Best supplements for fatty liver can support liver function when fat builds up inside liver cells. Fatty liver disease happens when the liver stores excess fat and struggles to clear it. This slows detox work, affects blood sugar control, and raises liver enzymes.
Table of Contents
ToggleSupplements do not replace diet or weight control. They work as support tools. Some help reduce liver fat. Some lower inflammation. Others protect liver cells from damage. Some can harm the liver if used wrong. Knowing the benefits and risks matters before you add anything.
15 Supplements for Fatty Liver Disease
These 15 supplements for fatty liver disease work by reducing liver fat buildup, calming inflammation, and improving insulin control. Supplements that target only one pathway often show limited results unless combined with diet and activity changes. This is why some people see enzyme improvement without major fat reduction on scans.
Not all supplements act directly on liver fat. Some protect liver cells from further damage, while lifestyle changes do the actual fat reduction.
Milk Thistle (Silymarin)
Milk thistle protects liver cells from toxins. It stabilizes cell membranes and supports repair. Many clinicians use it when liver enzymes stay mildly high. It may reduce ALT and AST levels over time. It does not remove fat quickly. It mainly limits ongoing damage. Some people feel bloating or loose stools. Serious reactions stay rare.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E acts as a strong antioxidant. It reduces oxidative stress inside liver cells. This matters because oxidative stress pushes fatty liver toward inflammation. Vitamin E shows benefit mainly in non-diabetic adults. High doses for long periods raise bleeding risk. Doctors usually monitor use closely. It remains one of the best supplements for fatty liver for select patients.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fats help the liver export fat instead of storing it. They also lower blood triglycerides. This reduces fat flow into the liver. Fish oil remains the main source. Plant sources work but act more slowly. Some people notice nausea or reflux. Omega-3s help liver fat more than liver enzymes.
Probiotics
Probiotics change gut bacteria balance. The gut sends blood directly to the liver. Harmful gut bacteria increase liver inflammation. Helpful bacteria lower toxin load. Probiotics for fatty liver often reduce enzyme levels and insulin resistance. Effects depend on strain and dose. Results build slowly.
Turmeric (Curcumin)
Curcumin lowers inflammatory signals in the liver. It may improve enzyme levels and insulin sensitivity. Absorption stays low unless paired with black pepper extract. High doses can irritate the stomach. People with gallbladder disease need caution.
Choline
Choline helps package fat so the liver can export it. Low choline intake links to fatty liver progression. Eggs and fish provide choline naturally. Supplements help when diet intake stays low. Excess choline can cause body odor and sweating.
N-Acetylcysteine (NAC)
NAC increases glutathione levels. Glutathione is a key liver antioxidant. It protects liver cells from toxin damage. NAC shows benefit in reducing oxidative stress markers. Headache or nausea can occur. It does not directly burn liver fat.
Green Tea Extract
Green tea extract increases fat oxidation. It may reduce liver fat accumulation. Concentrated extracts can stress the liver if overdosed. Whole green tea appears safer. Low-dose extracts are usually preferred.
Berberine
Berberine improves insulin sensitivity. This reduces fat delivery to the liver. It also affects gut bacteria. Many clinicians use it for metabolic fatty liver. Digestive upset remains common early on. It can interact with diabetes medications.
Zinc
Zinc supports liver enzyme activity and immune balance. Low zinc levels appear often in chronic liver disease. Supplementation helps deficiency states. Too much zinc reduces copper absorption. Balance matters.
Selenium
Selenium supports antioxidant enzymes inside liver cells. Deficiency worsens oxidative stress. A narrow safety range makes dosing important. Excess selenium harms the liver and nerves.
Coenzyme Q10
CoQ10 supports mitochondrial energy production. Mitochondria help burn fat inside liver cells. Improved energy handling may reduce fat buildup. Side effects remain mild.
Vitamin D
Low vitamin D levels are linked to insulin resistance and liver fat. Supplementation improves metabolic markers in deficient people. Blood testing guides used. It works best with diet changes.
Artichoke Leaf Extract
Artichoke extract supports bile flow. Bile helps remove fat and waste from the liver. Some people see lower cholesterol and enzyme levels. Gas and cramps can occur.
Betaine
Betaine supports methylation (a chemical process that helps fat metabolism). It helps the liver process and export fat. Studies show enzyme improvement in some patients. Nausea appears at higher intakes.
These 15 supplements for fatty liver disease vary in strength and safety. Combining several without guidance increases risk. The best supplements for fatty liver depend on your labs, weight, blood sugar control, and medication use. Some people benefit from one targeted option. Others need none if lifestyle changes work well.
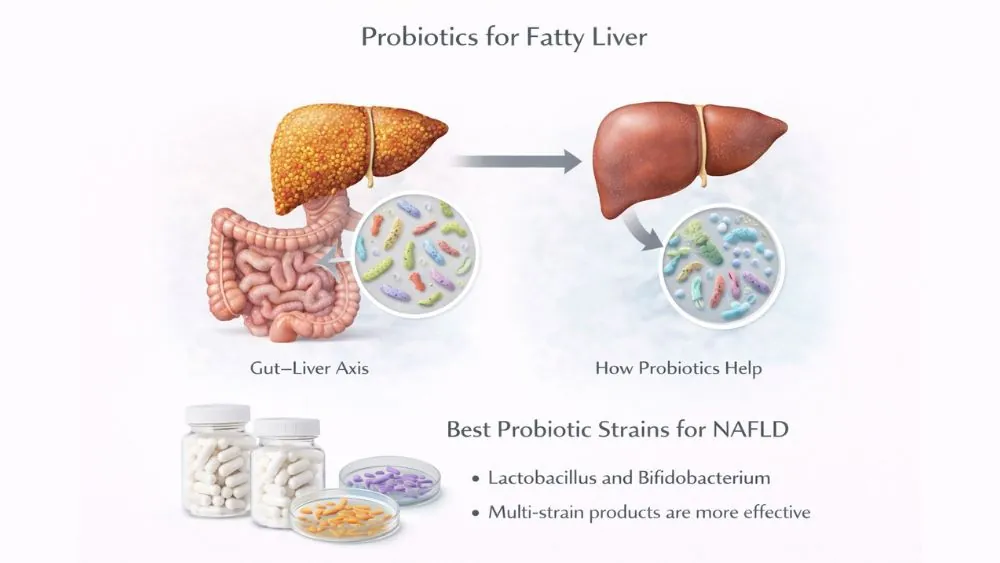
Probiotics for Fatty Liver
The gut and liver share a direct blood route. When gut bacteria stay imbalanced, toxins reach the liver faster. This raises inflammation and worsens fat buildup. Probiotics for fatty liver aim to correct this imbalance. They do not act like drugs. They shift the gut environment slowly. Over time, this reduces stress on liver cells and improves metabolic signals.
People with fatty liver often show higher gut permeability, meaning toxins leak more easily. Certain probiotic strains tighten this barrier. This reduces endotoxin flow into the liver. When used consistently, the best supplements for fatty liver plans often include probiotics because they work upstream, not just on symptoms.
Gut–Liver Axis and Fatty Liver
The gut–liver axis refers to the constant communication between gut microbes and liver cells. Poor diet feeds harmful bacteria. These bacteria release toxins that reach the liver. The liver responds with inflammation and fat storage. This cycle keeps repeating unless the gut environment improves.
Probiotics support beneficial bacteria that produce short-chain fatty acids. These compounds lower inflammation and improve insulin signaling. This makes probiotics for fatty liver useful in early and moderate disease stages.
How Probiotics Reduce Liver Inflammation
Probiotics reduce harmful bacterial byproducts. This lowers immune activation inside the liver. Less immune activation means less scarring risk over time. Improved gut balance also supports bile acid metabolism, which helps fat digestion.
Probiotics may also lower ammonia and oxidative stress. These effects protect liver cells indirectly. They do not burn fat directly but reduce conditions that worsen fat accumulation.
Best Probiotic Strains for NAFLD
Strains from the Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium families show the most benefit. Multi-strain products work better than single strains. Consistency matters more than dose size. Effects usually appear after several weeks.
Some people respond better than others. Gut makeup differs between individuals. For this reason, supplements for NAFLD often include probiotics as part of a broader plan, not as a single fix.
Supplements for NAFLD
NAFLD is often linked to insulin resistance, weight gain, and chronic inflammation. Supplements for NAFLD target these drivers rather than the fat itself. They support pathways that control glucose, fat transport, and cell protection.
Using the best supplements for fatty liver in NAFLD requires lab monitoring. Improvements often show first in insulin markers, then in liver enzymes. Fat reduction comes later and depends heavily on diet.
Supplements That Improve Insulin Resistance
Berberine, vitamin D, and omega-3 fats improve insulin signaling. Better insulin control means less fat enters the liver. This slows new fat storage. These supplements work best alongside carbohydrate control and weight loss.
Insulin resistance improvement often precedes enzyme changes. This explains why some people feel better before labs improve.
Supplements That Reduce Liver Fat
Choline, betaine, and omega-3 fats help move fat out of liver cells. They support fat packaging and export. Without these processes, fat stays trapped. These supplements do not force fat loss. They support normal fat handling.
Among the best supplements for fatty liver , omega-3 fats show consistent fat reduction in imaging studies. Others show benefit mainly in people with low baseline levels.
Supplements That Lower ALT and AST Levels
Milk thistle, curcumin, and CoQ10 help lower liver enzymes by reducing oxidative stress. Lower enzymes suggest less active liver injury. Enzymes can drop even if fat remains. This does not mean the disease is gone.
Enzyme changes should always be viewed with imaging and metabolic markers for full context.
Fatty Liver Supplements Side Effects
Side effects of fatty liver supplements often appear when doses exceed individual tolerance or when multiple products overlap in function. Digestive upset is common early, but more serious effects develop quietly with long-term misuse.
Liver stress from supplements may not cause pain. Rising enzymes are often the first sign. This is why routine monitoring matters even when supplements feel well tolerated.
Common Digestive Side Effects
Nausea, bloating, and diarrhea occur most often. Berberine, magnesium-containing products, and probiotics cause these early effects. Taking supplements with food reduces irritation. Digestive effects usually fade after adjustment. Persistent symptoms require stopping the product.
Supplement-Drug Interactions
Some supplements change how drugs work. Berberine affects diabetes and blood pressure drugs. Vitamin E increases bleeding risk with blood thinners. These interactions increase danger silently. This is why the best supplements for fatty liver should be chosen with a full medication review.
Risks of Long-Term Supplement Use
Long-term high-dose use stresses detox pathways. Fat-soluble vitamins build up in the liver. Minerals compete for absorption. Side effects of fatty liver supplements often show only after months. Periodic breaks and lab monitoring reduce long-term risk.
What Supplements Are Bad for Your Liver
Some products labeled as natural directly injure liver cells or overload detox pathways. Many supplements that are bad for your liver contain hidden compounds, contaminants, or excessive doses that bypass safety checks.
Liver injury from supplements often mimics viral hepatitis on blood tests. Early recognition prevents permanent damage, making avoidance more effective than treatment.
Herbal Supplements Linked to Liver Injury
Kava, comfrey, chaparral, and certain traditional remedies cause liver toxicity. These herbs impair liver cell regeneration. Injury may appear suddenly and severely. These remain among the most documented supplements that are bad for your liver and should be avoided fully.
Overdosed Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamin A accumulates in liver tissue. Excess iron promotes scarring. Selenium excess damages nerves and liver cells. These nutrients become toxic above narrow limits. Blood testing helps prevent overdose-related injury.
Supplements That Worsen Fatty Liver
High-dose niacin increases liver fat. Some muscle-building products contain hidden steroids. These raise liver enzymes rapidly. These products often market aggressively but harm quietly. Avoiding supplements that are bad for your liver protects long-term liver function.
Diet and Lifestyle Changes That Support Supplements
Supplements alone cannot reverse fatty liver. Diet and movement drive recovery. The best supplements for fatty liver only support what lifestyle already improves. Fat loss inside the liver responds best to calorie control and insulin balance.
Diet for Fatty Liver Disease
Whole foods reduce liver fat faster than supplements. Fiber improves insulin response. Reducing sugar lowers fat creation in the liver. Protein preserves muscle during weight loss. Diet changes show measurable enzyme improvement within weeks.
Weight Loss and Physical Activity
Losing even a small amount of weight reduces liver fat. Walking improves insulin sensitivity. Resistance training preserves metabolic rate. Exercise improves supplement response. Movement also lowers inflammation independent of weight loss.
Alcohol Reduction and Liver Recovery
Alcohol worsens fat accumulation and inflammation. Even moderate intake slows recovery. Removing alcohol often improves enzymes quickly. Liver recovery accelerates when alcohol intake stays near zero.
FAQs
Which supplements work best for fatty liver?
The best supplements for fatty liver depend on your labs and risks. Milk thistle, omega-3 fats, and vitamin E help some people. Results vary based on diet and insulin control.
Can supplements reverse fatty liver disease?
Supplements support reversal but cannot act alone. Fat loss, diet changes, and movement drive recovery. Supplements help protect liver cells during this process.
Are probiotics effective for NAFLD?
Probiotics for fatty liver improve gut balance and reduce inflammation. They work best in early disease stages and when paired with diet changes.
What supplements should be avoided in fatty liver?
Avoid vitamin A excess, niacin, and risky herbal blends. These rank among supplements that are bad for your liver and worsen liver stress.
Are fatty liver supplements safe long-term?
Some are safe with monitoring. Long-term misuse raises risk. Side effects of fatty liver supplements often appear slowly without warning.
How long do supplements take to show results?
Most supplements show lab changes after eight to twelve weeks. Fat reduction takes longer and depends on weight loss and insulin control.
Can supplements lower liver enzymes naturally?
Yes, some supplements lower enzymes by reducing inflammation. This does not always mean liver fat is gone. Imaging gives better insight.
Do supplements work without diet changes?
No. Without diet control, supplements fail. The best supplements for fatty liver only enhance lifestyle-driven improvements.
Are supplements safe for diabetics with NAFLD?
Some help, some interfere. Supplements for NAFLD in diabetes require careful drug interaction review and glucose monitoring.
Should supplements be stopped if enzymes rise?
Yes. Rising enzymes signal stress. Stop the supplement and seek medical guidance before restarting or switching products.
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Nivedita Pandey, MD, DM (Gastroenterology)
Senior Gastroenterologist & Hepatologist
Dr. Nivedita Pandey is a U.S.-trained gastroenterologist and hepatologist with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating liver diseases and gastrointestinal disorders. She specializes in liver enzyme abnormalities, fatty liver disease, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and digestive health.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current clinical guidelines.
About Author | Instagram | Linkedin