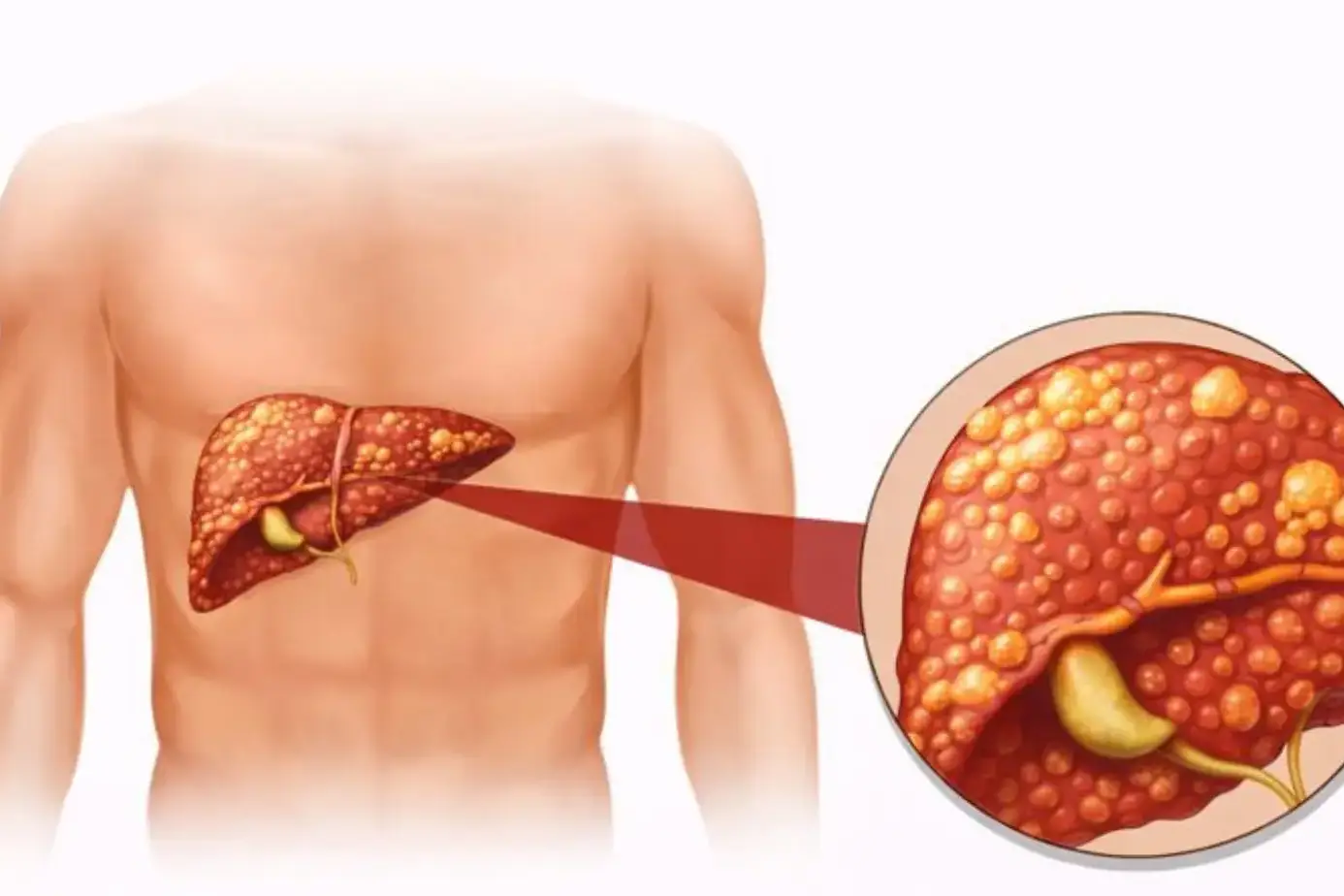
Treatment for fatty liver focuses on removing excess fat from liver cells and stopping silent damage before scarring begins. In most people, fatty liver develops from long-term calorie overload, poor sugar control, or alcohol exposure that forces the liver to store fat instead of clearing it.
Table of Contents
ToggleEffective treatment for fatty liver relies on steady weight reduction, tighter blood sugar control, and daily physical activity that pushes the liver to burn stored fat. Medicines play a limited role and are used only when metabolic risks stay high or inflammation appears.
What Causes Fatty Liver
Fatty liver develops when the liver receives more fat than it can process or export. This imbalance usually comes from excess calories, poor sugar handling, alcohol exposure, or disrupted fat metabolism. Over time, fat droplets crowd liver cells and reduce normal liver function.
Alcohol-Related Fatty Liver Disease (ALD)
Alcohol breaks down into harmful byproducts inside liver cells. These byproducts slow fat removal. Even short-term heavy drinking raises liver fat. Stopping alcohol is the core treatment for fatty liver linked to alcohol. Continued drinking increases risk of liver swelling and scarring.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD develops without alcohol use. It links strongly to poor sugar control and excess weight. This form now affects teenagers and adults. Doctors detect it during routine blood tests or scans. Lifestyle-based treatment for fatty liver works best here.
Obesity And Insulin Resistance
Extra body fat disrupts insulin action. Insulin resistance means sugar stays high in blood. The liver converts this sugar into fat. This process explains many causes of fatty liver seen today.
High Cholesterol And Triglycerides
High blood fats overload the liver. Fat enters liver cells faster than removal. Over time, fat droplets crowd liver tissue. Lipid control supports treatment for fatty liver outcomes.
Diabetes And Metabolic Syndrome
Diabetes raises liver fat and inflammation risk. Metabolic syndrome means high sugar, high blood pressure, and excess waist size. These factors combine to worsen liver stress.
Treatments For Fatty Liver
Effective treatment for fatty liver targets fat reduction inside liver cells while preventing inflammation and scarring. Most care plans rely on sustained lifestyle correction, metabolic control, and regular monitoring rather than aggressive drug therapy. Early treatment lowers long-term liver and heart risks.
Lifestyle-Based Treatment Approach
Lifestyle change remains the first-line treatment for fatty liver . You reduce liver fat by improving food choices and daily movement. Even small weight loss improves liver enzyme levels.
Medical Management And Monitoring
Doctors track liver enzymes and imaging results. Blood tests show ongoing stress. Imaging shows fat trends. Monitoring ensures treatment for fatty liver stays effective and safe.
Treating Underlying Metabolic Conditions
Controlling blood sugar and cholesterol lowers liver fat supply. Treating these conditions improves response to treatments for fatty liver .
Role Of Weight Loss In Fatty Liver Treatment
Losing 7-10%of body weight reduces liver fat significantly. Slow weight loss protects muscle mass. Crash dieting harms liver cells and slows recovery.
When Specialist Care Is Required
Advanced disease needs specialist input. Signs include persistent enzyme rise or fibrosis (scar tissue). Early referral prevents irreversible damage.
Home Remedies For Fatty Liver
Evidence-based home remedies for fatty liver work by lowering sugar load, improving gut health, and reducing oxidative stress (cell damage caused by excess fat). These methods support liver repair but work best when paired with medical guidance and consistent habits.
Dietary Changes To Reduce Liver Fat
Whole foods reduce liver workload. Vegetables, fruits, and lean protein improve fat handling. Diet-based treatment for fatty liver lowers inflammation markers.
Limiting Sugar And Refined Carbohydrates
Sugar converts directly into liver fat. Sweet drinks and white bread worsen damage. Cutting sugar is one of the strongest home remedies for fatty liver .
Increasing Fiber-Rich Foods
Fiber slows sugar absorption and improves gut balance. Better gut health lowers liver inflammation. This supports long-term treatment for fatty liver success.
Drinking Coffee For Liver Protection
Coffee improves liver enzyme levels in many adults. It also lowers fibrosis risk. Benefits appear strongest without added sugar or cream.
Natural Remedies With Scientific Evidence
Omega-3 fats lower liver fat content. Green tea improves fat metabolism. Evidence remains limited, so doctors guide use.
Medicine Should Be Taken For Fatty Liver
Whether medicine should be taken for fatty liver depends on disease severity and metabolic risk. Drugs do not remove fat directly but may reduce inflammation, insulin resistance, or cholesterol levels. Doctors prescribe medication only when lifestyle measures alone fall short.
Are Medicines Mandatory For Fatty Liver?
Most early cases improve without drugs. Lifestyle correction remains the safest treatment for fatty liver . Medicines support care when risks stay high.
Role Of Vitamin E And Insulin Sensitizers
Vitamin E reduces inflammation in selected adults. Insulin sensitizers improve sugar handling. Doctors weigh benefits against side effects before prescribing.
Cholesterol-Lowering Medications
Statins lower heart risk and help liver fat indirectly. They remain safe for most patients with liver fat.
Medicines Under Clinical Evaluation
New drugs target fat buildup and inflammation. Doctors use them only after approval. Long-term safety data still develops.
Why Self-Medication Should Be Avoided
Unsupervised drugs strain liver cells. Supplements may interact with prescriptions. Medical guidance prevents harm.
Physical Exercise For Fatty Liver
Regular physical exercise for fatty liver improves insulin sensitivity and forces the liver to release stored fat for energy. Exercise also lowers inflammation and improves blood fat levels. These benefits occur even if body weight changes slowly.
How Exercise Reduces Liver Fat
Exercise burns stored fat and sugar. The liver releases fat for energy. This process supports treatment for fatty liver .
Aerobic Exercise Recommendations
Walking, cycling, and swimming work well. Moderate pace improves fat clearance without stressing joints.
Strength Training And Muscle Mass
Muscle burns sugar at rest. Two weekly strength sessions support liver recovery.
Frequency And Duration Of Workouts
Aim for 150 minutes weekly. Spread sessions across days. Consistency matters more than intensity.
Exercise Tips For Beginners
Start slow and increase gradually. Choose activities you enjoy. This supports long-term physical exercise for fatty liver adherence.
Diet Plan For Fatty Liver Treatment
Diet-based treatment for fatty liver focuses on stabilizing blood sugar, lowering calorie overload, and reducing harmful fats. Food quality matters more than extreme restriction. A balanced diet protects liver cells while supporting gradual fat loss.
Foods To Include For Liver Healing
Vegetables, beans, fish, and olive oil help liver repair. Lean protein protects muscle mass during weight loss.
Foods To Avoid To Prevent Progression
Avoid fried foods, sugary drinks, and processed meats. These raise liver fat quickly.
Mediterranean-Style Diet Benefits
This diet lowers inflammation and improves insulin sensitivity. It supports heart and liver health together.
Portion Control And Calorie Balance
Large portions slow fat loss. Smaller meals improve calorie balance and liver recovery.
Can Fatty Liver Be Reversed
Fatty liver reversal depends on how early damage is detected and how consistently risk factors are corrected. In many cases, liver cells can clear stored fat once metabolic stress is removed. Advanced scarring limits full reversal but damage progression can still slow.
Reversibility In Early-Stage Fatty Liver
Early fatty liver, also called simple steatosis (fat buildup without scarring), is often reversible. When you remove triggers like excess calories, sugar, or alcohol, liver cells release stored fat. Many people see improvement within months when they follow a structured treatment for fatty liver plan that includes diet and activity changes.
Timeline For Liver Improvement
Liver enzymes often improve within 6 to 12 weeks after lifestyle changes. Fat reduction on imaging may take 3 to 6 months. Full structural recovery can take longer. Progress depends on how well you follow treatments for fatty liver without long breaks.
Factors Affecting Recovery Speed
Recovery slows with older age, poor sugar control, ongoing alcohol use, or sleep disorders. Gut health, stress levels, and muscle mass also influence healing speed. Addressing these factors improves response to treatment for fatty liver .
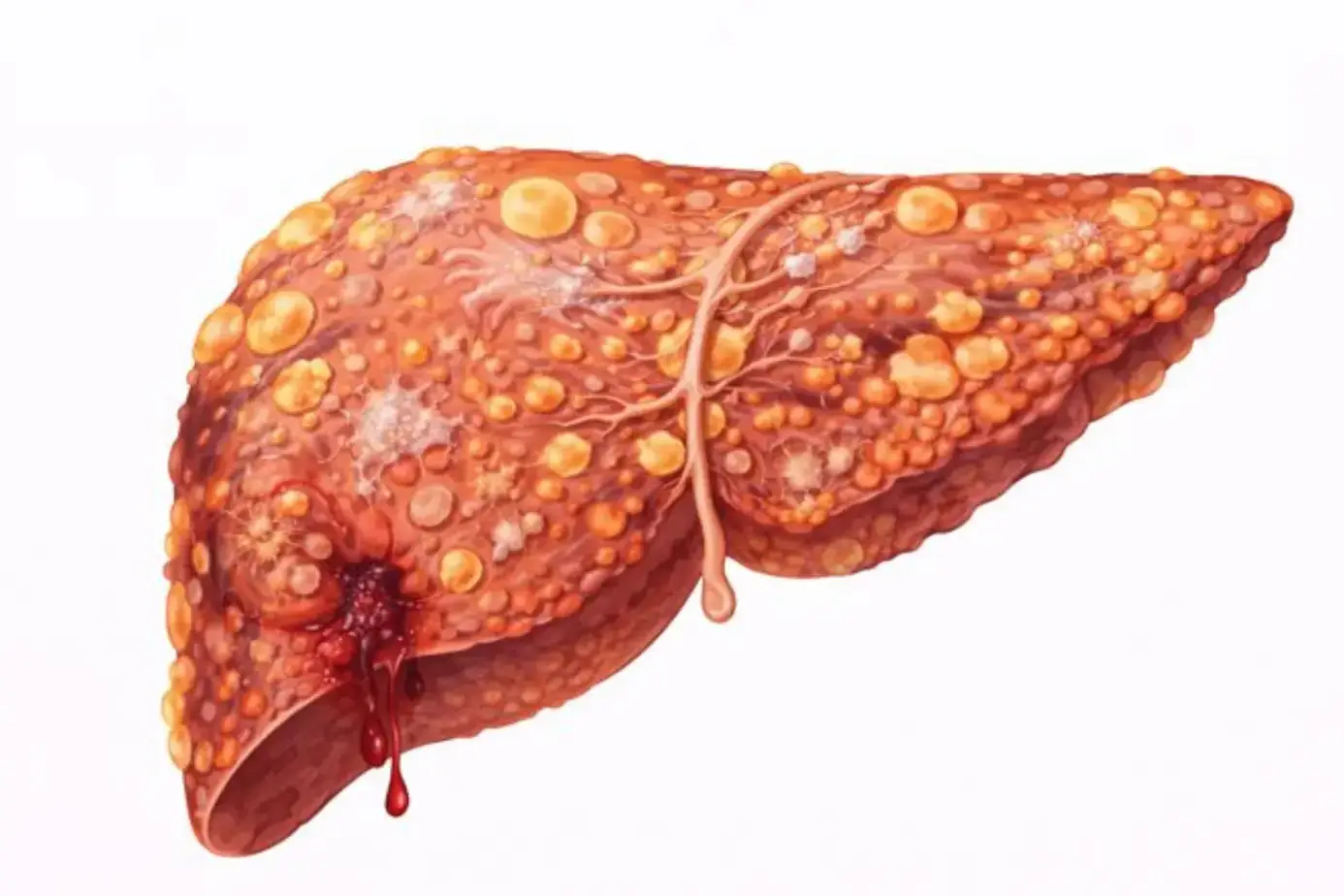
When Fatty Liver Becomes Irreversible
Once fibrosis (scar tissue) becomes advanced, full reversal is unlikely. Cirrhosis means permanent scarring. At this stage, treatment for fatty liver focuses on slowing damage and preventing complications, not reversal.
When To See A Doctor For Fatty Liver
Medical review becomes necessary when liver enzymes remain high, symptoms appear, or imaging shows progression. Timely evaluation helps determine whether lifestyle-based treatment for fatty liver remains sufficient or if closer monitoring is needed.
Warning Signs Requiring Medical Attention
Persistent fatigue, right-sided belly discomfort, or unexplained weight loss need evaluation. Swelling in legs or abdomen signals advanced disease. These signs mean home-based treatments for fatty liver are no longer enough.
Abnormal Liver Function Test Results
Raised liver enzymes over repeated tests require follow-up. Doctors look for trends, not single values. Persistent elevation suggests inflammation that needs targeted treatment for fatty liver .
Imaging And Diagnostic Follow-Up
Ultrasound shows fat buildup. MRI-based scans estimate fat and stiffness. In selected cases, biopsy confirms severity. These tools guide whether medicine should be taken for fatty liver or lifestyle care remains enough.
FAQs
What Is The Best Treatment For Fatty Liver?
The best treatment for fatty liver combines calorie control, sugar reduction, and regular movement. This approach lowers liver fat, improves insulin action, and reduces inflammation without relying on long-term medication.
Can Fatty Liver Be Cured Completely?
Fatty liver can clear fully in early stages if triggers are removed. Advanced scarring cannot reverse fully, but treatments for fatty liver can still slow damage and protect remaining liver function.
How Long Does Fatty Liver Take To Heal?
Liver enzymes may improve within weeks, but fat clearance takes months. Healing speed depends on consistency with treatment for fatty liver , body weight changes, and sugar control.
Is Fatty Liver A Serious Condition?
Fatty liver can become serious if ignored. It may progress to inflammation, scarring, or liver failure. Early treatment for fatty liver prevents these outcomes in most people.
Which Medicines Are Safest For Fatty Liver?
Doctors choose medicines based on risk profile. Some patients benefit from antioxidants or insulin-related drugs. Medicine should be taken for fatty liver only under medical supervision to avoid harm.
Does Exercise Really Reduce Liver Fat?
Yes. Physical exercise for fatty liver lowers liver fat by improving insulin use and burning stored energy. Benefits occur even without major weight loss when activity stays consistent.
Can Home Remedies Reverse Fatty Liver?
Some home remedies for fatty liver support recovery, such as sugar reduction and fiber intake. They work best when combined with medical guidance and structured lifestyle care.
What Foods Worsen Fatty Liver Disease?
Sugary drinks, refined carbs, fried foods, and processed meats worsen fat buildup. Avoiding these foods strengthens treatment for fatty liver and lowers inflammation risk.
Is Fatty Liver Common In Non-Drinkers?
Yes. Many non-drinkers develop fatty liver due to insulin resistance, weight gain, or genetics. These causes of fatty liver now account for most global cases.
Can Fatty Liver Come Back After Treatment?
Yes. Fatty liver can return if old habits resume. Long-term success depends on maintaining diet control, movement, and follow-up after completing treatment for fatty liver .
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Nivedita Pandey, MD, DM (Gastroenterology)
Senior Gastroenterologist & Hepatologist
Dr. Nivedita Pandey is a U.S.-trained gastroenterologist and hepatologist with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating liver diseases and gastrointestinal disorders. She specializes in liver enzyme abnormalities, fatty liver disease, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and digestive health.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current clinical guidelines.
About Author | Instagram | Linkedin