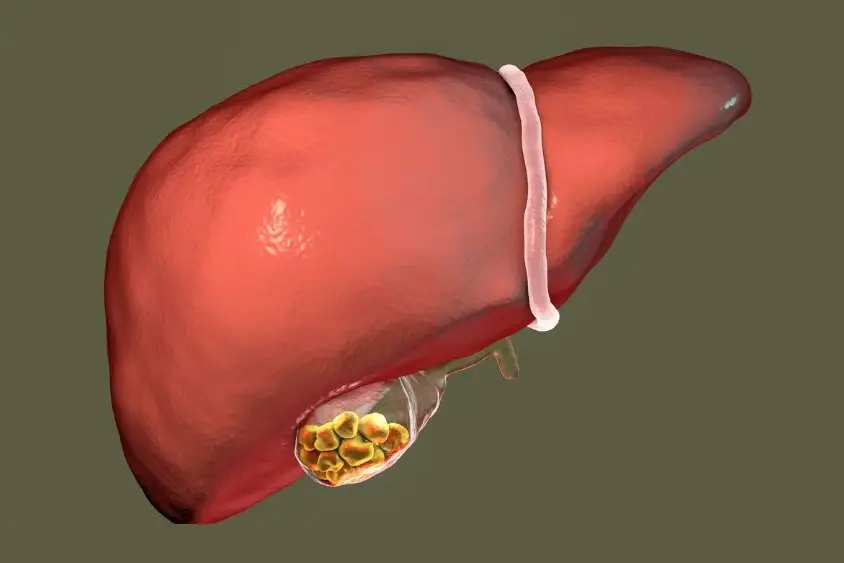
Liver abscess is a serious infection where a pocket filled with pus forms inside your liver. This happens when bacteria or parasites enter liver tissue, and your immune system cannot clear them fast enough. Without early care, a liver abscess can damage liver cells, spread infection to the blood, and become life-threatening. If you delay care because early signs feel mild, the condition can worsen quickly.
Table of Contents
ToggleCauses of Liver Abscess
A liver abscess forms when bacteria or parasites reach liver tissue through blood, bile ducts, or nearby organs. The liver filters gut blood, which increases exposure to harmful germs. Blocked bile flow, untreated gut infections, and weakened immunity allow these organisms to multiply and form pus-filled cavities.
Bacterial Infections
Bacteria are the most common reason you develop a liver abscess . These germs often start in your intestines or bile ducts and then move into liver tissue. Certain bacteria survive well in low-oxygen areas, which allows pus to form. People with diabetes, poor immunity, or long hospital stays face higher risk. When bacteria grow inside the liver, your body walls them off, creating one of the main types of liver abscess seen worldwide.
Parasitic Infections (Entamoeba histolytica)
A parasite called Entamoeba histolytica causes amoebic infection. You pick it up through contaminated water or food. The parasite first infects your intestines and then travels through blood vessels to the liver. This form of liver abscess often affects people living in or traveling to areas with poor sanitation. Amoebic cases usually involve a single large abscess rather than many small ones, which helps doctors separate it from other types of liver abscess .
Spread From Biliary Tract Infections
Your bile ducts drain digestive fluid from the liver. When gallstones or swelling block these ducts, bacteria multiply. Infection can then spread backward into liver tissue. This route explains many hospital cases of liver abscess , especially in older adults. These biliary infections represent an important group of causes of liver abscess because they often require drainage along with medicine.
Abdominal Infections and Sepsis
Infections like appendicitis, bowel perforation, or severe intestinal inflammation allow bacteria to enter the bloodstream. Once in the blood, germs can settle in the liver. If infection spreads widely through the blood, called sepsis (a dangerous whole-body infection), liver abscess formation becomes more likely. This pathway explains why untreated abdominal infections appear among the causes of liver abscess in emergency settings.
Post-Surgical or Traumatic Causes
Surgery near the liver or blunt injury to the abdomen can introduce bacteria directly. Even small injuries may allow germs to grow if immunity is weak. Hospital-acquired bacteria often cause these infections. These cases usually involve mixed bacteria and fall under complex types of liver abscess that need careful monitoring.
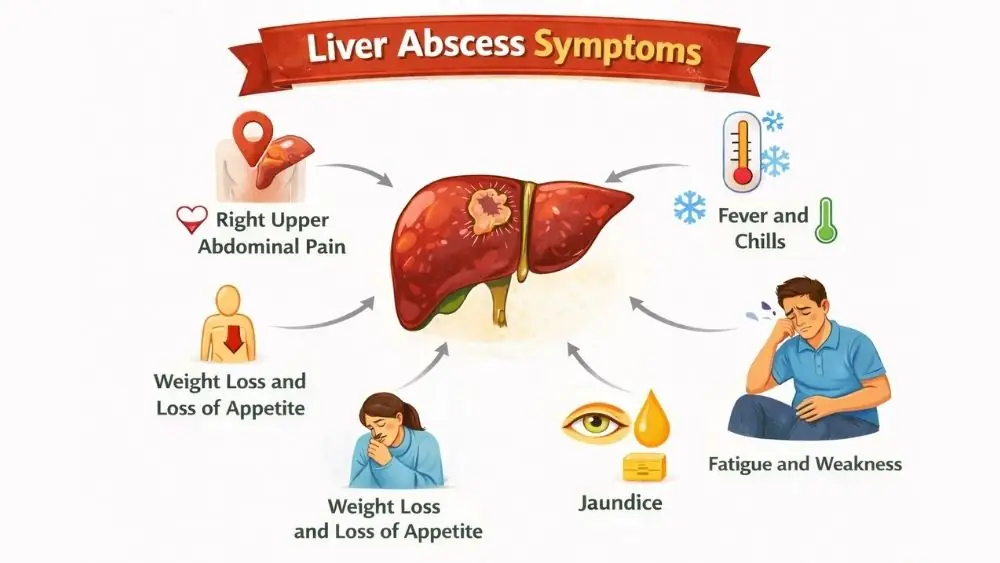
Liver Abscess Symptoms
The symptoms of liver abscess often start vague and worsen over days or weeks. Infection causes liver swelling, capsule stretching, and inflammatory chemical release, which explains pain, fever, and fatigue. Symptoms vary based on abscess size, number, and cause.
Right Upper Abdominal Pain
Pain under your right ribs is common. It may spread to your right shoulder due to shared nerve pathways. The pain often feels deep and constant rather than sharp. This symptom appears in most patients and ranks high among the symptoms of liver abscess doctors look for during exams.
Fever and Chills
Persistent fever signals active infection. You may notice chills, shaking, or night sweats. Fever occurs because your immune system releases chemicals to fight germs. When fever lasts several days without clear cause, doctors consider liver abscess as a possible reason.
Nausea and Vomiting
Digestive upset happens because liver inflammation affects bile flow. You may feel sick after eating or vomit without relief. This symptom often appears alongside abdominal pain and adds to the typical symptoms of liver abscess .
Weight Loss and Loss of Appetite
Loss of appetite develops as infection progresses. Food may taste unpleasant. Weight loss can happen within weeks due to poor intake and increased energy use by the immune system.
Jaundice
Jaundice means yellowing of the skin and eyes. It occurs when bile cannot drain properly. Dark urine and pale stools often appear at the same time. Jaundice usually signals a more advanced liver abscess and possible bile duct involvement.
Fatigue and Weakness
Ongoing infection drains energy. You may feel weak even after rest. Fatigue becomes worse when fever continues or anemia (low red blood cells) develops.
Diagnosis of a Liver Abscess
Accurate diagnosis of a liver abscess requires combining blood tests with imaging. Blood work shows infection stress, while scans reveal fluid-filled cavities. Identifying the organism matters because bacterial and amoebic types of liver abscess need different treatments.
Blood Tests and Infection Markers
Blood tests often show high white blood cell counts, which signal infection. Liver enzymes may rise because liver cells become inflamed. Inflammatory markers increase when infection spreads. These findings support suspicion but cannot confirm the diagnosis alone.
Ultrasound of the Liver
Ultrasound uses sound waves to show fluid pockets inside the liver. It is quick and safe. Doctors often start with ultrasound when symptoms of liver abscess and blood tests point toward infection. Ultrasound also helps guide drainage procedures.
CT Scan or MRI
CT scans give detailed images that show abscess size, number, and exact location. MRI helps when soft tissue detail matters, such as in complicated cases. These scans play a major role in confirming the diagnosis of a liver abscess and planning treatment.
Stool Tests for Amoebic Infection
When doctors suspect a parasite, stool tests look for cysts or parasite DNA. Blood tests can also show immune response to amoebic infection. These tests help separate amoebic cases from bacterial types of liver abscess .
Aspiration and Culture of Abscess Fluid
Doctors sometimes insert a needle into the abscess to drain fluid. The fluid is tested to identify the germ. This step guides antibiotic choice and confirms the diagnosis of a liver abscess when imaging alone cannot provide full answers.
Treatment for a Liver Abscess
Effective treatment for a liver abscess depends on the abscess size, the germ involved, and your overall health. Doctors focus on clearing infection, draining pus when needed, and preventing spread. Delay or partial treatment raises the risk of rupture and sepsis, so care usually starts as soon as imaging confirms a liver abscess .
Antibiotic Treatment
Doctors usually start antibiotics as soon as a liver abscess is suspected. The first choice often covers several bacteria at once because lab results take time. Once culture reports return, doctors adjust medicines to target the exact germ. Antibiotic courses usually last several weeks because liver tissue heals slowly. Stopping early increases relapse risk, which affects long-term outcomes of treatment for a liver abscess .
Anti-Amoebic Medications
Amoebic cases require specific drugs that kill the parasite inside liver tissue and the intestines. Doctors often add a second medicine to clear parasites from the gut and prevent recurrence. This step matters because untreated intestinal infection can lead to another liver abscess later. Dosage varies by age, weight, and liver function.
Percutaneous Needle Aspiration
Doctors use a thin needle to drain pus when antibiotics alone do not shrink the abscess. Imaging guides the needle to avoid healthy tissue. Removing pus reduces pressure, pain, and fever quickly. This method works best for single abscesses and supports faster recovery during treatment for a liver abscess .
Catheter Drainage
Large or thick abscesses often need a catheter, which is a small tube left in place for days. The tube allows continuous drainage. Doctors monitor output and repeat imaging to track healing. Catheter drainage lowers rupture risk in complex types of liver abscess .
Surgical Treatment
Surgery becomes necessary when abscesses rupture, spread widely, or fail to drain. Surgeons remove infected tissue and wash the abdominal cavity. This option carries higher risk and longer recovery. Doctors reserve it for severe cases where other treatment methods for a liver abscess fail.
Complications of Liver Abscess
Pressure from pus can rupture tissue, while bacteria entering blood trigger sepsis. These outcomes explain why untreated liver abscess carries significant mortality despite modern care.
Rupture of Liver Abscess
A liver abscess can burst into the abdomen or chest. This releases pus and bacteria, causing sudden severe pain and infection of surrounding organs. Rupture requires emergency surgery and intensive care. Mortality rises sharply after rupture.
Spread of Infection to Lungs or Bloodstream
Infection can travel through blood vessels to the lungs, causing breathing problems or chest infection. Bloodstream spread worsens fever and weakness. This complication explains why doctors treat liver abscess aggressively even when symptoms seem mild.
Sepsis
Sepsis occurs when infection triggers a body-wide inflammatory response. Blood pressure drops, organs receive less oxygen, and failure may follow. A liver abscess ranks among known abdominal sources of sepsis, especially in older adults.
Liver Failure
Extensive infection destroys liver cells. The liver then fails to process toxins or produce proteins needed for clotting. Jaundice worsens, confusion may appear, and bleeding risk rises. Liver failure remains a feared outcome of untreated liver abscess .
Risk Factors for Liver Abscess
Risk increases when immunity weakens or liver defense drops. Diabetes, liver disease, and alcohol use impair infection control. Poor sanitation raises parasite exposure, which explains regional differences in causes of liver abscess .
Diabetes Mellitus
High blood sugar impairs white blood cell function. Infection spreads faster and heals slower. Diabetic patients face higher rates of complications and recurrence. Diabetes appears repeatedly among major causes of liver abscess in hospital records.
Chronic Liver Disease
Cirrhosis and long-term hepatitis damage liver structure. Blood flow changes reduce immune surveillance inside the liver. These changes allow bacteria to settle and grow, increasing risk of severe types of liver abscess .
Alcohol Use Disorder
Alcohol injures liver cells and lowers immunity. Poor nutrition often follows heavy drinking, which further weakens defenses. Alcohol use also raises the risk of bile duct disease, adding to the causes of liver abscess .
Weakened Immune System
Cancer treatment, steroid use, or immune disorders reduce infection control. Even small infections can progress quickly. In these patients, a liver abscess may present with fewer symptoms but more severe damage.
Poor Sanitation and Contaminated Water
Unsafe water spreads parasites and bacteria. Poor hygiene increases intestinal infections, which later seed the liver. This risk factor explains regional differences in types of liver abscess seen worldwide.
Prevention of Liver Abscess
Prevention focuses on stopping germs before they reach the liver. Clean water, early gut infection treatment, and chronic disease control lower risk. Protecting bile flow and liver health reduces future liver abscess formation.
Safe Drinking Water and Food Hygiene
Boiled or treated water lowers parasite exposure. Hand washing before meals prevents ingestion of germs. Proper food storage limits bacterial growth. These steps directly reduce causes of liver abscess linked to gut infection.
Early Treatment of Intestinal Infections
Persistent diarrhea or abdominal pain needs medical care. Early treatment prevents bacteria or parasites from entering blood vessels. This step protects against future liver abscess formation.
Managing Diabetes and Chronic Diseases
Good sugar control improves immune response. Regular follow-up for liver disease helps detect bile duct problems early. Disease control reduces recurrence after treatment for a liver abscess .
Avoiding Unnecessary Alcohol Intake
Limiting alcohol protects liver cells and immunity. Reduced intake lowers risk of bile duct disease and infection spread. This simple step improves long-term liver health.
FAQs
Can a liver abscess heal on its own?
A liver abscess does not heal without treatment. Infection continues to grow and damage tissue. Antibiotics and drainage are usually required to prevent rupture and life-threatening spread.
Is liver abscess contagious?
A liver abscess itself does not spread from person to person. However, parasites or bacteria that cause it can spread through contaminated food or water.
How long does liver abscess treatment take?
Treatment for a liver abscess often lasts four to six weeks. Duration depends on abscess size, response to drugs, and whether drainage was required .
Can liver abscess recur?
Yes, recurrence can happen if the underlying causes of liver abscess remain untreated. Poor diabetes control, bile duct disease, or persistent intestinal infection increase repeat risk.
What foods should be avoided during recovery?
During recovery from a liver abscess , avoid alcohol, oily foods, and heavy meals. Simple, balanced meals support liver healing and reduce digestive stress.
How does a liver abscess develop from abdominal infections?
Abdominal infections allow bacteria to enter blood vessels. The liver filters this blood, trapping germs that can form a liver abscess when immunity fails.
Can gallbladder or bile duct infections cause a liver abscess?
Yes, bile duct blockage traps bacteria. Infection spreads backward into liver tissue, making biliary disease a common cause of liver abscess .
What are the early symptoms of a liver abscess?
Early symptoms of liver abscess include fever, right upper abdominal pain, fatigue, and nausea. These signs often feel mild at first but worsen quickly.
Is right upper abdominal pain a common sign of liver abscess?
Yes, right upper abdominal pain is one of the most frequent symptoms of liver abscess because the liver capsule stretches during infection.
Can fever and chills indicate a liver abscess?
Persistent fever with chills can signal a liver abscess , especially when combined with abdominal pain or jaundice. Medical evaluation becomes essential in such cases.
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Nivedita Pandey, MD, DM (Gastroenterology)
Dr. Nivedita Pandey is a U.S.-trained gastroenterologist and hepatologist with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating liver diseases and gastrointestinal disorders. She specializes in liver enzyme abnormalities, fatty liver disease, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and digestive health.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current clinical guidelines.