscopy Useful For Diagnosing IBD?
Yes. Endoscopy directly visualizes inflammation patterns and ulcer depth. This allows accurate diagnosis and monitoring of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) .
Can Gallbladder Problems Be Seen On Endoscopy?
Standard endoscopy cannot see the gallbladder. Advanced procedures assess bile ducts and detect blockages related to gallstones or infection.
Does Endoscopy Detect Stomach Cancer?
Yes. Endoscopy identifies early and advanced stomach cancer through visual changes and biopsy confirmation, improving treatment success.
Is A Scope Test Painful?
Most patients receive sedation. You may feel mild discomfort, but pain is uncommon. Recovery usually occurs within hours.
How Long Does An Endoscopy Take?
Most procedures last fifteen to thirty minutes. Complex cases may take longer if treatment occurs during the test.
Are Biopsies Done During Endoscopy?
Yes. Doctors routinely take biopsies to confirm infection, inflammation, or cancer. This does not add pain.
Can Endoscopy Detect Early-Stage Disease?
Yes. Many early changes show before symptoms worsen. This prevents advanced complications.
When Should I Consult A Doctor For Endoscopy?
Seek medical advice if symptoms persist, worsen, or include bleeding, weight loss, or swallowing trouble. Early testing reduces risk.
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Nivedita Pandey, MD, DM (Gastroenterology)
Dr. Nivedita Pandey is a U.S.-trained gastroenterologist and hepatologist with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating liver diseases and gastrointestinal disorders. She specializes in liver enzyme abnormalities, fatty liver disease, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and digestive health.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current clinical guidelines.