Pain during a colonoscopy usually stays low because doctors use sedation and a gentle technique. You may feel pressure, short cramps, and gas. You usually do not feel sharp pain when sedation works well. You may remember almost nothing after the test. However, bloating and gas often happen afterward, and walking often helps.
Table of Contents
ToggleYou should still plan for a few real sensations. Pain during a colonoscopy can show up if your colon has tight bends, if your belly muscles tense, or if gas stretches the bowel. Your team can adjust sedation, body position, and scope technique. These steps often reduce the pain during a colonoscopy .
What Does a Colonoscopy Feel Like During the Procedure
You usually feel pressure more than pain. You may feel movement in your lower belly and an urge to pass gas.
Sensations you may feel without sedation
Without sedation, you can feel the scope move inside your colon. You can feel cramping when the scope rounds a bend. You can feel fullness when the doctor adds gas. Some people also feel a brief pinch. That pinch often comes from colon stretching, not injury. Pain during a colonoscopy varies because every colon curves differently.
Without sedation, you also notice sounds and pulling sensations. You may hear suction sounds when fluid gets removed, and feel pressure when the doctor pauses to inspect. These moments can feel strange, but they often pass quickly. Your breathing and muscle control matter a lot here.
How pressure and gas cause discomfort
Doctors add air or carbon dioxide to open the colon. That gas helps them see small polyps clearly. The extra gas can stretch the colon wall and cause cramps. That stretch can create pain during a colonoscopy for short periods.
Using carbon dioxide often reduces bloating and pain compared with room air. Carbon dioxide absorbs faster through the bowel wall. So you may feel less gas pressure after the test. If your center offers carbon dioxide, you can ask about it.
Why most patients feel little to no pain
Sedation relaxes your body and lowers your pain signals. That makes pain during a colonoscopy much less likely. Many clinics use moderate sedation, so you feel sleepy. Some clinics use deep sedation with propofol. With deeper sedation, you often sleep through the exam.
Technique also matters a lot. A skilled endoscopist avoids looping the scope. They may change your position to smooth a sharp turn. These choices reduce stretching and reduce cramps. When those steps work well, pain during colonoscopy stays low.
Pain During Colonoscopy: What Actually Causes Discomfort
When discomfort happens, it usually comes from mechanics, not damage. That fact helps you worry less about pain during a colonoscopy .
Colon stretching and air insufflation
Gas stretches the colon so the camera can see the lining. Stretching can trigger cramp signals in the bowel wall. You often feel this as pressure that rises and falls. Pain during a colonoscopy often tracks with how much stretching you feel.
Some centers use water-aided methods in certain cases. Water exchange or water immersion uses water to help advance the scope. These methods can reduce pain when little or no sedation is used. Water techniques are one way to reduce discomfort. That option may not fit every center or every case. Evidence looks promising, but use varies across clinics.
Sharp turns in the colon
Your colon has several natural bends. Some people also have extra loops. When the scope meets a bend, the bowel can stretch. That stretch can cause a cramp or a deep pressure feeling. If you feel pain during a colonoscopy , it often happens at these turns.
Your doctor can manage bends in a few practical ways. They may pause and reduce gas. They may apply gentle pressure on your abdomen. They may change your position from the left side to the back. These moves often lower discomfort without adding risk.
Anxiety and muscle tension effects
Anxiety can tighten your belly and pelvic muscles. Tight muscles can make scope movement feel harder. Anxiety can also sharpen your focus on each sensation. That combination can increase pain during colonoscopy even when the scope moves gently.
You can lower this risk with clear communication. Tell the nurse if you feel panic or strong worry. Ask them to explain each step in simple terms. When your body relaxes, your colon often relaxes too. That usually reduces pain during colonoscopy .
Colonoscopy Without Pain
Many people want the smoothest experience possible. You can often get close to a colonoscopy without pain with the right plan.
Conscious sedation vs deep sedation
Moderate sedation often uses a benzodiazepine plus an opioid. You feel very relaxed and sleepy with that mix. Deep sedation often uses propofol under close monitoring. Both approaches aim to reduce pain during colonoscopy and reduce fear.
Deep sedation can wear off faster for some people, but it still affects judgment. You still need a ride home after any sedation. You should avoid driving and making major decisions that day.
Will you be awake or asleep?
With moderate sedation, you may wake briefly and then drift back. You may respond to a simple request like, “Take a deep breath.” With deep sedation, you usually sleep through the exam. Your clinic decides based on staffing and safety rules. If you fear pain during colonoscopy , tell them before the day starts.
Why do many patients remember nothing?
Some sedation plans affect memory formation. You may not store clear memories of the procedure. That does not mean nothing happened. It means your brain did not record it well. Many people later describe a quick “time skip” feeling. This effect supports the goal of colonoscopy without pain for many patients.
Sedation and Colonoscopy Pain
You should think about comfort and safety together. The goal of sedation and colonoscopy pain control is relief with careful monitoring.
Medications commonly used for sedation
Clinics often use midazolam for relaxation and amnesia. They may pair it with fentanyl for pain control. Many centers also use propofol for deeper sedation.
You do not need exact dosages to plan well. Dosing varies by age, weight, health, and medical history. Your doctor usually adjusts doses during the exam. That adjustment helps prevent pain during a colonoscopy while keeping breathing safe.
Safety of sedation during colonoscopy
Teams monitor oxygen level, heart rate, and blood pressure. They also watch your breathing and responsiveness. ASGE sedation guidelines outline training, monitoring, and rescue planning. That structure lowers risks during sedation.
Some evidence also addresses propofol safety in practice. Propofol administration models and safety outcomes. Evidence can vary by setting, staffing, and patient risk. Experts still agree that proper monitoring matters most.
Who should avoid deep sedation
Some health situations call for extra caution with deep sedation. Severe lung disease can raise breathing risk. Certain heart rhythm problems can also matter. Sleep apnea can raise airway concerns during sedation. Your team will review your risks before they choose a plan. They can still manage pain during a colonoscopy with a safer approach.
Colonoscopy Pain After Procedure:
After the scope comes out, the most common issue is trapped gas. You can also feel mild cramping when your colon settles back down. Most people worry that colonoscopy pain after the procedure means something went wrong. In most cases, it does not, but persistent pain or fever needs a doctor’s call.
Bloating and gas pain after colonoscopy
Your doctor adds gas to open the colon so they can see well. Some gas stays inside for a while, even after they suction some out. That leftover gas can press on the bowel wall and cause bloating. It can also cause shoulder or upper belly aches in some people. This happens because gas pressure can irritate nerves that share pathways. Many people feel relief after they pass gas a few times.
Some clinics use carbon dioxide instead of room air. Carbon dioxide absorbs faster than room air in many studies, so you may feel less bloating later. Evidence supports less pain during and after in several trials, although results can vary by setting.
Mild cramping vs warning signs
Mild cramping feels like a dull squeeze that comes and goes. It usually improves when you walk, sip fluids, and pass gas. Mild discomfort can also happen if the doctor removes a polyp. A small amount of blood on the first stool can happen, especially after a biopsy.
Warning signs feel different from ordinary cramps. Severe pain that keeps building matters. Pain with a hard, swollen belly also matters. Early perforation signs can include persistent abdominal pain and distention. That issue stays uncommon, but you should treat it seriously.
How long does post-procedure discomfort last?
For many people, bloating improves in hours, and it often fades by the next day. The exact timing depends on how much gas stayed inside and how your body absorbs it. If you had a polyp removal, you may feel mild soreness longer.
You should seek care for severe abdominal pain, fever, bleeding that does not stop, dizziness, or weakness. Those symptoms do not belong in normal colonoscopy pain after the procedure .
How to Reduce Colonoscopy Pain Before and During the Test
You can lower discomfort by planning for the parts you control. These steps can reduce pain during a colonoscopy and reduce stress.
Importance of proper bowel prep
A clean colon lets your doctor see clearly and move smoothly. Stool left behind can slow the exam and increase scope movement. More movement can mean more stretching and more cramps. Follow the liquid diet rules exactly as your clinic states.
Drink the prep at the time they give you, even when it tastes awful. Good prep can shorten the procedure and may lower pain during colonoscopy .
If you vomit the prep or cannot finish it, call the clinic. They often have fixes that keep you safe and help the exam.
Asking for appropriate sedation
If you fear pain during a colonoscopy , say it clearly during scheduling. Ask what sedation types your center offers and who provides them. Some places mainly use moderate sedation.
Others often use propofol-based deep sedation. Your medical history decides what fits best, so disclose sleep apnea, lung disease, and prior anesthesia issues. Those details help them manage sedation and colonoscopy pain safely.
You can also ask about comfort tools besides drugs. Ask if they use carbon dioxide. Ask if they use the water-aided technique in low-sedation cases. These options do not exist everywhere, but asking can help.
Relaxation and breathing techniques
Your belly muscles can tighten when you feel worried. Tight muscles can increase cramping and raise pain during a colonoscopy . Slow breathing helps your muscles loosen. Keep your inhale steady and your exhale longer than your inhale. You can also relax your jaw and unclench your hands. Small muscle changes can lower pain signals.
If you feel embarrassed about passing gas, let that go early. Passing gas reduces pressure and often reduces cramps. The staff expects it and will not judge you.
Is Colonoscopy Painful Compared to Other Screening Tests?
Different tests trade comfort for accuracy and convenience. Your best choice depends on your risk level and your goals.
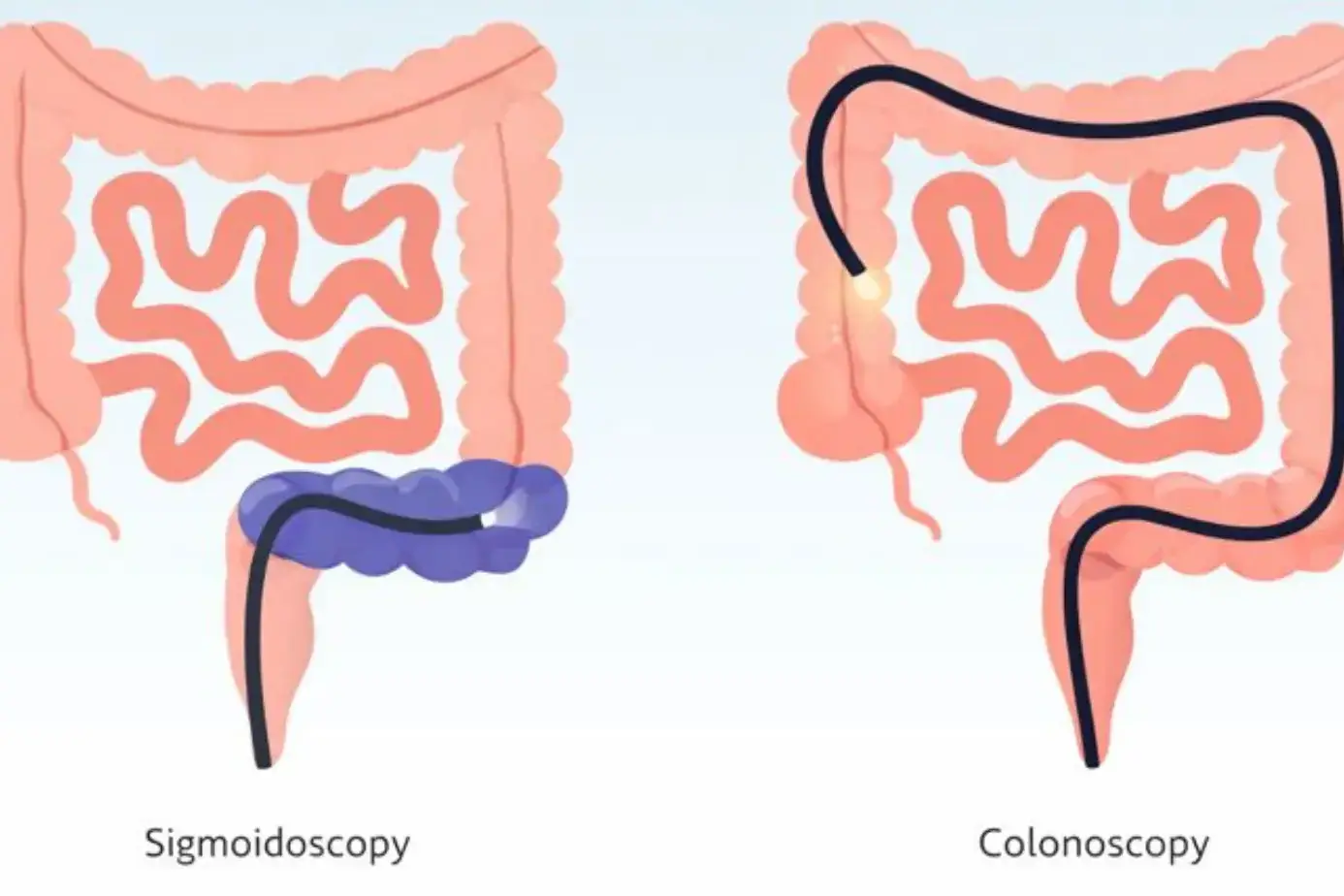
Colonoscopy vs Sigmoidoscopy
Sigmoidoscopy checks only the rectum and lower colon. The scope travels a shorter distance, so some people feel less pressure. Many centers use less sedation for it, which can change your experience.
Colonoscopy checks the whole colon, so it can find problems higher up. Colonoscopy also lets the doctor remove polyps right away.
Colonoscopy vs Cologuard
Cologuard is a stool DNA test you do at home. You avoid a scope and avoid sedation, so you avoid procedure discomfort. The trade-off is follow-up. A positive stool test usually leads to a colonoscopy anyway. Also, a stool test cannot remove polyps. Colonoscopy can detect and treat in the same visit, which can prevent cancer.
Why colonoscopy is still the gold standard
A colonoscopy lets the doctor see the colon lining directly. They can biopsy suspicious areas right away. They can remove many polyps during the same procedure. That matters because many colorectal cancers develop from polyps over time. For many patients, that prevention benefit outweighs short-term pain during a colonoscopy .
When Colonoscopy Pain Is Not Normal
Most discomfort stays mild and improves. Some symptoms need urgent attention.
Severe abdominal pain after the procedure
If you feel severe pain that does not ease, call right away. Severe pain with a swollen belly also needs urgent evaluation. Persistent pain and distention are early red flags for perforation. This complication remains rare, but fast care matters.
Fever, bleeding, or dizziness
Fever after colonoscopy is not a normal “prep hangover” sign. Heavy bleeding is also not normal, especially blood clots or bleeding that continues. Dizziness, fainting, or unusual weakness also matters.
When to contact your doctor immediately
Call your doctor if pain keeps rising hour by hour. Call if you cannot keep fluids down. Call if bleeding does not stop, even if it seems “not that much.” Call if you feel short of breath or chest pain. You should never “tough out” scary symptoms because you fear bothering the clinic.
Benefits of Colonoscopy That Outweigh Temporary Discomfort
Even if you worry about pain during a colonoscopy, the benefits can protect you for years.
Early detection of colorectal cancer
Colonoscopy can catch cancer early, when treatment often works better. Early detection can also prevent emergency surgery later. Screening guidelines differ by risk, so your doctor will personalize timing. Still, the central benefit stays the same: finding danger early.
Polyp removal during the same procedure
Polyps are growths on the colon lining. Some polyps can turn into cancer over time. Colonoscopy lets your doctor remove many polyps right away. That immediate step can lower future cancer risk. It turns one appointment into prevention, not just detection.
Long-term prevention benefits
A normal colonoscopy can buy you years of reassurance. It can also reduce repeated testing if your risk stays average. If you fear repeated discomfort, this spacing can matter. Many people feel that one controlled day of pain during a colonoscopy outweighs years of uncertainty.
FAQs
Is a colonoscopy painful without sedation?
Without sedation, you can feel pressure, cramping, and gas fullness. Some people tolerate it with steady breathing. Others feel more pain during a colonoscopy because of tight bends or anxiety.
Does colonoscopy pain last for days?
Most bloating and cramps improve within hours and often fade by the next day. If colonoscopy pain after the procedure lasts days or keeps worsening, you should contact your doctor promptly.
Can women feel more pain during a colonoscopy?
Some people with prior pelvic surgery or endometriosis may feel more discomfort. Body shape and colon looping can also change sensation. If you worry, ask about sedation and colonoscopy pain planning ahead of time.
Is a colonoscopy more painful the first time?
First-time worry can tighten muscles and amplify sensations. That tension can increase pain during a colonoscopy even when the scope moves gently. Clear explanations and the right sedation choice often make later exams easier.
Can anxiety make colonoscopy pain worse?
Yes, anxiety can tighten your belly muscles and sharpen your attention on sensations. That can increase cramps and pressure points. If anxiety runs high, discuss colonoscopy without pain options with your team.
Does gas pain after colonoscopy mean something is wrong?
Gas pain usually means leftover gas needs to move out. Walking, changing positions, and passing gas often help quickly. Severe colonoscopy pain after the procedure, with fever or heavy bleeding needs urgent care.
Can I request stronger sedation if I’m anxious?
Yes, you can ask about deeper sedation options during scheduling. Your medical history will guide what is safe. A careful plan for sedation and colonoscopy pain can lower fear and discomfort.
Is colonoscopy painful for elderly patients?
Many older adults do well, but doctors review heart and lung health carefully. They may adjust sedation to reduce risks. With good monitoring, pain during colonoscopy still often stays low.
How soon can I eat after colonoscopy?
Many people eat once they feel fully awake and not nauseated. Some start with light foods and fluids first. If you had a polyp removal, follow the clinic’s advice, and watch for colonoscopy pain after the procedure changes.
Is colonoscopy pain worse than endoscopy?
Upper endoscopy often feels shorter and involves less gas in the intestines. Colonoscopy can cause more bloating because of the insufflation of gas. With the right sedation, pain during a colonoscopy can feel minimal, similar to an endoscopy.
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Nivedita Pandey, MD, DM (Gastroenterology)
Dr. Nivedita Pandey is a U.S.-trained gastroenterologist and hepatologist with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating liver diseases and gastrointestinal disorders. She specializes in liver enzyme abnormalities, fatty liver disease, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and digestive health.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current clinical guidelines.