Jaundice makes your skin, the whites of your eyes, and mucous membranes turn yellow. It happens when there’s too much bilirubin in your blood. Normally, your liver removes bilirubin, sending it out in stool. But sometimes, either too much bilirubin or an overloaded liver causes jaundice.
Table of Contents
ToggleIt can signal different health issues, like liver problems, blocked bile ducts, or pancreatic cancer. Knowing these causes is vital for getting the right treatment. This is especially crucial for infants with jaundice.
Overview of Jaundice
Jaundice causes the skin, eyes, and fluids to turn yellow. This happens because of too much bilirubin in the blood. Knowing the signs and causes of jaundice is important to treat it well.
Definition and Symptoms
Jaundice makes the skin and eyes yellow. It happens when there’s a lot of bilirubin in the blood. People with jaundice might also have fever, stomach pain, and dark urine.
How Jaundice Occurs
Jaundice comes from too much bilirubin. This can be because the liver doesn’t work well or there’s a blockage. Liver diseases and some medications can also cause jaundice.

Types of Jaundice
Jaundice is grouped into four types based on where bilirubin builds up in the body. These are prehepatic, hepatic, posthepatic, and obstructive jaundice. Knowing these types is important to find the cause and right treatment.
Prehepatic Jaundice
With prehepatic jaundice, bilirubin can’t reach the liver, building up outside. This happens when red blood cells break down too quickly. Causes include malaria and certain genetic blood disorders. Symptoms are yellow skin, tiredness, and itching. Tests like blood work help diagnose it. Then, treatment matches the cause.
Hepatic Jaundice
Hepatic jaundice is linked to liver issues that slow down bilirubin processing. Liver disease, hepatitis, and certain cancers are common causes. It shows up with yellow skin, dark urine, and tiredness. Doctors use several tests to pin it down. Treatment focuses on the root cause.
Posthepatic Jaundice
Post-hepatic jaundice happens from blockages in the bile ducts. It’s often from gallstones or cancer. Symptoms include yellow skin, dark urine, and stomach pain. Conditions like pancreatitis and cancer can block the ducts, leading to these symptoms.
Obstructive Jaundice
Obstructive jaundice is one form of post-hepatic jaundice. In this case, blockages stop bile from leaving the liver. Just like post-hepatic jaundice, its symptoms are abdominal pain and yellow skin. Gallstones and some cancers can cause these issues.
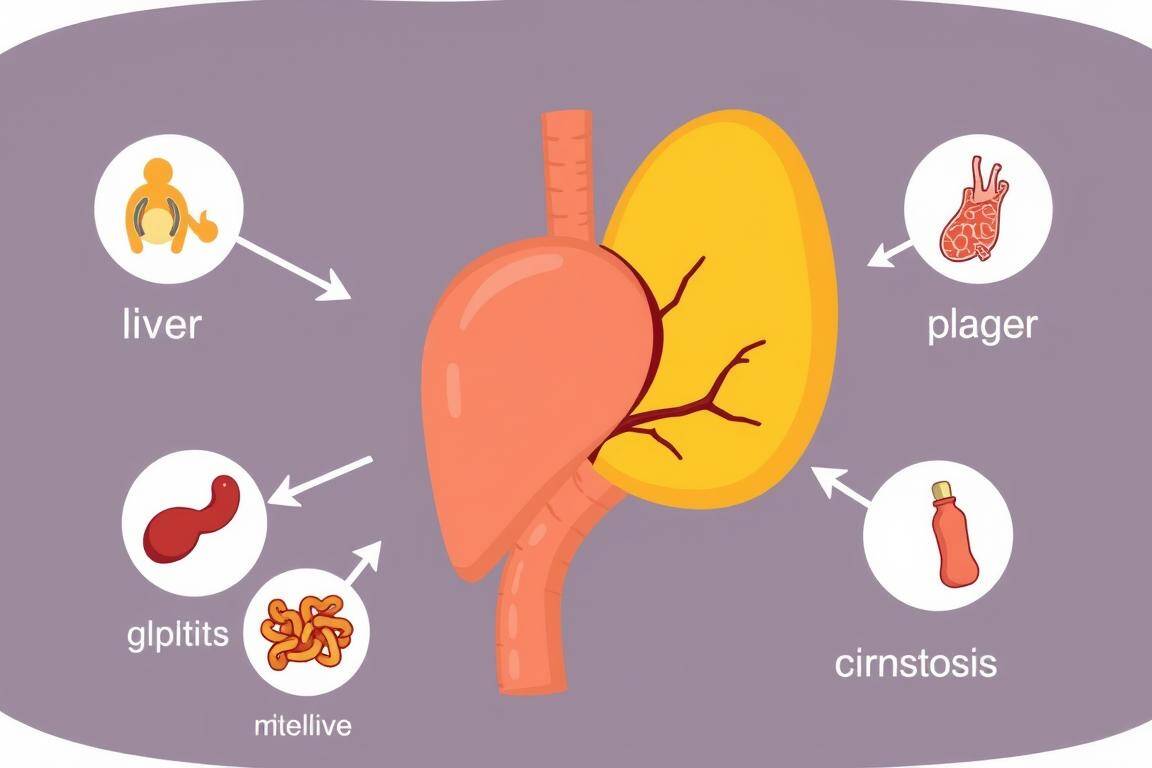
Causes of Jaundice in Adults
Jaundice in adults can come from many medical reasons. This includes hepatitis, liver swelling, some drugs, and blood issues. Knowing these causes helps in getting the right treatment early.
Hepatitis and Liver Inflammation
Various factors like viruses, immune problems, heavy drinking, or toxic substances can hurt the liver and cause jaundice. Viral hepatitis from type A to E is a main cause. It responds well to specific drugs.
Alcohol-related Liver Diseases
Drinking heavily for a long time can damage the liver, leading to jaundice. It’s important to cut down on alcohol to prevent this.
Other Liver Diseases
Issues including cirrhosis, fatty liver disease, and genetic problems can also lead to jaundice. Early detection and the right treatment are key.
Blocked Bile Ducts
Gallstones and other factors can block the bile ducts, causing jaundice. Sometimes, surgery is needed to fix it.
Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer can block the bile duct, leading to jaundice. It’s a serious symptom that needs medical attention.
Certain Medications
Some medicines, like acetaminophen or steroids, can harm the liver and cause jaundice. Always talk to your doctor about medicine risks.
Blood Clots and Hemolytic Anemias
Conditions speeding up the breakdown of red blood cells can up bilirubin levels, causing jaundice. This includes blood clots and certain types of anemia.
By knowing the various causes of jaundice, people can spot the signs earlier. This leads to faster care and lower risk of complications.
Symptoms of Jaundice
The main sign of jaundice is when the skin and eyes turn yellow.
Other signs include fever, stomach pain, and chills. You might also notice dark urine along with pale stools.
Feeling like you have the flu, itchy skin, and weight loss are also common. Others can be irritable, confused, unusually tired, and find they bruise or bleed easily.

what is jaundice
Jaundice makes the skin, eyes, and fluids in the body look yellow. It’s usually because of too much bilirubin in the blood. This can come with yellow skin and eyes, fever, stomach ache, chills, dark pee, light poop, and feeling like you have the flu.
Common Signs and Symptoms
The main sign of jaundice is a yellowness in the skin and eyes. You might also feel sick with fever, stomach pain, chills, and muscle aches. Your urine could be dark, and your stools might be light.
Jaundice Duration in Adults
The time jaundice lasts in adults changes with the reason behind it. Some medications can cause it, but it goes away when you stop taking them. For diseases like hepatitis, it might stick around until your liver is better. If gallstones are blocking something, you might need surgery to get rid of the jaundice.

Diagnosing Jaundice
When you have jaundice symptoms, your doctor will start by examining you closely. They look at your skin and eyes for yellowing. They also check your abdomen for any issues with your liver.
Physical Examination
Your doctor asks you about your health history and current symptoms. They want to know if you have any health problems or take medications. This info helps them figure out what’s causing your jaundice.
Blood and Urine Tests
Your provider will order blood and urine tests to confirm jaundice. These tests can also pinpoint the cause. The tests may include:
- Bilirubin levels to measure the amount of this yellow pigment in your bloodstream
- Liver enzyme tests to assess how well your liver is functioning
- A hepatitis panel to check for viral hepatitis infections
Imaging and Liver Biopsy
If tests don’t give a clear answer, you might need more imaging studies. These could be an ultrasound, CT scan, or MRCP. These scans help find problems in your bile ducts, gallbladder, or liver.
Sometimes, a liver biopsy is needed. It means taking a small piece of liver for a closer look. This helps identify liver damage, which is key for treating the root of your jaundice.
Treatment Options for Jaundice
If you have jaundice, treating its cause is key. Your doctor might suggest many ways to manage it. These can include fixing the liver’s function.
Treating Underlying Conditions
It’s crucial to treat what’s behind the jaundice. This could mean taking medicines for hepatitis or managing liver issues from alcohol. Surgery might be necessary to fix problems like blocked bile ducts. By dealing with the main issue, your body can lower the bilirubin levels. That usually helps ease jaundice symptoms.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy is often recommended for newborns with jaundice. It breaks down bilirubin with special lights. This makes it easier for the body to get rid of bilirubin. Luckily, this therapy works well for babies and some adults with jaundice.
Surgical Interventions
In some cases, a bile duct blockage needs surgery. Procedures like clearing or rebuilding ducts can fix the root problem. Surgical help is usually the last resort when other treatments haven’t worked.
Working with your doctor is vital to manage jaundice. Together, you can find the right treatment plan. This could involve meds, phototherapy, or even surgery. Remember, there are many options to help you get better.

Risk Factors and Prevention
Jaundice can happen to anyone, but some are more at risk. Knowing these risk factors can help avoid it. This way, you keep your health and prevent problems.
High-Risk Groups
If you’ve had liver issues, hepatitis, drink a lot, or use certain drugs, you’re at higher risk. These things can make it hard for your liver to work properly. As a result, you might get jaundice.
Lifestyle Changes for Prevention
To stay clear of jaundice, adults should do a few things:
- Avoid too much alcohol
- Stay away from illegal drugs
- Keep a healthy weight
- Practice safe sex
- Avoid liver-harming medicines and supplements
These changes can reduce your jaundice risk. Early action and health precautions are very important.
Complications of Untreated Jaundice
If jaundice is not treated, it can cause serious problems. Too much bilirubin can hurt the liver, raise infection risk, and lead to organ failure. Without help, it might also damage the brain permanently. This is called kernicterus.
Kernicterus occurs when high bilirubin levels reach the brain. This can lead to problems like shaky muscles, trouble hearing, and issues thinking. Sadly, this damage can’t be fixed, affecting how a child grows and lives.
Getting help quickly for jaundice is very important. Quick diagnosis and the right treatment manage bilirubin. This can stop the terrible impacts on a baby’s health and life.
Jaundice in Newborns
Jaundice is more common in babies than in adults. About 60% of newborns get jaundice in the first few days of life. It happens because their liver is still developing, making it hard to process a substance called bilirubin. This is why most cases go away without treatment.
Usually, babies born full term to 35 weeks don’t need treatment. But, if they leave the hospital before 72 hours, they should be checked for jaundice within two days. There are certain things that raise the risk of serious jaundice, like being born early, hard delivery with lots of bruising, blood type differences from the mother, trouble breastfeeding, and certain races. For example, babies of East Asian descent tend to have a higher risk.
Breast-fed babies should feed 8 to 12 times a day in the first few days. Formula-fed babies might need 1 to 2 ounces every two to three hours for the first week. If jaundice gets too bad, it can cause serious problems like seizures, trouble moving, or hearing loss.
The American Academy of Pediatrics says doctors should check babies for jaundice often during their first few days. Parents should look for signs, like yellow skin, and make sure their baby is seen by a doctor. This is really important to prevent any serious issues because of jaundice.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you notice jaundice symptoms, getting medical help is crucial. Signs like fever, confusion, and strong belly pain may show a serious issue. They need urgent medical attention. Adults with jaundice should check with their doctor. This is to find the reason and get treatment to avoid further problems.
Jaundice doesn’t often harm adults and can get better on its own. Yet, it might mean there’s a deeper health issue. Different things can cause jaundice in adults, from viral infections to cancers and more.
Feeling very sick with jaundice, like having a high fever, being confused, or feeling lots of belly pain, needs quick action. It could be a sign of something very serious that needs treatment fast. If you’re worried, don’t wait – call emergency services (triple zero – 000) right away.
Getting diagnosed early and treating the root problem of jaundice is key. By knowing the signs that you need to see a doctor for jaundice and getting proper care, you can stay healthier. This approach helps to avoid complications and have a good outcome.
Conclusion
Jaundice is easily spotted, as it makes the skin and eyes turn yellow. This change happens because of too much bilirubin in the blood. It’s important to know the causes, symptoms, and risks of jaundice. This knowledge can help you get treated fast and find the right care. Several things can lead to jaundice, like liver issues, blocked bile ducts, and some drugs. Knowing about these can help you prevent or handle jaundice better.
Getting help early and following the right treatment can make jaundice less of a problem. This is good news for anyone with jaundice or those who care about them. It’s key to keep updated about the main points about jaundice. This can lead to a better outcome and lower the chance of serious issues.
It’s worth noting that jaundice happens a lot but can be well managed. When you put your health first and see a doctor quickly, you’re taking control. This way, jaundice won’t have a big impact on your life.
FAQ
What is jaundice?
Jaundice turns the skin, eyes, and mouth yellow. It happens when there’s too much bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin is a yellow-orange substance the body makes.
What causes jaundice?
Jaundice happens because of too much bilirubin. This could be from issues in the liver, or a block in the bile ducts. The liver might not process bilirubin well, or it might not leave the body properly.
What are the symptoms of jaundice?
The main sign is yellow skin and eyes. You might also have a fever and stomach pain. Dark urine, pale stools, and flu-like symptoms can show as well.
What are the different types of jaundice?
There are four main types. Each is named based on why bilirubin builds up. These names are prehepatic jaundice, hepatic jaundice, posthepatic jaundice, and obstructive jaundice.
What can cause jaundice in adults?
In adults, it can be many things. These include hepatitis, liver inflammation, or alcohol liver disease. Blocked bile ducts, pancreatic cancer, certain meds, or blood problems can also cause it.
How is jaundice diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose jaundice with a physical exam and history. They also use blood tests for bilirubin and imaging tests. These include ultrasounds, CT scans, and MRIs.
How is jaundice treated?
Treatments focus on the cause. This might involve antiviral meds, managing liver diseases, or fixing bile ducts. In some cases, surgery is needed.
Who is at higher risk of developing jaundice?
People with liver disease, hepatitis, or who use a lot of alcohol are at more risk. So are those taking certain meds. To reduce the risk, avoid too much alcohol and practice safe sex.
What are the complications of untreated jaundice?
Untreated jaundice can lead to serious issues. These include more liver damage, high infection risk, organ failure, and brain or nerve problems.
Is jaundice common in newborns?
Yes, jaundice is common in newborns. About 60% have it within days of birth. Newborns’ livers are still growing, which can make this happen.
When should you seek medical attention for jaundice?
If you see jaundice and develop sudden symptoms like confusion, fever, or severe belly pain, see a doctor right away. This could mean a more serious problem.
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Nivedita Pandey, MD, DM (Gastroenterology)
Dr. Nivedita Pandey is a U.S.-trained gastroenterologist and hepatologist with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating liver diseases and gastrointestinal disorders. She specializes in liver enzyme abnormalities, fatty liver disease, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and digestive health.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current clinical guidelines.