An anti-inflammatory diet is one of the simplest yet most powerful ways to manage health. Chronic swelling in the body may not always show up as pain right away, but it quietly affects energy, mood, and long-term health. Food choices can either soothe or trigger inflammation.
Table of Contents
ToggleBy learning what an anti-inflammatory diet is, what to eat, and what to avoid, you can take charge of your health in a natural and sustainable way.
What Is An Anti-Inflammatory Diet?
An anti-inflammatory diet does not consist of a strict set of regulations; it is a dietary approach aimed at reducing inflammation. It focuses on natural foods rich in fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants. The aim is to lower internal stress that often fuels long-term illnesses.
This diet is different from a short-term weight-loss plan. Instead, it supports the body over time. This method prioritizes the intake of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats to mitigate inflammation. It limits packaged items, fried foods, and sugar that are known foods that cause inflammation.
An anti-inflammatory diet is a daily eating plan that calms the immune system and prevents damage caused by chronic swelling.
Types of Anti-Inflammatory Diets
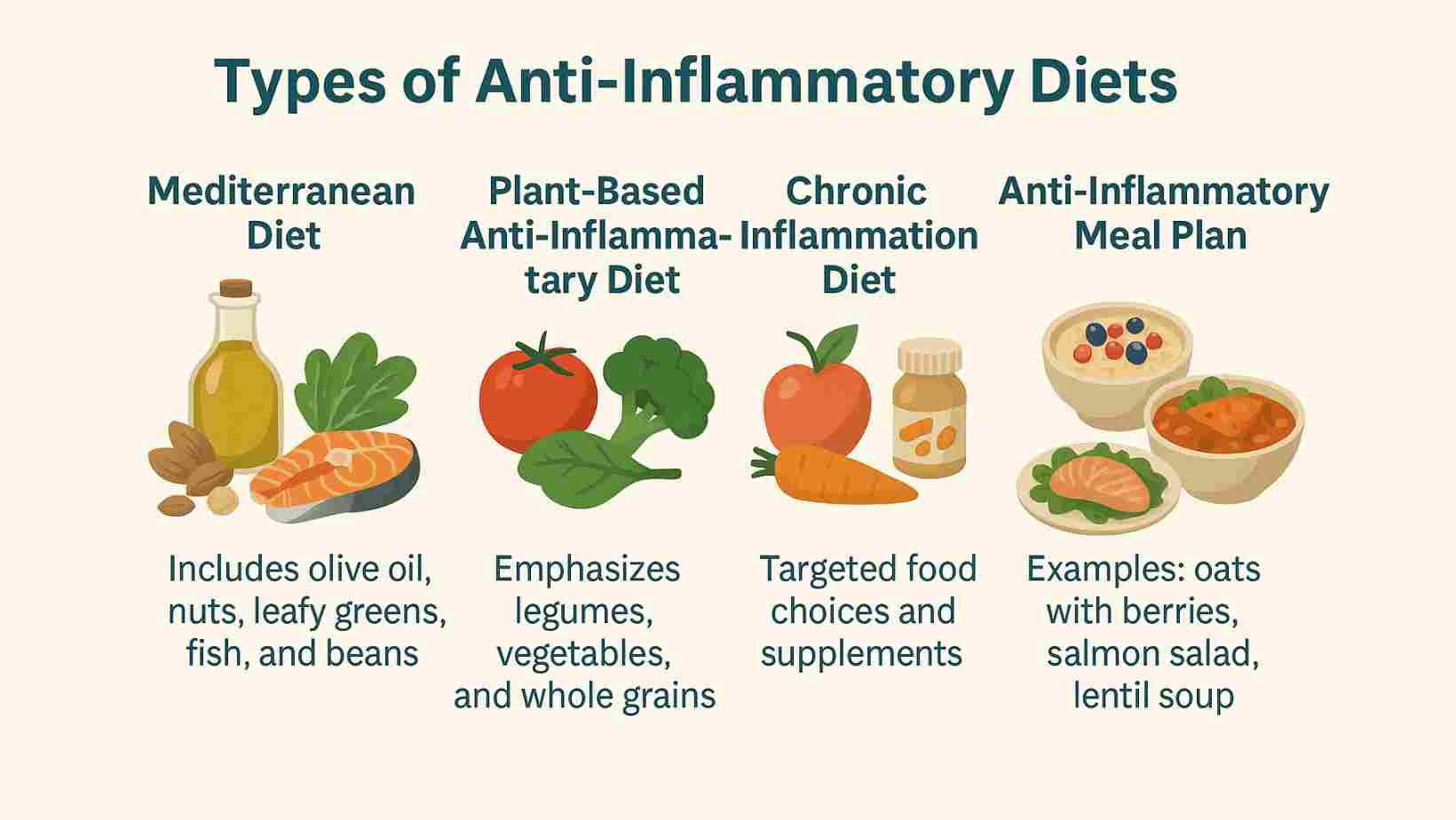
There are several versions of this diet. Each type highlights natural and clean foods but differs in focus.
- Mediterranean Diet and Inflammation: This plan includes olive oil, nuts, leafy greens, fish, and beans. It is widely studied for protecting the heart and reducing inflammation.
- Plant-Based Anti-Inflammatory Diet: This option emphasizes legumes, vegetables, and whole grains. It avoids animal products and can help with energy and gut balance.
- Chronic Inflammation Diet: Doctors may advise this version for those with ongoing health problems. It involves more targeted food choices and may include supplements when needed.
- Anti-Inflammatory Meal Plan: A weekly plan can include oats with berries for breakfast, salmon salad for lunch, and lentil soup for dinner. Planning reduces reliance on processed foods.
Conditions An Anti-Inflammatory Diet Can Help
This diet supports overall wellness but is especially valuable for certain conditions:
- Arthritis: Reduces joint pain and stiffness.
- Heart Disease: Protects arteries and lowers risk factors.
- Diabetes: Stabilizes blood sugar and improves insulin response.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Soothes gut lining and improves digestion.
- Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia: May protect brain cells from long-term inflammation damage.
- Obesity: Helps with weight management by cutting high-calorie, inflammatory foods.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods That Fight Inflammation
The inclusion of anti-inflammatory foods is fundamental to this dietary strategy. Examples include:
- Fatty fish: Salmon, sardines, and mackerel provide omega-3 fatty acids and inflammation support.
- Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, and collard greens supply key nutrients.
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are rich in antioxidants.
- Nuts: Almonds and walnuts improve cholesterol and provide fiber.
- Whole grains: Oats, brown rice, and quinoa are rich in fiber and improve gut balance.
- Soy: Edamame or tofu can be helpful if tolerated.
These foods that fight inflammation work best when eaten daily in place of sugary or fried meals.
Anti-Inflammatory Herbs and Spices
Simple seasoning can turn food into medicine.
- Spices for inflammation (turmeric, ginger): Turmeric contains curcumin, which reduces swelling. Ginger aids digestion and calms the stomach.
- Garlic and onions contain beneficial compounds that enhance immune function and assist in managing inflammation.
- Cinnamon helps balance blood sugar.
Adding these spices daily enhances taste and health.
Anti-Inflammatory Drinks for Better Health
Beverages can also play a role in reducing inflammation.
- Tea: Green and black tea are rich in antioxidants.
- Coffee: In moderate amounts, it may protect against diabetes and brain decline.
- Anti-inflammatory drinks: Lemon water, turmeric tea, or ginger-infused water help reduce swelling.
- It is recommended to limit caffeine intake if it interferes with sleep and to refrain from excessive alcohol consumption, as it increases the risk of liver complications and heart disease.
Foods That Cause Inflammation To Avoid
Some foods directly worsen inflammation. Examples include:
- Processed foods and inflammation: Packaged snacks, instant noodles, and sugary drinks are high in additives.
- Refined sugars and inflammation: Items such as cakes, pastries, and sodas can lead to increased blood sugar levels.
- Red meat and inflammation: High intake may promote swelling due to saturated fat.
- Dairy and inflammation: Some people may react poorly to cheese or milk.
- Saturated fats and omega-6 oils: Common in fried foods and fast food.
These are the major foods that cause inflammation and should be reduced.
Foods To Eat For Inflammation Relief
Healing comes from consistent food choices. Foods to eat for inflammation include:
- Healthy fats for inflammation: Avocado, olive oil, and nuts.
- Fruits and vegetables for inflammation: Tomatoes, citrus fruits, berries, and cruciferous vegetables.
- Whole grains and inflammation: Quinoa, barley, oats.
- Legumes and lentils for protein and fiber.
These items repair cells and protect against disease.
Foods To Avoid For Inflammation Control

Beyond the obvious junk food, some everyday items worsen symptoms:
- White bread and white rice.
- Sweetened breakfast cereals.
- Deep-fried fast food.
- Packaged desserts and chips.
- Large servings of cheese and butter.
Reducing these foods to avoid inflammation makes a big difference in overall health.
Tips For Following An Anti-Inflammatory Diet
- Shop fresh and seasonal produce.
- Prepare meals at home to control ingredients.
- Plan ahead with an anti-inflammatory meal plan to avoid unhealthy cravings.
- Stay hydrated with water or herbal teas.
- Pair this diet with an anti-inflammatory lifestyle that includes exercise, stress control, and enough sleep.
Risks Of An Anti-Inflammatory Diet
While generally safe, some risks exist. Completely eliminating certain food groups may result in nutritional deficiencies. Too many supplements can create side effects. People with chronic illness should follow a tailored plan with medical guidance.
Health Risks Of Chronic Inflammation
Long-term inflammation can quietly damage the body. It contributes to heart disease, arthritis, diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, dementia, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). It also increases cancer risk and reduces quality of life.
Natural Remedies To Reduce Inflammation
Besides food, natural remedies help control inflammation:
- Adequate sleep reduces stress hormones.
- Gentle exercise improves circulation.
- Omega-3 supplements support cell repair.
- Probiotics improve inflammation and gut health.
- Mindfulness and meditation calm daily stress.
The Bottom Line
The anti-inflammatory diet is not centered on rigid regulations but rather on making more informed choices. Replace refined snacks with whole foods and incorporate natural anti-inflammatory options, and reduce daily triggers.
With time, you will notice better energy, less pain, and improved focus. Using an anti-inflammatory foods list pdf can help with planning meals.
FAQs
Which foods should I avoid on an anti-inflammatory diet?
Avoid fried food, packaged snacks, refined sugar, processed meats, and high-fat dairy. These are foods to avoid inflammation and increase risk for chronic illness.
How to stop inflammation in kids?
Serve fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fish. Limit sugary drinks and fried snacks. Encourage daily play, proper sleep, and stress-free routines to reduce inflammation naturally.
Is banana anti-inflammatory?
Yes, bananas are considered natural anti-inflammatory foods. They contain fiber, vitamin B6, and potassium that support digestion, energy, and calm inflammation in children and adults alike.
Are eggs inflammatory?
Eggs are not inflammatory for most healthy people. In moderation, they provide protein and vitamins. Individual response differs, so monitor symptoms when including eggs in meals.
How to stop inflammation permanently?
Permanent cure is unlikely, but lifestyle choices control symptoms. Combine foods that fight inflammation, exercise, stress reduction, and quality sleep. Follow medical guidance for long-term chronic inflammation.
What is a good breakfast for inflammation?
A balanced breakfast can include oats, nuts, and berries. Adding whole grains and inflammation-friendly foods creates energy balance, fiber intake, and anti-inflammatory effects throughout the morning.
What can I drink before bed to reduce inflammation?
Warm herbal tea with turmeric or ginger can help. Chamomile aids sleep. Avoid caffeine and alcohol, which may disturb rest and worsen inflammation during nighttime recovery.
What is the main cause of inflammation in the body?
Common causes include poor diet, long stress, lack of exercise, and infections. Processed foods and inflammation are linked with higher risk. Lifestyle changes greatly reduce chronic inflammation.
About The Author

This article is medically reviewed by Dr. Nivedita Pandey, Senior Gastroenterologist and Hepatologist, ensuring accurate and reliable health information.
Dr. Nivedita Pandey is a U.S.-trained gastroenterologist specializing in pre and post-liver transplant care, as well as managing chronic gastrointestinal disorders. Known for her compassionate and patient-centered approach, Dr. Pandey is dedicated to delivering the highest quality of care to each patient.
→ Book a consultation to discover which remedies suit your needs best.
About Author | Instagram | Linkedin