Causes of abdominal bloating are more common than you think. A swollen stomach with pain can make simple tasks hard. Sometimes it’s harmless, but other times it can mean a health problem that needs care.
Table of Contents
ToggleLet’s break down the possible reasons for abdominal pain and bloating, when to see a doctor, and what you can do to prevent it.
Causes Of Abdominal Bloating And Pain
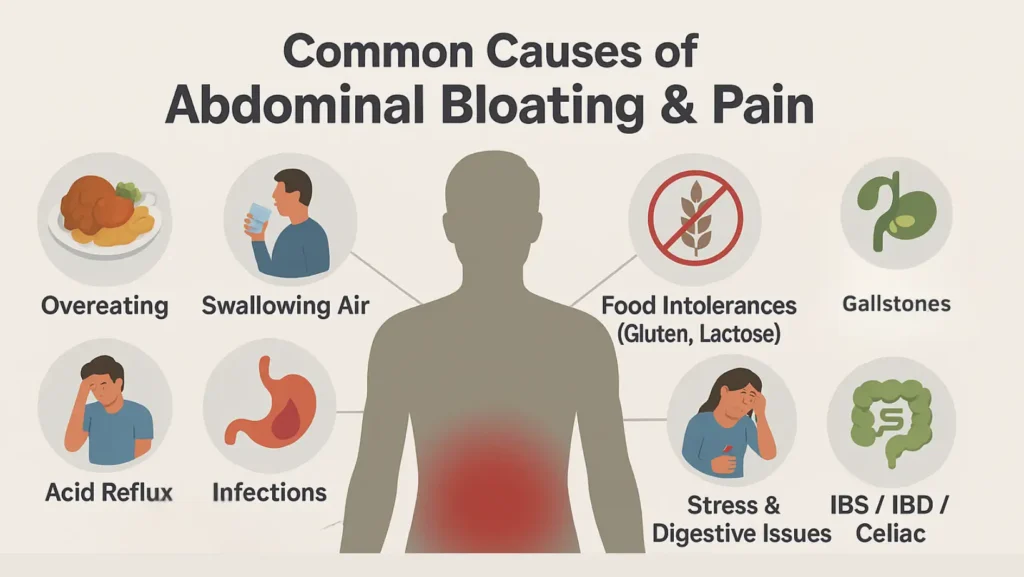
There is no single answer to why your belly swells and hurts. Both short-term and long-term issues may be behind it.
Here are the most common categories.
Common Reasons For Abdominal Pain And Bloating
- Overeating: A heavy meal stretches the stomach and triggers discomfort.
- Swallowing air: Eating fast, chewing gum, or drinking fizzy drinks can cause gas pain and bloating.
- Constipation: Stool stuck in theLarge intestine / colon (ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid)builds pressure.
- Food intolerances (gluten, lactose): These prevent proper digestion and lead to cramps, gas, and swelling.
- Stress and digestive issues: The brain-gut link is strong. Stress slows digestion and worsens bloating.
These everyday triggers are the most frequent reasons for abdominal pain and bloating.
Causes Of Stomach Pain And Bloating
Problems higher in the digestive tract often explain discomfort:
- Acid reflux and bloating: Backflow of stomach acid irritates the esophagus and causes tightness.
- Infections (viral gastroenteritis, H. pylori, E. coli, UTIs, etc.): These cause diarrhea, fever, and swelling.
- Gallstones: Hardened deposits in the Gallbladder cause severe cramps after fatty foods.
- Abdominal cramps: Can result from poor digestion or sudden infections.
- Cancer (stomach, ovarian, lymphoma): While less common, persistent swelling and weight loss may signal something serious.
These are key causes of stomach pain and bloating that should not be ignored.
Chronic Abdominal Bloating And Discomfort
When symptoms last weeks or months, it is called chronic abdominal bloating.
Conditions that cause this include:
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): Causes alternating constipation and diarrhea with bloating.
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Chronic inflammation damages the bowel and leads to swelling.
- Celiac disease: A reaction to gluten that harms the Small intestine.
- Gut microbiome imbalance: Too many “bad” bacteria in the gut increase gas production.
These conditions need long-term care and regular medical follow-up.
Severe Abdominal Pain And Bloating Concerns
Not all belly pain is mild. Signs of severe abdominal pain and bloating include:
- Sudden swelling with a hard belly
- Intense cramps that do not ease with rest
- High fever with nausea and vomiting
- Blood in stool or black tarry stools
- Fainting, sweating, or dizziness
If these occur, urgent hospital care is needed because the cause could be gastrointestinal disorders or problems with the Liver or Pancreas.
When To Get Medical Attention For Abdominal Pain And Bloating?

Seek medical help if:
- Pain is sharp and sudden
- There is ongoing fever
- You lose weight without trying
- Swelling does not go away
- Pain wakes you from sleep
Babies, pregnant women, and older adults should not delay medical care because complications progress faster in these groups.
How Doctors Treat The Causes Of Abdominal Pain And Bloating?
Treatment depends on the cause. Doctors start with history, diet review, and physical exam.
- Infections: May require antibiotics or antivirals.
- Gallstones: Often treated by removing the Gallbladder.
- IBS: Managed with diet changes, stress control, and medicine.
- IBD: Treated with anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Celiac disease: Strict gluten-free diet is essential.
Home Care Remedies For Gas Pain And Bloating
You can ease discomfort at home:
- Drink warm water and herbal teas
- Walk after meals to reduce trapped gas
- Eat smaller, frequent meals
- Limit fizzy drinks
- Use a heating pad on the belly
- Add Fiber (high-fiber foods) gradually to prevent constipation
These steps often relieve gas pain and bloating quickly.
Where’s Your Abdominal Bloating And Pain?
The exact spot of pain can reveal which organ is involved.
Here’s a quick guide:
| Location | Possible Causes |
| Left side abdominal pain and bloating | Constipation, diverticulitis, ovarian cysts, kidney stones |
| Middle abdominal bloating and pain | Gastritis, indigestion and abdominal pain, reflux, infections |
| Right side abdominal bloating and pain | Gallstones, liver disease, appendicitis |
| Lower abdominal pain and bloating | Bladder infection, IBS, pelvic causes in women, constipation |
Knowing the pain site helps your doctor decide what tests you may need.
Left Side Abdominal Pain And Bloating
This often comes from problems in the descending colon or sigmoid colon. Constipation, diverticulitis, and even kidney stones can cause left-sided pain.
Middle Abdominal Bloating And Pain
Pain in the middle usually links to the Stomach or Small intestine. Indigestion and abdominal pain, reflux, or stomach infections commonly cause this pattern.
Right Side Abdominal Bloating And Pain
When the right side hurts, the Gallbladder, Liver, or appendix may be involved. Gallstones are the most common trigger here.
Lower Abdominal Pain And Bloating
Pain low in the belly is often from the large intestine or colon, rectum or anus, or Urinary bladder. In women, reproductive organs may also be responsible. This is classed as lower abdominal pain and bloating.
How Doctors Diagnose Abdominal Pain And Bloating
Doctors use several tests to find the cause:
- Blood tests (CBC) check infection, anemia, and inflammation.
- Imaging tests (CT, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray) provide a picture of the belly organs.
- Stool analysis detects infections, blood, or parasites.
- Endoscopy allows a direct look into the stomach and intestines.
The choice of test depends on symptoms and pain location.
How To Prevent Abdominal Bloating And Abdominal Pain?
Prevention is often simple lifestyle care:
- Eat smaller meals and chew well
- Limit fatty and fried foods
- Avoid excessive salt and alcohol
- Drink plenty of Water / hydration
- Stay active with daily walking
- Manage stress with relaxation techniques
- Track foods that trigger swelling and avoid them
- Test for food intolerances (gluten, lactose) if symptoms repeat
Making these steps a habit lowers the chance of abdominal bloating / distension.
The Bottom Line
Abdominal swelling with pain is common but can have many causes. From simple gas to gastrointestinal disorders, the reason may vary. Most mild cases settle with home remedies and diet care, but lasting or severe abdominal pain and bloating requires a doctor’s opinion.
Your belly pain is a signal. Listen to it early, and you can prevent bigger health issues later.
FAQs
What can cause bloating and abdominal pain?
Bloating with pain may come from overeating, constipation, food intolerances, infections, stress, or more serious problems like gallstones or bowel diseases that disturb digestion.
When to worry about bloating and pain?
You should worry if pain is sharp, swelling is sudden, or symptoms include blood, fever, weight loss, or vomiting. These require urgent medical advice to avoid complications.
Does drinking more water reduce bloating?
Yes. Staying hydrated helps stool pass, prevents constipation, and supports smooth digestion. Water also lowers fluid retention, which reduces the chance of visible bloating and swelling.
What is gastritis stomach pain like?
Gastritis pain feels like burning or aching in the upper belly. It often worsens after eating spicy meals, alcohol, or medicines that irritate the stomach lining.
What does serious bloating look like?
Serious bloating is constant, hard, and painful. It may come with fever, vomiting, or blood. Unlike mild swelling, it does not improve with walking, hydration, or gas relief.
How do I debloat my stomach?
To debloat, drink water, eat smaller meals, limit gas-producing foods, walk after eating, and add fiber gradually. Warm compresses and probiotics may also improve digestion and comfort.
What are the three types of abdominal pain?
Doctors classify abdominal pain into sharp, crampy, and dull pain. Each type can signal different causes ranging from gas and infections to more serious organ or intestinal problems.
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Nivedita Pandey, MD, DM (Gastroenterology)
Senior Gastroenterologist & Hepatologist
Dr. Nivedita Pandey is a U.S.-trained gastroenterologist and hepatologist with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating liver diseases and gastrointestinal disorders. She specializes in liver enzyme abnormalities, fatty liver disease, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and digestive health.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current clinical guidelines.
About Author | Instagram | Linkedin