Colonoscopy can detect serious colon problems early, including cancer, polyps, long-term inflammation, and hidden bleeding sources. Doctors rely on this test because it shows the inside of your colon directly.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhen done correctly, a colonoscopy can detect disease before symptoms appear, which often changes outcomes completely. This test does not find every possible digestive problem, but it remains the most complete tool for checking colon health today.
What Does a Colonoscopy Diagnose?
A colonoscopy helps doctors identify structural and tissue-level changes inside your colon and rectum. These changes often explain symptoms like bleeding, long-lasting diarrhea, anemia, or unexplained pain. In many cases, colonoscopy can detect problems years before they turn dangerous.
How A Colonoscopy Visualizes The Colon And Rectum
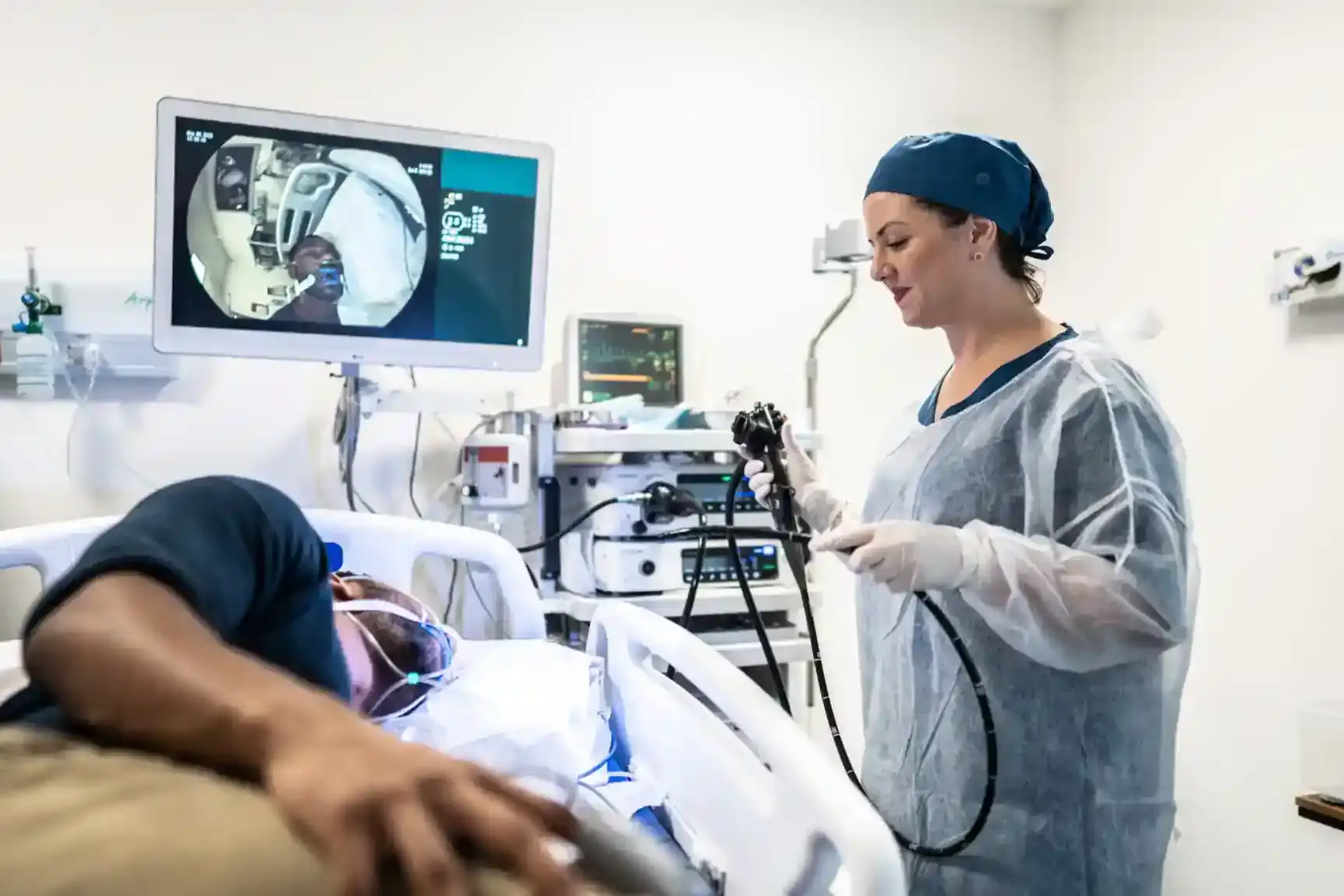
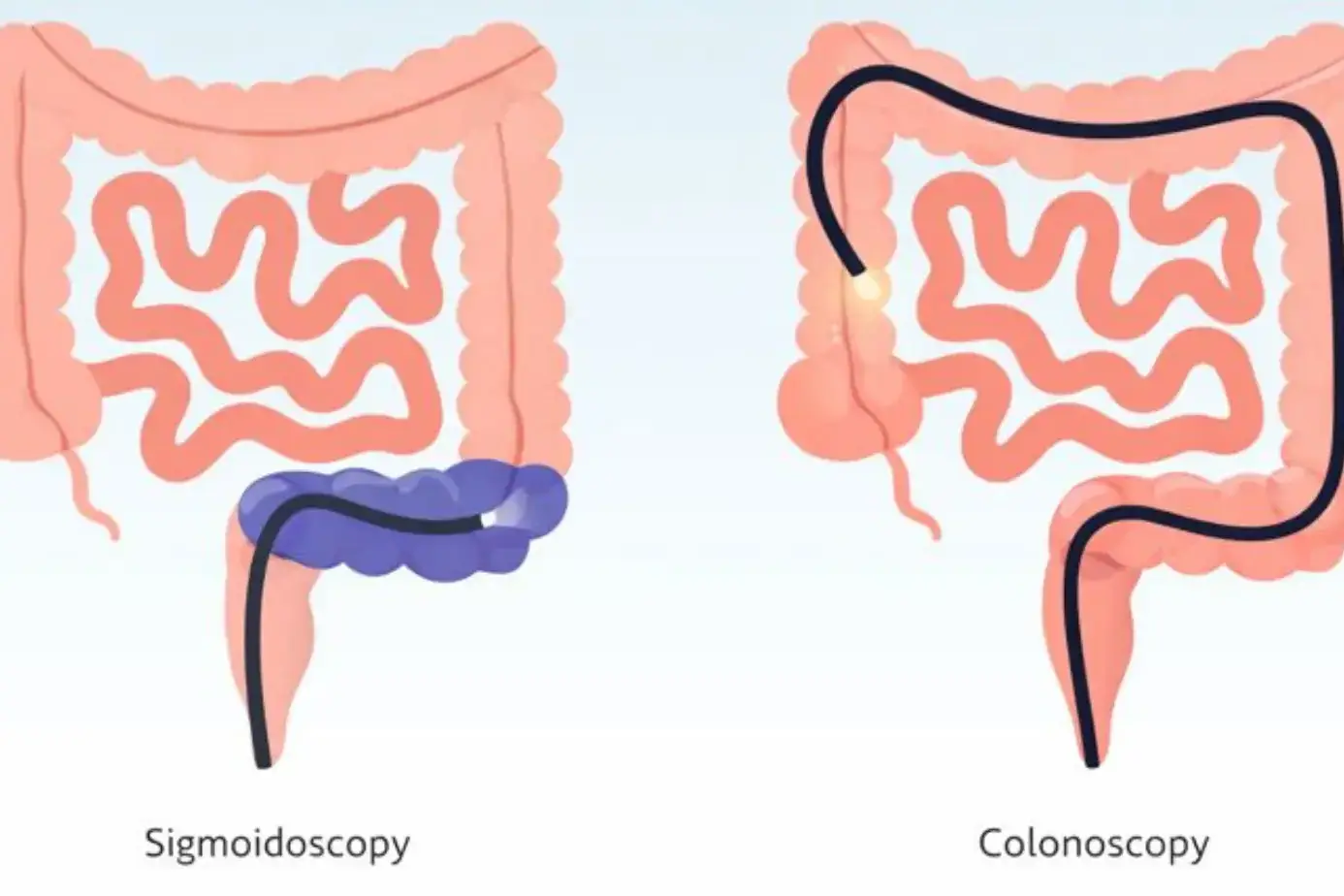
During the procedure, a flexible tube with a tiny camera moves through your colon. The camera sends live images to a monitor. This direct view allows doctors to examine the lining for swelling, growths, ulcers, or color changes.
Because the camera sees real tissue, colonoscopy can detect flat lesions that scans often miss. Air or carbon dioxide gently opens the colon so folds do not hide abnormal areas.
Difference Between Screening And Diagnostic Colonoscopy
A screening colonoscopy is done when you feel fine and have no symptoms. Its goal is prevention. A diagnostic colonoscopy is done when symptoms already exist, such as bleeding or bowel changes.
The process stays the same, but the reason differs. In both cases, a colonoscopy can diagnose disease with higher accuracy than stool tests or imaging alone.
Colonoscopy Cancer Detection
Colorectal cancer often grows silently. Many patients feel normal until the disease advances. This is why doctors depend on colonoscopy.
How Colonoscopy Detects Colorectal Cancer
Cancer appears as abnormal tissue, a mass, or an ulcer that does not heal. The camera allows doctors to inspect these changes closely. If needed, they take a biopsy, meaning a small tissue sample, for lab testing. This step confirms whether cells are cancerous. Because of this direct process, colonoscopy can detect cancer rather than estimate risk.
Early-Stage Vs Advanced Cancer Findings
Early cancer may appear as a small lesion or a flat, abnormal area. These early changes often cause no pain or bleeding. Advanced cancer may narrow the colon, bleed easily, or block stool movement. Detecting cancer early matters because treatment is often simpler. This explains why colonoscopy can detect disease at a stage where survival rates improve greatly.
Accuracy Of Colonoscopy For Cancer Detection
Colonoscopy is considered the most accurate test for colorectal cancer. Its accuracy depends on bowel preparation quality and exam time. When preparation is good, colonoscopy can detect most cancers present at the time of testing. No test is perfect, but colonoscopy remains the reference standard doctors compare others against.
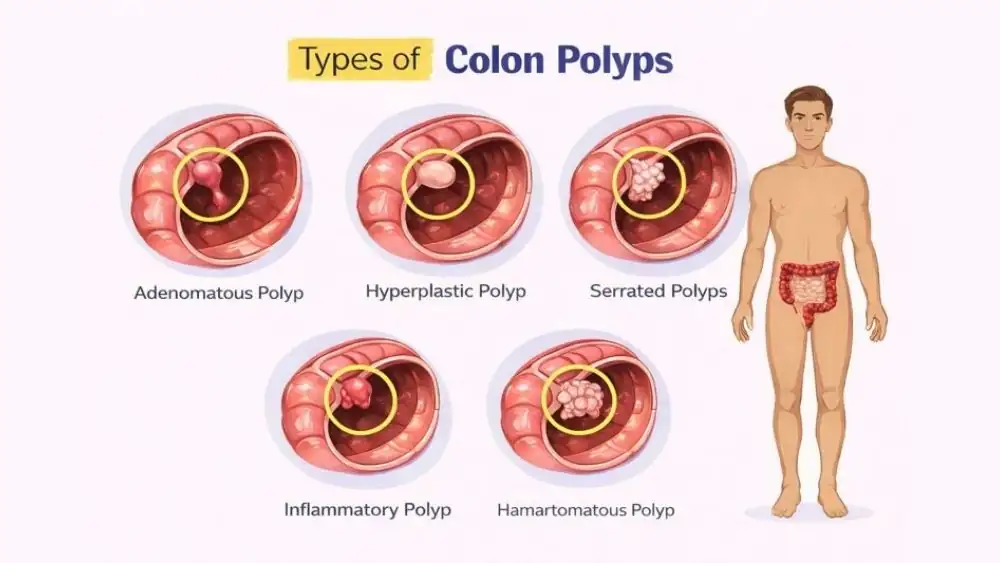
Colonoscopy Detects Polyps
Polyps are growths that form on the colon lining. Many are harmless, but some can slowly turn into cancer.
Types Of Colon Polyps
There are three main types doctors look for.
- Adenomatous polyps are gland-like growths that can slowly change into colon cancer over several years if they are not removed.
- Hyperplastic polyps are small growths usually found in the lower colon and rectum and are considered harmless in most cases.
- Serrated polyps have a saw-like shape under a microscope, and some types can become cancerous, especially when large or located in the upper colon.
Because colonoscopy detects polyps directly, doctors can classify them accurately and decide the next steps.
Why Polyp Removal Prevents Colon Cancer
Most colon cancers start as polyps. Removing them stops cancer before it forms. During the same procedure, doctors remove polyps using small tools passed through the scope. This is why colonoscopy can detect and prevent cancer at the same time. Few tests offer both detection and treatment in one step.
What Polyp Findings Mean In Screening Results
The number, size, and type of polyps matter. One small low-risk polyp means a longer time before the next test. Multiple or high-risk polyps mean closer follow-up. These decisions come directly from colonoscopy screening results . Clear findings help doctors plan safer long-term care.
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Detected By Colonoscopy
Inflammatory bowel disease means long-term swelling and damage inside the digestive tract. These conditions often come and go over the years. Symptoms alone are not enough for diagnosis. This is where colonoscopy can detect clear patterns that separate one disease from another.
Crohn’s Disease Findings
Crohn’s disease can affect any part of the digestive tract, but the colon is commonly involved. During the exam, doctors often see patchy inflammation, meaning some areas look damaged while others look normal.
Deep ulcers, cracks in the tissue, and narrowed sections may also appear. These findings explain pain, diarrhea, and weight loss. Because blood tests cannot show these patterns, a colonoscopy can diagnose Crohn’s disease with far more confidence.
Ulcerative Colitis Findings
Ulcerative colitis usually starts in the rectum and spreads upward through the colon. Unlike Crohn’s disease, the inflammation is continuous. The lining often looks red, swollen, and fragile, and it may bleed easily. In severe cases, ulcers cover large areas.
Seeing this continuous pattern helps doctors confirm the diagnosis. This is another reason colonoscopy can detect specific disease behavior rather than vague inflammation.
Role Of Biopsy During Colonoscopy
A biopsy means removing tiny tissue samples for lab testing. Even when the colon looks normal, biopsies matter for conditions like microscopic colitis. Lab results also rule out infections or cancer. Without a biopsy, many diagnoses stay uncertain. This step strengthens why colonoscopy can detect diseases that scans and stool tests cannot confirm.
Other Conditions Detected By Colonoscopy
Not every abnormal finding means cancer or inflammatory bowel disease. Colonoscopy also reveals common structural problems and bleeding sources.
Diverticulosis And Diverticulitis
Diverticulosis means small pouches form in the colon wall, often with age. These pouches are usually painless and found by chance. When they become infected, the condition is called diverticulitis. Colonoscopy can safely identify diverticulosis once active infection settles. This shows how colonoscopy can detect age-related changes that explain pain or bleeding.
Hemorrhoids And Rectal Bleeding Sources
Internal hemorrhoids are swollen veins inside the rectum. They often cause painless bleeding. Colonoscopy helps confirm whether bleeding comes from hemorrhoids or deeper areas like polyps or tumors. This matters because conditions detected by colonoscopy include both harmless and dangerous causes of bleeding.
Microscopic Colitis And Unexplained Diarrhea
Microscopic colitis causes chronic watery diarrhea, often without visible damage. The colon lining may look normal during the exam. Only biopsies reveal the problem. This condition is often missed without a colonoscopy. This proves again that colonoscopy can detect disease even when the surface appears healthy.
Colonoscopy Screening Results
After the exam, results guide future care. Understanding them prevents confusion and unnecessary fear.
Normal Vs Abnormal Colonoscopy Results
A normal result means no polyps, cancer, or inflammation was found. An abnormal result may include polyps, redness, ulcers, or bleeding areas. Each finding has a different meaning. Colonoscopy screening results help doctors decide whether you need treatment, monitoring, or reassurance.
What Biopsies Can Confirm
Biopsies confirm cancer type, inflammation severity, infections, or microscopic disease. Results often return within one to two weeks. These findings explain symptoms that visuals alone cannot. This is why a colonoscopy can diagnose complex conditions accurately.
How Findings Affect Follow-Up Plans
Follow-up timing depends on risk. High-risk polyps mean shorter screening intervals. Normal results mean longer gaps between tests. Chronic inflammation may require regular monitoring. These decisions rely fully on colonoscopy screening results , not general age rules alone.
When Is a Colonoscopy Recommended?
Doctors follow evidence-based guidelines to decide who needs this test and when.
Age-Based Screening Recommendations
Most adults should start routine screening at age forty-five. Some may start earlier due to risk factors. Screening matters because colonoscopy can detect disease before symptoms begin, which often saves lives.
Symptoms That Require Diagnostic Colonoscopy
Persistent rectal bleeding, unexplained anemia, long-term diarrhea, sudden bowel habit changes, or unexplained weight loss require investigation. In these cases, a colonoscopy can diagnose the cause directly instead of relying on assumptions.
Family History And High-Risk Individuals
People with close relatives who had colon cancer face a higher risk. Genetic conditions increase the risk further. Doctors recommend earlier and more frequent exams because colonoscopy can detect disease at a stage when treatment works better.
Risks And Complications Of Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is generally safe, but no medical test is risk-free.
Common Minor Side Effects
Temporary bloating, gas, or mild cramping may occur after the exam. These symptoms usually fade within hours. Sedation may cause brief drowsiness. Despite these effects, colonoscopy can detect serious disease with minimal long-term discomfort.
Rare But Serious Complications
Serious complications include bleeding or a tear in the colon wall. These are rare and occur more often during large polyp removal. Doctors weigh these risks carefully because colonoscopy can detect life-threatening conditions early.
Risk Comparison With Benefits
The risk of missing colon cancer is far greater than the risk of complications for most people. Early detection reduces surgery, chemotherapy, and death rates. This balance explains why colonoscopy can detect problems worth the small procedural risk.
What To Expect After A Colonoscopy
Recovery is usually fast, but knowing what is normal helps avoid worry.
Recovery Timeline
Most people return to normal activities the next day. Sedation effects fade within hours. Mild bloating may linger briefly. This quick recovery supports why colonoscopy can detect disease without major disruption.
When Results Are Discussed
Doctors often explain visual findings right after the exam. Biopsy results come later. Together, they clarify what colonoscopy can detect and what needs further care.
When To Contact Your Doctor
Severe pain, fever, dizziness, or heavy bleeding are not normal. These symptoms require immediate medical attention, even though they are uncommon.
FAQs
What Conditions Can a Colonoscopy Detect?
Colonoscopy can detect colon cancer, polyps, inflammatory bowel disease, diverticulosis, bleeding sources, and microscopic colitis. It shows both visible damage and hidden disease through biopsies.
Can A Colonoscopy Detect Colon Cancer at an Early Stage?
Yes. Colonoscopy can detect early-stage cancer before symptoms appear, which often allows simpler treatment and better survival outcomes compared to late-stage diagnosis.
What Types of Polyps Are Found During Colonoscopy?
Doctors find adenomatous, hyperplastic, and serrated polyps. Because colonoscopy detects polyps directly, doctors can remove risky ones during the same procedure.
Can Colonoscopy Detect Precancerous Changes?
Yes. Precancerous polyps are visible and removable. This is how colonoscopy can detect future cancer risk and stop cancer before it starts.
Does a Colonoscopy Detect Inflammatory Bowel Disease?
Yes. Visual patterns and biopsies confirm chronic inflammation. This makes colonoscopy essential when symptoms persist without a clear cause.
Can Colonoscopy Diagnose Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis?
Yes. A colonoscopy can diagnose both by showing inflammation pattern, depth, and location, supported by biopsy results.
Can Hemorrhoids Be Seen During a Colonoscopy?
Internal hemorrhoids are often visible. Identifying them helps rule out more serious causes of bleeding found among conditions detected by colonoscopy .
Can A Colonoscopy Find The Cause Of Rectal Bleeding?
Yes. Bleeding may come from polyps, cancer, colitis, or hemorrhoids. Colonoscopy identifies the exact source.
Does Colonoscopy Detect Diverticulosis Or Diverticulitis?
Diverticulosis is commonly seen. Active diverticulitis is usually evaluated after infection has settled to avoid complications.
Can Microscopic Colitis Be Diagnosed With Colonoscopy?
Yes. Biopsies taken during colonoscopy confirm microscopic colitis even when the colon looks normal to the eye.
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Nivedita Pandey, MD, DM (Gastroenterology)
Dr. Nivedita Pandey is a U.S.-trained gastroenterologist and hepatologist with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating liver diseases and gastrointestinal disorders. She specializes in liver enzyme abnormalities, fatty liver disease, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and digestive health.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current clinical guidelines.