Liver disease skin rash often appears when the liver cannot filter toxins, balance hormones, or move bile properly. These skin changes are not random. They reflect internal liver stress. You may notice itching, redness, color changes, or strange marks before other symptoms start. In many people, liver disease skin rash acts as an early warning sign that liver function is already impaired. Ignoring it can delay diagnosis and allow silent damage to worsen.
Table of Contents
ToggleYour skin reacts because the liver controls bile flow, blood clotting, hormone breakdown, and nutrient balance. When these processes fail, skin cells suffer first. That is why liver disease skin rash deserves medical attention, not cosmetic cover-ups.
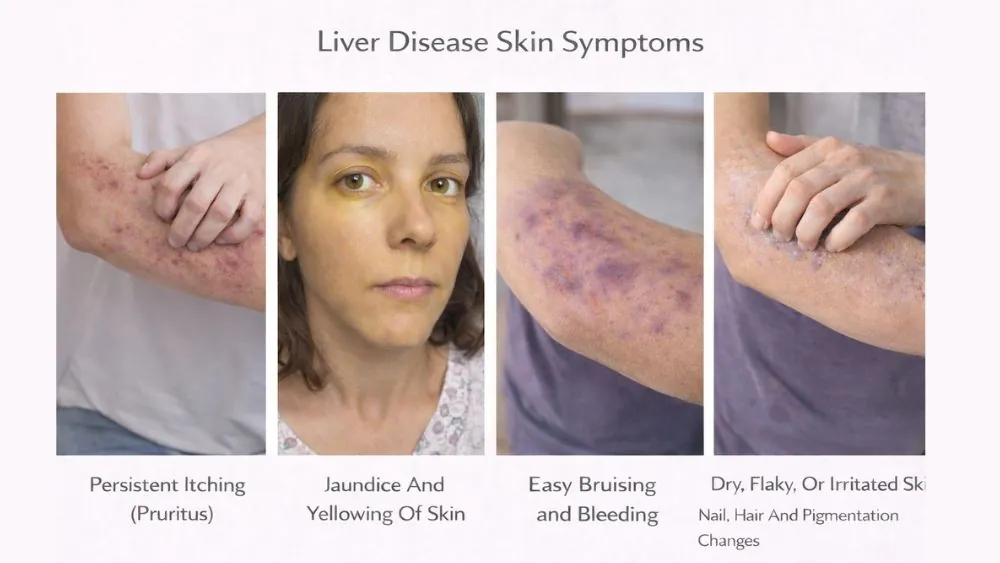
Liver Disease Skin Symptoms
Skin symptoms linked to liver dysfunction occur due to toxin buildup, bile flow disruption, hormone imbalance, and nutrient absorption failure. These changes often develop gradually and may appear before abdominal pain or lab abnormalities, making skin a valuable early indicator of liver stress.
Persistent Itching (Pruritus)
Persistent itching feels deep under the skin. Scratching gives no relief. This itching happens because bile acids stay in the bloodstream instead of draining into the gut. These acids irritate skin nerves. You may itch without seeing a rash at first. Over time, broken skin forms red patches. This is one of the most common symptoms of liver disease problems. Itching often worsens at night and disrupts sleep.
Severe itching does not mean severe pain. Many people delay care because there is no pain. That delay can be dangerous when liver disease or skin rash is the cause.
Jaundice And Yellowing Of Skin
Yellow skin and eyes appear when bilirubin builds up. Bilirubin forms when red blood cells break down. A healthy liver removes it. A damaged liver cannot. Yellowing usually starts in the eyes, then spreads to the skin. When jaundice appears with liver disease and skin rash , it suggests bile flow obstruction or advanced liver stress. You may also notice dark urine and pale stools.
Dry, Flaky, Or Irritated Skin
Dry skin happens when bile flow drops. Bile helps absorb fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K. Without them, skin loses moisture and strength. Cracks form easily. Rashes spread faster. Many people with fatty liver notice this first. Doctors often link dryness to fatty liver disease on the skin , especially in people with diabetes or obesity.
Easy Bruising And Bleeding
The liver produces clotting proteins. Damage reduces these proteins. Small bumps lead to bruises. Tiny blood vessels leak under the skin. Purple or red marks appear. These marks may look like a rash but are actually bleeding under the skin. This sign often appears with liver disease skin rash in chronic cases.
Nail, Hair, And Pigmentation Changes
Nails may turn pale or develop ridges. Hair may thin or fall out. Skin darkens in folds like the neck or underarms. These changes reflect long-term liver dysfunction and hormone imbalance. When combined with itching or redness, they point strongly toward liver disease skin rash rather than a simple skin disorder.
Liver Disease Red Spots On Skin
Red skin markings form when liver damage alters blood vessel regulation and clotting balance. Hormone accumulation and reduced platelet production allow small vessels to widen or leak, creating visible spots that signal deeper circulatory and liver function problems.
Spider Angiomas
Spider angiomas look like tiny red spiders. They have a red center with thin lines spreading outward. Pressing the center makes them fade briefly. They often appear on the face, neck, and chest. Hormone buildup causes these vessels to widen. Multiple spider angiomas strongly suggest liver disease and skin rash linked to chronic liver damage.
Palmar Erythema
Palmar erythema causes the palms to look red and warm. The redness spares the center of the palm. This happens due to increased blood flow from a hormone imbalance. It does not itch or hurt. When seen with other signs, it supports the diagnosis of liver disease with red spots on the skin .
Petechiae And Purpura
Petechiae are tiny red dots. Purpura are larger purple patches. Both result from bleeding under the skin. Low platelets and weak clotting cause them. These spots often appear after minor pressure. Many people mistake them for allergic rashes. In reality, they often point to liver disease and skin rash caused by clotting failure.
Xanthomas And Xanthelasma
Xanthomas are yellow fatty bumps. Xanthelasma appears on eyelids. They form when cholesterol handling fails. Bile problems prevent fat breakdown. These lesions often appear in bile duct disorders and advanced fatty liver. Doctors often associate them with fatty liver disease on the skin and chronic cholestasis.
Conditions That Cause Skin Rash In Liver Disease
Diagnosis relies on linking skin findings with liver function rather than treating the rash alone. Doctors correlate visible skin changes with blood markers, imaging results, and clinical patterns to confirm whether the rash reflects liver dysfunction.
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis causes permanent scarring of the liver. Scar tissue blocks blood flow and traps toxins. Hormones rise because the liver cannot break them down. These changes lead to itching, spider angiomas, bruising, and redness. In cirrhosis, liver disease skin rash often signals advanced disease rather than early damage.
Hepatitis (A, B, C)
Hepatitis causes liver inflammation. Acute hepatitis may trigger hives or red rashes due to immune reactions. Chronic hepatitis causes long-term itching and dryness. Many patients notice symptoms of liver disease in their skin before fatigue or pain appears. Skin signs can appear even when liver enzymes stay near normal.
Cholestatic Liver Diseases
Cholestatic diseases block bile flow. Bile buildup causes intense itching long before jaundice appears. Skin may look normal at first. Over time, thickened, darkened skin develops from constant scratching. These conditions cause some of the most severe liver disease skin rash cases seen in practice.
Alcohol-Related Liver Disease
Alcohol damages liver cells directly. It also causes vitamin loss and hormone imbalance. Skin becomes thin, dry, and prone to bruising. Spider angiomas multiply. Red palms become obvious. These signs often appear before liver pain. Many heavy drinkers first notice liver disease in red spots on the skin without realizing the cause.
Drug-Induced Liver Injury
Certain medications stress the liver. Antibiotics, seizure drugs, and pain relievers are common triggers. Skin rash may appear days or weeks after starting a drug. Itching often comes first. Stopping the drug usually improves liver disease and skin rash , but recovery time varies.
How Liver Disease Skin Rash Is Diagnosed
Diagnosis relies on linking skin findings with liver function rather than treating the rash alone. Doctors correlate visible skin changes with blood markers, imaging results, and clinical patterns to confirm whether the rash reflects liver dysfunction.
Physical Skin Examination
Doctors inspect the color, texture, and distribution of the rash. They check areas often missed, including palms, soles, scalp, eyelids, and inside the mouth. Scratch marks, yellow tones, red spots, and bruising patterns give clues. The combination of itching, redness, and vascular marks often confirms symptoms of liver disease skin involvement before lab results return.
Liver Function Tests
Blood tests measure enzymes, bilirubin, clotting factors, and proteins. Abnormal results indicate impaired liver processing. Elevated bilirubin explains jaundice. Abnormal clotting values explain bruising and petechiae. These tests help confirm that liver disease skin rash links to internal liver dysfunction rather than a primary skin disorder.
Imaging Studies
Ultrasound often checks for fatty liver, bile duct blockage, or scarring. CT or MRI may follow if the results stay unclear. Imaging explains why bile flow slows or blood backs up. These findings help explain fatty liver on the skin changes like dryness and discoloration.
Skin Biopsy (When Needed)
A skin biopsy is rare. Doctors use it only when the rash looks unusual or does not match liver findings. It helps rule out psoriasis, vasculitis (blood vessel inflammation), or drug allergies. A biopsy does not diagnose liver disease itself, but helps confirm that the liver disease skin rash is the correct explanation.
Liver Disease Skin Rash Treatment
Effective management focuses on correcting liver dysfunction while reducing skin irritation. Skin symptoms improve only when bile flow, toxin clearance, and hormone balance stabilize, making liver-directed treatment essential for lasting relief.
Treating The Underlying Liver Disease
Doctors focus on hepatitis control, bile flow improvement, alcohol cessation, or metabolic management. When liver function improves, skin symptoms often fade. In fatty liver, weight control and blood sugar balance reduce inflammation. Effective liver care remains the foundation of the treatment of liver disease skin rash .
Medications For Itching And Inflammation
Doctors usually prescribe bile-binding medicines to reduce itching. These drugs trap bile acids in the gut. Antihistamines may help with sleep but do not fix the cause. Dosage varies by age and condition. These medications support comfort but do not replace liver treatment in the treatment of liver disease skin rash .
Topical Treatments For Skin Relief
Moisturizers repair the skin barrier and reduce cracking. Mild steroid creams reduce redness when inflammation appears. Doctors avoid strong steroids due to thinning risk. Topicals only support surface healing, while liver treatment addresses liver disease skin rash internally.
Lifestyle And Dietary Adjustments
Low-fat meals reduce bile stress. Adequate protein supports skin repair. Hydration prevents dryness and cracking. Alcohol avoidance protects liver cells. These steps improve outcomes for fatty liver disease on the skin and chronic liver conditions.
Prevention Of Liver Disease Skin Rash
Controlling metabolic risk, avoiding toxins, and maintaining liver-friendly habits lowers the chance of skin changes tied to chronic liver stress.
Managing Fatty Liver And Metabolic Risk
Weight control reduces liver fat buildup. Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity. Managing cholesterol lowers bile stress. These steps reduce inflammation that leads to fatty liver, causing the skin changes like dryness and itching.
Alcohol Avoidance
Alcohol increases toxin buildup and hormone imbalance. Even moderate drinking worsens existing liver disease. Avoidance slows damage progression and reduces skin signs. Alcohol control plays a central role in the prevention of liver disease and skin rash .
Liver-Friendly Diet And Hydration
Fiber supports bile movement. Lean proteins aid tissue repair. Adequate water keeps skin elastic. Excess sugar and processed foods worsen liver fat. Diet consistency matters for long-term prevention of liver disease and skin rash .
Regular Monitoring Of Liver Health
Routine blood tests detect damage early. Imaging tracks fat and scarring. Early care prevents progression to severe liver disease, skin rash, and advanced liver failure.
When To See A Doctor
Certain skin changes suggest advancing liver disease and should not be ignored. Early evaluation prevents complications like infection, bleeding, or progression to liver failure when skin symptoms escalate.
Worsening Itching Or Rash
Persistent itching lasting weeks needs evaluation. Rapid spread or open sores raise concern. These signs suggest worsening liver disease or a skin rash rather than a mild reaction.
Skin Changes With Jaundice Or Swelling
Yellow skin with leg or belly swelling signals advanced liver stress. Immediate medical care is necessary when liver disease skin rash appears with these signs.
Signs Of Advanced Liver Disease
Confusion, easy bleeding, severe fatigue, or dark urine indicates serious liver dysfunction. Skin changes often worsen alongside these symptoms and require urgent attention.
FAQs
Can Liver Disease Cause Skin Rashes Without Pain?
Yes. Liver disease skin rash often causes itching, redness, or discoloration without pain. Pain usually appears only when infection or skin breakdown occurs, which means damage has progressed.
Is Itching Always A Sign Of Liver Disease?
No. Allergies and kidney disease also cause itching. However, long-lasting itching with fatigue or yellowing raises concern for symptoms of liver disease skin involvement.
Do Red Spots On Skin Indicate Cirrhosis?
They can. Spider angiomas and palmar redness often appear in cirrhosis. Multiple liver disease red spots on the skin increase suspicion of chronic liver damage.
Can Fatty Liver Cause Skin Problems?
Yes. Fatty liver causes skin dryness, itching, dark patches, and poor wound healing due to inflammation and vitamin absorption problems.
Are Liver-Related Skin Rashes Reversible?
Often yes. Early liver disease skin rash improves when liver function improves. Advanced scarring may limit full reversal, but symptoms can still ease.
What Liver Diseases Cause Severe Itching?
Cholestatic liver diseases cause the worst itching. Bile acid buildup strongly irritates nerves, making liver disease skin rash intense even without visible redness.
Can Liver Rash Appear Before Other Symptoms?
Yes. Skin changes may appear before pain, jaundice, or fatigue. Many people first notice symptoms of liver disease skin without realizing the cause.
How Long Does Liver-Related Itching Last?
Itching lasts until bile flow improves. Treatment shortens duration, but chronic disease may cause recurring liver disease skin rash episodes.
Can Diet Improve Liver Skin Symptoms?
Yes. Balanced nutrition supports liver repair and skin healing. Diet changes play a role in the treatment of liver disease, skin rash , especially in fatty liver.
When Is Liver Skin Rash An Emergency?
It becomes urgent when rash appears with jaundice, confusion, bleeding, or swelling. These signs indicate severe liver disease skin rash linked to advanced liver failure.
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Nivedita Pandey, MD, DM (Gastroenterology)
Dr. Nivedita Pandey is a U.S.-trained gastroenterologist and hepatologist with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating liver diseases and gastrointestinal disorders. She specializes in liver enzyme abnormalities, fatty liver disease, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and digestive health.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current clinical guidelines.